From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Terflavin B
|
| Identifiers
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
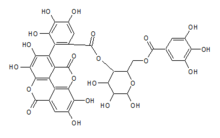
C1=C(C=C(C(=C1O)O)O)C(=O)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)O)O)O)OC(=O)C3=CC(=C(C(=C3C4=C(C(=C5C6=C4C(=O)OC7=C6C(=CC(=C7O)O)C(=O)O5)O)O)O)O)O
|
| Properties
|
|
|
C34H24O22
|
| Molar mass
|
784.54 g/mol
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
Chemical compound
Terflavin B is an ellagitannin, a type of hydrolysable tannin. It can be found in Myrobalanus chebula (Terminalia chebula), the black chebulic, and in Terminalia catappa, the Indian almond.[1]
It is formed from a nonahydroxytriphenic acid dilactone and a gallic acid linked to a glucose molecules.
|
|---|
| Moieties | |
|---|
| Lactones | |
|---|
| Monomers |
- Acetonyl geraniin
- Alnusiin
- Bicornin
- Carlesiin
- Casuarictin
- Emblicanin A and B
- Euscaphinin
- Galloyl pedunculagin
- Grandinin
- Helioscopinin B
- Jolkinin
- Lagerstannin A, B and C
- Macranganin
- Myrobalanitannin
- Nupharin A, B, C, D, E and F
- Pedunculagin
- Punicalagin
- Punigluconin
- Phyllanemblinin A, B, C, D, E and F
- Punicalin
- Roburin E
- Rugosin E
- Sanguiin H-5
- Stenophyllanin A, B and C
- Strictinin
- Tellimagrandin I and II
- Teracatain
- Terchebulin
- Terflavin A and B
- Tergallic acid
- Tergallic acid dilactone
|
|---|
| Oligomers | |
|---|
| Other | |
|---|

