Upsilon meson
Appearance
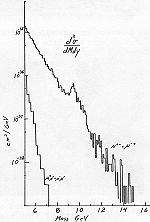 A plot of the invariant mass of muon pairs, from the Upsilon particle discovery paper. The peak at about 9.5 GeV is due to the contribution of the Upsilon meson. | |
| Composition | b b |
|---|---|
| Statistics | Bosonic |
| Family | Hadrons |
| Symbol | ϒ |
| Antiparticle | Self |
| Discovered | E288 experiment |
| Mass | 9.46030(26) GeV/c2 |
| Electric charge | 0 e |
| Spin | 1 |
The Upsilon meson (
ϒ
) is a quarkonium state (i.e. flavourless meson) formed from a bottom quark and its antiparticle. It was discovered by the E288 experiment team, headed by Leon Lederman, at Fermilab in 1977, and was the first particle containing a bottom quark to be discovered because it is the lightest that can be produced without additional massive particles. It has a lifetime of 1.21×10−20 s and a mass about 9.46 GeV/c2 in the ground state.
See also
- Oops-Leon, an erroneously-claimed discovery of a similar particle at a lower mass in 1976.
- The
ϕ
particle is the analogous state made from strange quarks. - The
J/ψ
particle is the analogous state made from charm quarks. - List of mesons
References
- D.C. Hom; et al. (1977). "Observation of a Dimuon Resonance at 9.5 Gev in 400-GeV Proton-Nucleus Collisions" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 39: 252–255. Bibcode:1977PhRvL..39..252H. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.39.252.
- J. Yoh (1998). "The Discovery of the b Quark at Fermilab in 1977: The Experiment Coordinator's Story" (PDF). AIP Conference Proceedings. 424: 29–42.
- S. Eidelman et al. (Particle Data Group) (2004). "Review of Particle Physics –
ϒ
meson" (PDF). Physics Letters B. 592: 1. arXiv:astro-ph/0406663. Bibcode:2004PhLB..592....1P. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2004.06.001.
