Trigonostylops
| Trigonostylops | |
|---|---|
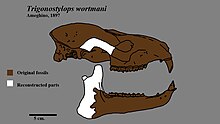
| |
| Skull restoration of Trigonostylops | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | †Trigonostylopidae
|
| Genus: | †Trigonostylops Ameghino 1897
|
| Type species | |
| Trigonostylops wortmani Ameghino 1897
| |
| Species | |
| |
Trigonostylops is an extinct genus of South American meridiungulatan ungulate, from the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene (Itaboraian to Tinguirirican in the SALMA classification) of South America (Argentina and Peru) and Antarctica (Seymour Island). It is the only member of the family Trigonostylopidae.
Description

A complete skull of the type species, T. wortmani, has been found, and it has been classified as an astrapothere based on its large lower tusks. In comparison with the later Astrapotherium magnum, it is estimated to have been around 1.50 metres (4.9 ft) long.[1] Teeth, primarily molars, have been found and assigned to other species.
Phylogeny
Cladogram based in the phylogenetic analysis published by Vallejo Pareja et al., 2015, showing the position of Trigonostylops:[2]
Distribution
Locations of Trigonostylops fossils
Not show: La Meseta Formation in Seymour Island, Antarctica
Fossils of Trigonostylops have been found in:[3]
- Paleocene
- Eocene
- La Meseta Formation, Antarctica[5]
- Casamayor, Divisadero Largo, Koluel Kaike and Sarmiento Formations, Argentina[6][7]
- Pozo Formation, Peru[8]
References
- ^ Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 249. ISBN 978-1-84028-152-1.
- ^ Vallejo Pareja et al., 2015
- ^ Trigonostylops at Fossilworks.org
- ^ Goin et al., 2009
- ^ Dzik & Gaździcki, 2001
- ^ Vera, 2012
- ^ Cifelli, 29185, p.5
- ^ Antoine et al., 2011
Bibliography
- Meridiungulata
- Paleocene mammals
- Eocene mammals
- Paleocene mammals of South America
- Eocene mammals of South America
- Tinguirirican
- Divisaderan
- Mustersan
- Casamayoran
- Riochican
- Itaboraian
- Paleogene Argentina
- Paleogene Peru
- Fossils of Argentina
- Fossils of Peru
- Paleogene animals of Antarctica
- Cenozoic mammals of Antarctica
- Fossils of Antarctica
- Fossil taxa described in 1897
- Taxa named by Florentino Ameghino

