Gymnodiniales
| Gymnodiniales | |
|---|---|

| |
| Karenia brevis, a member of the Kareniaceae; this organism is associated with red tides occurring in the Gulf of Mexico and produces brevetoxins that can harm aquatic life.[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Myzozoa |
| Superclass: | Dinoflagellata |
| Class: | Dinophyceae |
| Order: | Gymnodiniales |
| Families | |
|
See text | |
The Gymnodiniales are an order of dinoflagellates, of the class Dinophyceae.[2] Members of the order are known as gymnodinioid or gymnodinoid (terms that can also refer to any organism of similar morphology). They are athecate, or lacking an armored exterior, and as a result are relatively difficult to study because specimens are easily damaged. Many species are part of the marine plankton and are of interest primarily due to being found in algal blooms. As a group the gymnodinioids have been described as "likely one of the least known groups of the open ocean phytoplankton."[3]
Of the families in the order, the Polykrikaceae and Warnowiaceae are well known for possessing exceptionally complex assemblies of organelles, such as nematocysts, trichocysts, and pistons. The Warnowiaceae uniquely possess an ocelloid, an extremely complex light-sensitive subcellular structure composed of mitochondria and plastids.[4][5]
Families
Gallery
-
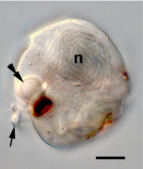
Proterythropsis sp. from the family Warnowiaceae, highlighting the distinctive ocelloid (double arrow)[5]
-
Gyrodinium spirale from the family Gymnodiniaceae
References
- ^ Landsberg, J.H.; Flewelling, L.J.; Naar, J. (March 2009). "Karenia brevis red tides, brevetoxins in the food web, and impacts on natural resources: Decadal advancements". Harmful Algae. 8 (4): 598–607. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2008.11.010.
- ^ Michael D. Guiry (2015). Guiry MD, Guiry GM (eds.). "Gymnodiniales". AlgaeBase. National University of Ireland, Galway. World Register of Marine Species.
- ^ Gómez, F (2007). "Gymnodinioid Dinoflagellates (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae) in the Open Pacific Ocean". Algae. 22 (4): 273–86. doi:10.4490/ALGAE.2007.22.4.273.
- ^ "Eye-like ocelloids are built from different endosymbiotically acquired components". Nature. 523 (7559): 204–7. 2015. doi:10.1038/nature14593. hdl:10754/566109. PMID 26131935.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ a b Hoppenrath, M; Bachvaroff, TR; Handy, SM; Delwiche, CF; Leander, BS (25 May 2009). "Molecular phylogeny of ocelloid-bearing dinoflagellates (Warnowiaceae) as inferred from SSU and LSU rDNA sequences". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 9: 116. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-9-116. PMC 2694157. PMID 19467154.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)