McMahon Line


The McMahon Line is the demarcation line between Tibet and the North-east region of India proposed by British colonial administrator Sir Henry McMahon at the 1914 Simla Convention signed between British and Tibetan representatives.[1] It is the legal boundary between China and India.[2][3]
The line is named after Henry McMahon, foreign secretary of British India and the chief negotiator of the convention at Simla. It was signed by McMahon and Lonchen Satra on behalf of the Tibetan Government.[4] It extends for 890 kilometres (550 miles) from Bhutan in the west to 260 km (160 mi) east of the great bend of the Brahmaputra River in the east, largely along the crest of the Himalayas. Simla (along with the McMahon Line) was initially rejected by the Government of India as incompatible with the 1907 Anglo-Russian Convention.[5] This convention was denounced in 1921. After Simla, the McMahon Line was forgotten until 1935, when British civil service officer Olaf Caroe convinced the government to publish the Simla Convention and use the McMahon Line on official maps.[6][unreliable source?]
The McMahon Line is regarded by India as the legal national border, but China rejects the Simla Accord and the McMahon Line, contending that Tibet was not a sovereign state and therefore did not have the power to conclude treaties.[7] Chinese maps show some 65,000 km2 (25,000 sq mi) of the territory south of the line as part of the Tibet Autonomous Region, known as South Tibet in China.[8] Chinese forces briefly occupied this area during the Sino-Indian War of 1962. China does recognise a Line of Actual Control which closely approximates most of the "so called McMahon line" in the eastern part of its border with India, according to a 1959 diplomatic note by Prime Minister Zhou Enlai.[9]
The 14th Dalai Lama did not originally recognise India's sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh. As late as 2003, he said that "Arunachal Pradesh was actually part of Tibet".[10] In January 2007, however, he said that both the Tibetan government and Britain recognized the McMahon Line in 1914. In June 2008, he explicitly recognized for the first time that "Arunachal Pradesh was a part of India under the agreement signed by Tibetan and British representatives".[10]
History
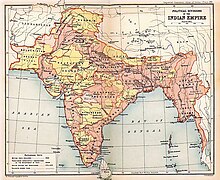
Drawing the line
Early British efforts to create a boundary in this sector were triggered by their discovery in the mid-19th century that Tawang, an important trading town, was Tibetan territory. In 1873, the British-run Government of India drew an "Outer Line," intended as an international boundary.[11] This line follows the alignment of the Himalayan foothills, now roughly the southern boundary of Arunachal Pradesh. Britain concluded treaties with Beijing concerning Tibet's boundaries with Burma[12] and Sikkim.[13] However, Tibet refused to recognise the boundaries drawn by these treaties.[citation needed] British forces led by Sir Francis Younghusband invaded Tibet in 1904 and imposed a treaty on the Tibetans.[14] In 1907, Britain and Russia acknowledged Chinese "suzerainty" over Tibet and that both nations "engage not to enter into negotiations with Tibet except through the intermediary of the Chinese Government."[15]
British interest in the borderlands was renewed when the Qing government sent military forces to establish Chinese administration in Tibet (1910–12). A British military expedition was sent into what is now Arunachal Pradesh and the North East Frontier Tracts was created to administer the area (1912). In 1912–13, this agency reached agreements with the tribal leaders who ruled the bulk of the region.[citation needed] The Outer Line was moved north, but Tawang was left as Tibetan territory.[16] After the fall of the Qing dynasty in China, Tibet expelled all Chinese officials and troops, and declared itself independent (1913).[17][18]
In 1913, British officials met at Simla, India to discuss Tibet's status.[5] The conference was attended by representatives of Britain, China, and Tibet.[19] "Outer Tibet," covering approximately the same area as the modern "Tibet Autonomous Region," would be under the administration of the Dalai Lama's government, under the "suzerainty" of China.[19] Suzerainty is an Asian political concept indicating limited authority over a dependent state. The final 3 July 1914 accord lacked any textual boundary delimitations or descriptions.[20] It made reference to a small scale map with very little detail, one that primarily showed lines separating China from "Inner Tibet" and "Inner Tibet" from "Outer Tibet." This map lacked any initials or signatures from the Chinese plenipotentiary Ivan Chen; however Chen had signed an earlier, similar draft of it from 27 April 1914.[citation needed]
Both drafts of this small scale map extend the identical red line symbol between "Inner Tibet" and China further to the southwest, approximating the entire route of the McMahon Line, and thus dead ending near Tawang at the Bhutan tripoint. However, neither draft labels "British India" or anything similar in the area that now constitutes Arunachal Pradesh.[citation needed]
The far more detailed eight miles to the inch McMahon Line map of 24–25 March 1914 is signed only by the Tibetan and British representatives. This map and McMahon Line negotiations were both done without Chinese participation.[21][22] After Beijing repudiated Simla, the British and Tibetan delegates attached a note denying China any privileges under the agreement and signed it as a bilateral accord.[23] British records show that the condition for the Tibetan government to accept the new border was that China must accept the Simla Convention. As Britain was not able to get an acceptance from China, Tibetans considered the MacMahon line invalid.[1]
Britain attempts to enforce line
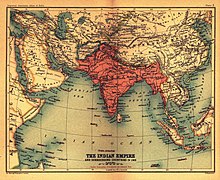
Simla was initially rejected by the Government of India as incompatible with the 1907 Anglo-Russian Convention. C.U. Aitchison's A Collection of Treaties, was published with a note stating that no binding agreement had been reached at Simla.[24] The Anglo-Russian Convention was renounced by Russia and Britain jointly in 1921,[25] but the McMahon Line was forgotten until 1935, when interest was revived by civil service officer Olaf Caroe.[6] The Survey of India published a map showing the McMahon Line as the official boundary in 1937.[6] In 1938, the British published the Simla Accord in Aitchison's Treaties.[24] A volume published earlier was recalled from libraries and replaced with a volume that includes the Simla Accord together with an editor's note stating that Tibet and Britain, but not China, accepted the agreement as binding.[26] The replacement volume has a false 1929 publication date.[24]
In April 1938, a small British force led by Captain G. S. Lightfoot arrived in Tawang and informed the monastery the district was now Indian territory.[27] The Tibetan government protested and its authority was restored after Lightfoot's brief stay. The district remained in Tibetan hands until 1951. However, Lhasa raised no objection to British activity in other sectors of the McMahon Line. In 1944, NEFT established direct administrative control for the entire area it was assigned, although Tibet soon regained authority in Tawang. In 1947, the Tibetan government wrote a note presented to the Indian Ministry of External Affairs laying claim to Tibetan districts south of the McMahon Line.[28] In Beijing, the Communist Party came to power in 1949 and declared its intention to "liberate" Tibet. India, which had become independent in 1947, responded by declaring the McMahon Line to be its boundary and by decisively asserting control of the Tawang area (1950–51).[5]
India and China dispute boundary
In the 1950s, when India-China relations were cordial and the boundary dispute quiet, the Indian government under Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru promoted the slogan Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai. (Indians and Chinese are brothers). Nehru maintained his 1950 statement that he would not accept negotiations if China brought the boundary dispute up, hoping that "China would accept the fait accompli.[29] In 1954, India renamed the disputed area the North East Frontier Agency.
India acknowledged that Tibet was a part of China and gave up its extraterritorial rights in Tibet inherited from the British in a treaty concluded in April 1954.[29] Nehru later claimed that because China did not bring up the border issue at the 1954 conference, the issue was settled. But the only border India had delineated before the conference was the McMahon Line. Several months after the conference, Nehru ordered maps of India published that showed expansive Indian territorial claims as definite boundaries, notably in Aksai Chin.[30] In the NEFA sector, the new maps gave the hill crest as the boundary, although in some places this line is slightly north of the McMahon Line.[9]
The failure of the 1959 Tibetan uprising and the 14th Dalai Lama's arrival in India in March led Indian parliamentarians to censure Nehru for not securing a commitment from China to respect the McMahon Line. Additionally, the Indian press started openly advocating Tibetan independence. Nehru, seeking to quickly assert sovereignty in response, established "as many military posts along the frontier as possible", unannounced and against the advice of his staff.[29] On discovering the posts, and already suspicious from the ruminations of the Indian press, Chinese leaders began to suspect that Nehru had designs on the region. In August 1959, Chinese troops captured a new Indian military outpost at Longju on the Tsari Chu (the main tributary, from the north, of the Subansiri River in Arunachal Pradesh.) Longju was and is just north of the McMahon Line according to the inside back cover map in Maxwell[5] and according to notable Indian mountaineer Harish Kapadia who explored the area in 2005. His published map and text[31] locate Longju a kilometer or two on the China side of the McMahon Line "near the Chinese garrison town of Migyitun" (which is now quite sizable, at 28-39-40 north latitude, over four kilometers north of the line.) (The rarely reliable coordinates in the Geonames database (National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency)[unreliable source?] incorrectly place "Longju" in snow and ice 10 kilometers away from the river at over 12,000 feet in elevation.) In a letter to Nehru dated 24 October 1959, Zhou Enlai proposed that India and China each withdraw their forces 20 kilometers from the line of actual control.(LAC)[32] Shortly afterward, Zhou defined this line as "the so-called McMahon Line in the east and the line up to which each side exercises actual control in the west".[9]
In November 1961, Nehru formally adopted the "Forward Policy" of setting up military outposts in disputed areas, including 43 outposts north of Zhou's LAC.[9] On 8 September 1962, a Chinese unit attacked an Indian post at Dhola in the Namka Chu valley immediately south of the Thag La Ridge, seven kilometres north of the McMahon Line according to the map on page 360 of Maxwell.[5] On 20 October China launched a major attack across the McMahon Line as well as another attack further north. The Sino-Indian War which followed was a national humiliation for India, with China quickly advancing 90 km (56 mi) from the McMahon Line to Rupa and then Chaku (65 km southeast of Tawang) in NEPA's extreme western portion, and in the NEFA's extreme eastern tip advancing 30 km (19 mi) to Walong.[33] The Soviet Union,[34] United States, and Great Britain pledged military aid to India. China then withdrew to the McMahon Line and repatriated the Indian prisoners of war (1963). The legacy of the border remains significant especially in India where the government sought to explain its defeat by blaming it on being caught by surprise.[35]
NEFA was renamed Arunachal Pradesh in 1972—Chinese maps refer to the area as South Tibet. In 1981, Chinese leader Deng Xiaoping offered India a "package settlement" of the border issue. Eight rounds of talks followed, but there was no agreement.
In 1984, India Intelligence Bureau personnel in the Tawang region set up an observation post in the Sumdorong Chu Valley just south of the highest hill crest, but three kilometres north of the McMahon Line (the straight line portion extending east from Bhutan for 30 miles). The IB left the area before winter. In 1986, China deployed troops in the valley before an Indian team arrived.[36][37] This information created a national uproar when it was revealed to the Indian public. In October 1986, Deng threatened to "teach India a lesson". The Indian Army airlifted a task force to the valley. The confrontation was defused in May 1987 though, as clearly visible on Google Earth, both armies have remained and recent construction of roads and facilities are visible.[38]
The Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi visited China in 1988 and agreed to a joint working group on boundary issues which has made little apparent positive progress. A 1993 Sino-Indian agreement set up a group to define the LAC; this group has likewise made no progress. A 1996 Sino-Indian agreement set up "confidence-building measures" to avoid border clashes. Although there have been frequent incidents where one state has charged the other with incursions, causing tense encounters along the McMahon Line following India's nuclear test in 1998 and continuing to the present, both sides generally attribute these to disagreements of less than a kilometre as to the exact location of the LAC.[38]
Border crossings
Maps
-
McMahon Line Simla Accord Treaty 1914 Map 1
-
McMahon Line Simla Accord Treaty 1914 Map 2
-
Simla Accord, treaty signed in 1914, Map 1
-
Simla Accord, treaty signed in 1914, Map 2
See also
References
Citations
- ^ a b Tsering Shakya (1999). The Dragon in the Land of Snows: A History of Modern Tibet Since 1947. Columbia University Press. pp. 279–. ISBN 978-0-231-11814-9.
- ^ Claude Arpi (2008). Tibet: The Lost Frontier. Lancer Publishers LLC. pp. 70–. ISBN 978-1-935501-49-7.
- ^ Emmanuel Brunet-Jailly (28 July 2015). Border Disputes: A Global Encyclopedia [3 volumes]: A Global Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. pp. 542–. ISBN 978-1-61069-024-9.
- ^ Veeranki Maheswara Rao (2003). Tribal Women of Arunachal Pradesh: Socio-economic Status. Mittal Publications. pp. 60–. ISBN 978-81-7099-909-6. Retrieved 25 May 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Maxwell, Neville, India's China War Archived 22 August 2008 at the Wayback Machine, New York, Pantheon, 1970.
- ^ a b c Guruswamy, Mohan, "The Battle for the Border", Rediff, 23 June 2003.
- ^ Lamb, Alastair, The McMahon line: a study in the relations between India, China and Tibet, 1904 to 1914, London, 1966
Grunfeld, A.T., The Making of Modern Tibet, 1996 - ^ "About South Tibet" (in Chinese). 21cn.com (China Telecom). 18 November 2008. Archived from the original on 22 January 2012. Retrieved 18 February 2012.
- ^ a b c d Noorani, A.G. "Perseverance in peace process", Frontline, 29 August 2003.
- ^ a b "Tawang is part of India: Dalai Lama". TNN. 4 June 2008. Retrieved 20 August 2012.
- ^ Calvin, James Barnard, "The China-India Border War", Marine Corps Command and Staff College, April 1984
- ^ "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Treaties and Conventions Relating to Tibet - Convention Relating to Burmah and Thibet (1886) [381]".
- ^ "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Treaties and Conventions Relating to Tibet - Convention Between Great Britain and China Relating to Sikkim and Tibet (1890) [382]".
- ^ "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Treaties and Conventions Relating to Tibet - Convention Between Great Britain and Thibet (1904) [385]".
- ^ "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Treaties and Conventions Relating to Tibet - Convention Between Great Britain and Russia (1907)[391]".
- ^ British maps published in 1904–1914 shows the Tibeto-Assamese boundary lying on the foothill, in conformity with China's claim. This was before the 1914 agreement. See North East Frontier of India (1910 & 1911 editions)
- ^ Goldstein 1997, pp. 30–31
- ^ "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Tibet - Proclamation Issued by His Holiness the Dalai Lama XIII (1913) [106]".
- ^ a b "Tibet Justice Center - Legal Materials on Tibet - Treaties and Conventions Relating to Tibet - Convention Between Great Britain, China, and Tibet, Simla (1914) [400]".
- ^ Prescott, J. R. V., Map of Mainland Asia by Treaty, Melbourne, Melbourne University Press, 1975, ISBN 0-522-84083-3, pages 276–7
- ^ Lamb, Alastair, The China-India Border, London, Oxford University Press, 1964, pages 144–5
- ^ Maxwell, Neville, India's China War New Delhi, Natraj Publishers, pages 48–9.
- ^ Goldstein 1989, pp. 48, 75
- ^ a b c Lin, Hsiao-Ting, "Boundary, sovereignty, and imagination: Reconsidering the frontier disputes between British India and Republican China, 1914–47"[permanent dead link], The Journal of Imperial & Commonwealth History, September 2004, 32, (3).
- ^ "UK relations with Tibet"
- ^ Schedule of the Simla Convention, 1914 Archived 12 September 2006 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Goldstein 1991, p. 307.
- ^ Lamb 1966, p580
- ^ a b c Chung, Chien-Peng (2004). Domestic politics, international bargaining and China's territorial disputes. Politics in Asia. Psychology Press. pp. 100–104. ISBN 978-0-415-33366-5.
- ^ Noorani, A.G. "Fact of History" Archived 13 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine, Frontline, 30 September 2003.
- ^ "404 - Page not found : Himalayan Club".
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ "Chou's Latest Proposals"[permanent dead link]
- ^ Maxwell, Neville, India's China War Archived 22 August 2008 at the Wayback Machine, p. 408-9, New York, Pantheon, 1970.
- ^ "Soviet Union - India".
- ^ "Remembering 1962 Sino-Indian Border War: Politics of Memory" Anand, Dibyesh. 2012. Journal of Defence Studies. 6, 4. Available
- ^ Vajpayee claps with one hand on border dispute, Asia Times Online, 1 August 2003
- ^ A.G. Noorani, "Perseverance in peace process", India's National Magazine, 29 August 2003.
- ^ a b Natarajan, V., "The Sumdorong Chu Incident" Archived 18 January 2013 at archive.today, Bharat Rakshak Monitor, Nov.-Dec. 2000, 3 (3)
Sources
- Goldstein, Melvyn C. A History of Modern Tibet, 1913–1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State (1989) University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-06140-8.
- Goldstein, Melvyn C. The Snow Lion and the Dragon: China, Tibet, and the Dalai Lama (1997) University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-21951-1.
- Grunfeld, A. Tom. The Making of Modern Tibet (1996) East Gate Book. ISBN 978-1-56324-713-2.
- Lamb, Alastair, The McMahon line: a study in the relations between India, China and Tibet, 1904 to 1914, London, 1966.
Further reading
- Why China is playing hardball in Arunachal by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, 13 May 2007
- China, India, and the fruits of Nehru's folly by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, 6 June 2007
- The British forgery at the heart of India and China’s Tibetan border dispute by Peter Lee
- The Myth of the McMahon Line by Peter Lee




