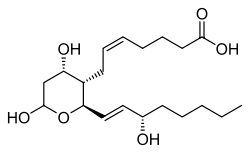
Thromboxane B2
Appearance
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.165.003 | ||
| MeSH | Thromboxane+B2 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C20H34O6 | |||
| Molar mass | 370.48 g/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Thromboxane B2 is an inactive metabolite/product of thromboxane A2. It is almost completely cleared in the urine.
It itself is not involved in platelet activation and aggregation in case of a wound, but its precursor, thromboxane A2, is. Thromboxane A2 synthesis is the target of the drug aspirin, which inhibits the COX-1 enzyme (the source of thromboxane A2 in platelets). [1]
2-(3,4-Di-hydroxyphenyl)-ethanol (DHPE) is a phenolic component of extra-virgin olive oil. An olive oil fraction containing DHPE can inhibit platelet aggregation and thromboxane B2 formation in vitro.[2]
References
- ^ "Definition: thromboxane b2 from Online Medical Dictionary". Retrieved 2008-11-02.
- ^ Inhibition of platelet aggregation and eicosanoid production by phenolic components of olive oil. Anna Petroni, Milena Blasevich, Marco Salami, Nadia Papini, Gian F. Montedoro and Claudio Gallia, Thrombosis Research, 15 April 1995, Volume 78, Issue 2, Pages 151–160, doi:10.1016/0049-3848(95)00043-7