2013 Nineveh governorate election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 39 seats for the Nineveh Governorate council | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 37.5%[1] ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
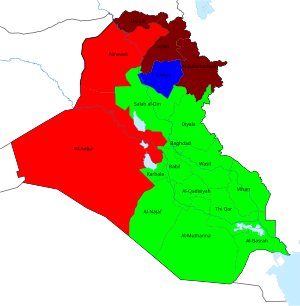 Elections in Nineveh and Al Anbar, marked in bright red, were delayed due to the deteriorating security situation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2013 Nineveh Governorate election in Iraq was held on 20 June with elections for the Al Anbar Governorate. Due to security problems, turnout was less than half that of the 2009 election. This election saw Sunni Arab parties lose a number of seats to minority parties.
Background
Nineveh is one of Iraq's most demographically-diverse governorates. Out of a population of about 2.8 million, 2013 estimates cited by Niqash claim about 300,000 Turkmen, (primarily in Tal Afar and Rashidiya. A similarly-sized population of Yazidis live in the districts of Shekhan and Sinjar and near the town of Bashiqa. Some 250,000 Shabaks live in villages north and east of Mosul, and 200,000 Christians live in Bashiqa, Bartella and Bakhdida. There is a sizable Kurdish population, with many Yazidis also identifying as Kurds.[2] Although elections for 13 of Iraq's 18 governorates were held on 20 April, elections in Al Anbar and Nineveh were delayed due to security concerns in the ongoing insurgency and Sunni-led protests.[3]
Violence
As of 14 June there were eight attacks on provincial-council candidates in Nineveh, resulting in six deaths (including Muhanad Ghazi, a Sunni Arab candidate for the Iraqi Republican Gathering—a party supporting Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki). Ghazi was shot dead by unknown gunmen whilst walking home from the East Mosul mosque.[4][5]
Another local politician, Younis al-Rammah (leader of the moderate United Iraqi Gathering party), was killed on 19 June—the day before the election. Rammah was hosting a family gathering at a residence in Hadhar when a man embraced him, detonating a suicide vest and killing Rammah and four relatives. No group claimed responsibility for the attack, although Iraqi officials blamed it on attempts by the Islamic State of Iraq to disrupt the political process and return to sectarian violence.[6][7][8] There was also violence on election day, with four Iraqi soldiers wounded by mortar rounds and roadside bombs in the Mosul area.[9]
Results
Template:Ninawa governorate election, 2013
Analysis
The Uniters List, composed of al-Hadba and the Iraqi Islamic Party, had won 49.82 percent of the vote and 22 of 37 seats in the Nineveh Governorate Council in 2009. The party held eight of 39 council seats after the 2013 election. The local Arab parties lost control of the council, although Atheel al-Nujaifi remained governor. The new council president was Bashar Kiki, a Kurd; the new vice-president, Nour ad-Din Qabalan, was a Turkmen. Nujaifi's deputy, Abdul Qader Battoush, is also Kurdish. His second deputy, Hassan al-Allaf, is an Arab and one of three politicians elected from Mosul (which had produced a large number of Arab politicians in the previous election).[2]
According to local political scientist Hamza Hussein, the number of seats won by minorities demonstrated popular discontent and lack of confidence in the previous council. Local activist Rabea Mustafa said that opposition to the previous council arose largely from resentment of its fractured nature, which hampered its ability to deliver basic services. Mustafa also said that the election result was due to minorities being driven out of Mosul because of violence;[2] these minorities then settled elsewhere in Nineveh. Voter turnout in Mosul was low, due to security problems and a lack of confidence in the political process and the previous council. Candidates were better able to canvass outside Mosul due to better security, and many Mosul-based candidates withdrew from the election.[2] Voter turnout was about half that of 2009: 581,449, compared to 995,169 in the previous election.
References
- ^ http://www.ncciraq.org/en/breaking-news/item/1200-al-shorfa-ballot-counting-begins-in-ninawa-and-anbar
- ^ a b c d Abdullah Salem (22 August 2013). "Voter's Revolution in Ninawa: Local Minorities take over Provincial Govt". Niqash. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- ^ "Two Iraqi policemen dead in attacks during provincial elections". Al-Akhbar. 20 June 2013. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ "Another Iraq candidate killed ahead of provincial polls". The Daily Star. 14 June 2013. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ^ Sameer N Yacoub (13 June 2013). "Gunmen Kill Election Candidate in Iraq". ABC News. Retrieved 23 June 2013.
- ^ Ziad al-Sanjary & Ahmed Rasheed (19 June 2013). "Suicide bomber embraces and kills Sunni politician in Iraq". Reuters. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ "Iraq election candidate killed in suicide bomb attack". The Independent. 19 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ Ruth Brown (19 June 2013). "Suicide Bomber Hugs, Blows Up Sunni Leader". newser. Retrieved 21 June 2013.
- ^ "Five killed in Iraq during provincial elections". Al-Akhbar. 21 June 2013. Archived from the original on 24 June 2013. Retrieved 21 June 2013.


