HMS Thrush (1889)
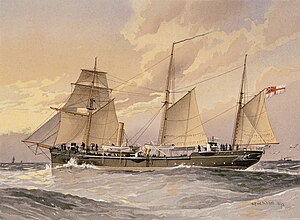 HMS Thrush, First Class gunboat by W. Fred Mitchell
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | HMS Thrush |
| Builder | Scotts, Greenock |
| Cost | £39,000[1] |
| Yard number | 262[1] |
| Launched | 22 June 1889 |
| Fate |
|
| General characteristics [1] | |
| Class and type | Template:Sclass- |
| Displacement | 805 tons |
| Length | 165 ft 0 in (50.3 m) pp |
| Beam | 31 ft 0 in (9.4 m) |
| Draught | 11 ft 0 in (3.35 m) min, 13 ft 9 in (4.19 m) max |
| Installed power | 1,200 ihp (890 kW) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Sail plan | Barquentine-rigged |
| Speed | 13 kn (24 km/h) |
| Range | 2,500 nmi (4,600 km) at 10 kn (19 km/h)[1] |
| Complement | 76 |
| Armament |
|
HMS Thrush was a Redbreast-class[1] composite gunboat,[2] the third ship of the name to serve in the Royal Navy.
Design
The Redbreast-class were designed by Sir William Henry White, the Royal Navy Director of Naval Construction in 1888.[1]
Construction
Thrush was launched on 22 June 1889 at Greenock.[3] Her triple-expansion reciprocating steam engine was built by the Greenock Foundry, and developed 1,200 indicated horsepower (890 kW), sufficient to propel her at 13 kn (24 km/h) through her single screw.
Career
Her first station was the North America and West Indies Station based in Halifax where, in 1891, she was commanded by Prince George, later to become King George V of the United Kingdom.[2] In 1896 Thrush, along with Sparrow, played a part in the 40 minute Anglo-Zanzibar War.[4] She was also on active service during the Second Boer War, which lasted between October 1899 and June 1902 where she was commanded by Lieutenant Warren Hastings D'Oyly.[5] In early 1902 she helped a British force in Nigeria re-open trade routes on the Lower Niger, closed by piracy of some locals.[6] Lieutenant Hector Lloyd Watts-Jones was appointed in command on 5 July 1902.[7]
From 1906 Thrush worked for HM Coastguard before becoming a cable ship in 1915.[3] She then became a salvage ship in 1916 before being wrecked off Glenarm in Northern Ireland on 11 April 1917.[3]
In January of 1917, Thrush was involved in the dramatic rescue of 46 submariners and shipyard officials, from the sunken K-13. The unusual 'steam-powered', and newly built submarine suffered an uncontrolled descent to the bottom of the Gareloch, on the Firth of Clyde, during sea trials. The Thrush was called in from a nearby mooring and, along with the Gossamer and the Ranger, were able to partially raise the stricken vessel with cables, just enough to allow rescue of more than half the people onboard. [8]
References
- ^ a b c d e f Winfield (2004), pp.299-300
- ^ a b Canadian Military Heritage site
- ^ a b c Entry in Clydebuilt database
- ^ Patience 1994, p. 7.
- ^ "Anglo-Boer War site". Archived from the original on 8 January 2009. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ^ "No. 27473". The London Gazette. 12 September 1902. p. 5879.
- ^ "Naval & Military intelligence". The Times. No. 36814. London. 8 July 1902. col e, p. 11. template uses deprecated parameter(s) (help)
- ^ "The Unlucky K 13 - Shipping Wonders of the World". www.shippingwondersoftheworld.com. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
Bibliography
- Patience, Kevin (1994), Zanzibar and the Shortest War in History, Bahrain: Kevin Patience
- Winfield, R.; Lyon, D. (2004). The Sail and Steam Navy List: All the Ships of the Royal Navy 1815–1889. London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-032-6. OCLC 52620555.
