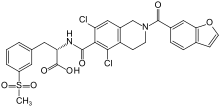
Lifitegrast
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xiidra |
| Other names | SAR-1118 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | xiidra |
| Routes of administration | Eye drops |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.245.695 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H24Cl2N2O7S |
| Molar mass | 615.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Lifitegrast (trade name Xiidra) is an FDA approved drug indicated for the treatment of signs and symptoms of dry eye, a syndrome called keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Lifitegrast reduces inflammation by inhibiting inflammatory cell binding.[1] It is often used in conjunction with ciclosporin (Ikervis or Restasis) for dry eye treatment including meibomian gland dysfunction and inflammatory dry eye.
Adverse effects
Common side effects in clinical trials were eye irritation, discomfort, blurred vision, and dysgeusia (a distortion of the sense of taste).[2]
Pharmacology
Lifitegrast is supplied as an eye drop and typically applied two times a day.
Mechanism of action
Lifitegrast inhibits an integrin, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), from binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). This mechanism down-regulates inflammation mediated by T lymphocytes.[1][3]
History
Lifitegrast was initially designed and developed by SARcode Bioscience[4] which was acquired by Shire in 2013,[5] who submitted a new drug application to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2015. The FDA granted Shire a priority review a month later, and requested additional clinical data, which were supplied in January 2016; approval was granted on 11 July 2016.[6][7] Lifitegrast was approved by Health Canada in January 2018, and available in Canadian pharmacies as of March 2018.
Shire has been acquired by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in late 2018.[8] In May 2019 Novartis has reached an agreement to purchase the assets associated with lifitegrast. Novartis will pay Takeda an upfront payment of $3.4 billion, while the latter drugmaker is eligible for milestone payments of as much as $1.9 billion. Novartis noted that the drug amassed approximately $400 million in revenue in 2018.[9]
See also
- Restasis (ciclosporin eye drops for keratoconjunctivitis sicca)
References
- ^ a b Tauber J, Karpecki P, Latkany R, Luchs J, Martel J, Sall K, et al. (December 2015). "Lifitegrast Ophthalmic Solution 5.0% versus Placebo for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease: Results of the Randomized Phase III OPUS-2 Study". Ophthalmology. 122 (12): 2423–31. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.08.001. PMID 26365210.
- ^ Drugs.com: Patient information for xiidra.
- ^ Murphy CJ, Bentley E, Miller PE, McIntyre K, Leatherberry G, Dubielzig R, et al. (May 2011). "The pharmacologic assessment of a novel lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 antagonist (SAR 1118) for the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca in dogs". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 52 (6): 3174–80. doi:10.1167/iovs.09-5078. PMID 21330663.
- ^ Semba CP, Gadek TR (2016). "Development of lifitegrast: a novel T-cell inhibitor for the treatment of dry eye disease". Clinical Ophthalmology. 10: 1083–94. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S110557. PMC 4910612. PMID 27354762.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Shire To Acquire Sarcode Bioscience, Expands Presence In Ophthalmology". 25 March 2013.
- ^ "FDA Approves Shire's Xiidra". 11 July 2016.
- ^ Drugs.com: Xiidra (lifitegrast) FDA Approval History
- ^ "Takeda Completes Acquisition of Shire, Becoming a Global, Values-based, R&D-Driven Biopharmaceutical Leader". Takeda. January 8, 2019.
- ^ "Novartis to acquire Xiidra, expanding front-of-eye portfolio and strengthening leadership in eye care". Novartis. May 9, 2019.
