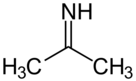
Acetone imine
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Propanimine | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Propan-2-imine[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| MeSH | Imine Acetone Imine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C3H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 57.096 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.8 g cm−3 (25 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −76.32 °C (−105.38 °F; 196.83 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 71.64 °C (160.95 °F; 344.79 K)[2] | ||
| 4.083e+005 mg/L | |||
| log P | -0.56 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 123 kPa (25 °C)[2] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.394 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H319, H336 | |||
| P210, P261, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 14.7 °C (58.5 °F; 287.8 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Butanone Isopropanol Urea Carbonic acid Carbonyl fluoride Ammonia Trimethylamine Acetone | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Acetone imine, or 2-propanimide is an organic compound and an imide with the chemical formula (CH3)2CNH. It is a volatile and flammable liquid at room temperature. It is the simplest ketimide. This compound does not have many uses industrially currently. It is not very soluble in water. When in contact with water, it hydrolyzes to give acetone and ammonia[3].
Synthesis
The method to synthesize acetone imine is similar to the production of acetone oxime. The only difference is that it is made by the condensation of acetone and anhydrous ammonia in the presence of hydrogen chloride.
- (CH3)2CO + NH3 → (CH3)2CNH + H2O
Unlike acetone oxime, the acetone imine must be dried because it hydrolyzes when exposed to water[3]
Properties
Acetone imine is a colorless, flammable, volatile, and water reactive liquid in normal conditions. It will ignite readily at temperatures above 14.7 °C (58.5 °F; 287.8K)[2]. When this compound is exposed to moisture, it fumes to give off acetone and ammonia due to hydrolysis[3].
Like acetone oxime, it is not very toxic to humans, however if swallowed, it might be harmful.
References
- ^ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2-Propanimine#section=Synonyms.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ a b c "2-Propanimine - C3H7N - ChemSpider". www.chemspider.com.
- ^ a b c "Hydrolysis of imines to give ketones (or aldehydes) — Master Organic Chemistry". www.masterorganicchemistry.com.