Barbaro family

The Barbaro family was a patrician family of Venice. They were wealthy and influential and owned large estates in the Veneto above Treviso.[1]: 112 Various members were noted as church leaders, diplomats, patrons of the arts, military commanders, philosophers, scholars, and scientists.[2]: 150 [3]: 275
History
Barbaro family tradition claims they were descended the Roman gens Catellia[3]: 274 [4]: 11 and more distantly from the Fabii.[4]: 11 Like other Venetian patrician families, they also claimed descent from Roman families with similar names, in this case Ahenobarbus.[5][6] Tradition also says they fled to Istria to avoid persecution during the reign of Emperor Diocletian.[3]: 274 The family’s wealth came from the salt trade.[7]
Records show the family moved from Pula to Trieste in 706 and then to Venice in 868.<[3]: 274 [4]: 11 [8]: 161 At this time the family's surname was Magadesi.[9]: 87 [10]: 136 (Alternate spellings were Magadezzi[4]: 11 [8]: 161 and Maghadesi.)[11]: 7
The first recorded member of the family was Paolo Magadesi, who was Procurator of San Marco.[4]: 14 [11]: 8 Charles Yriarte says this occurred when Pietro Tradonico was Doge of Venice (836-864),[11]: 8 though most sources say the family did not live in Venice until later.[3]: 274 [4]: 11 [8]: 161 An Antonio Magadesi was also Procurator of San Marco in 968.[12]: 346 and Johannes Magadesi was a presbyter of the Church of San Zorzi in 982 and has also been cited as the first member of the Barbaro family that we have a historical record of.[3]: 274
Recorded genealogy of the Barbaro family begins in 1121 with Marco, naval commander and creator of the modern coat of arms,[3]: 275 who changed his surname name from Magadesi to Barbaro.[4]: 12 [9]: 87
The Barbaro family was recognized as one of the leading families (Ottomati) of the Republic of Venice in the year 992. In 1297, the Maggior Consiglio (Senate of Venice) recognized the family as patricians[3]: 275 The Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia confirmed the family status as Patricians as part of a series of resolutions issued from 1818-1821.[3]: 275 This status was officially recorded again in Venice in 1891 for all members of the family.[3]: 275
In the sixteenth century there was a division between those Venetian families who opposed or favored the influence of the Holy See. The latter opposed the law that barred holders of church offices from also holding political appointments in Venice. The Barbaro family was part of this "papalist" group, along with the Badoer, Corner, Emo, Foscari, Grimani, and Pisani families.[13]: 113 These families also acted as patrons of Battista Franco, Palladio, Francesco Salviati, Michele Sanmicheli, Giovanni da Udine, and Federico Zuccari.[13]: 113
The Barbaro family fortunes diminished after Napoleon's defeat of Venice and they had to turn most of the Palazzi Barbaro into apartments.[2]: 150 By the time art critic John Ruskin visited Venice in 1851 all that was left of the once powerful Barbaro family were a pair of elderly brothers living in poverty in the garret of the Palazzo Barbaro.[14]: 20
Ruskin wrote that the poverty of these last members of the Barbaro family was justice for the family having rebuilt the Church of Santa Maria Zobenigo as a monument to themselves, which Ruskin called “a manifestation of insolent atheism”.[14]: 78 The last of the family died in the mid-nineteenth century.[2]: 150
Some branches of the family survived outside Venice. The most prominent was in Malta, but there were also branches in Galatia and other parts of Italy.[3]: 277
Family arms
There is disagreement over the form of the ancient Barbaro coat of arms. Johannes Rietstap and others identify it as “'D'or, à deux bandes d'azur, accompagne de deux roses du même”, a gold field with two bands of blue between two roses of the same color.[4]: 13 [11]: 9 [15] d'Eschavannes identifies it as “D'azur, à trois roses d'or”', a blue field with three gold roses.[16]: 53
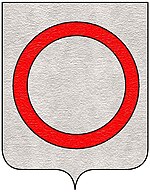
Sources agree that the modern Barbaro coat of arms is ’'D'argent, au cyclamore de gueules, a red ring on a white field.[3]: 503 [16]: 53 [17]
The modern Barbaro family arms were officially recognized by the Venetian Senate in 1125 in remembrance of Marco Barbaro cutting off the hand of a Moor during a naval action near Ascalon and using the bleeding stump to draw a circle onto a turban, which he flew as a pennant from his masthead.[10]: 135 [11]: 7 [18][19][20][21]
Until this incident, he was known as Marco Magadesi.[4]: 12 [8]: 161 [9]: 87 Saracens boarded the galley he commanded and tore down the ship's flag, which bore the family coat of arms.[4]: 12 [8]: 161 Marco Magadesi used the bloody turban as an improvised flag to let the rest of the fleet know his ship had not been captured.[4]: 12 [8]: 161 After the action, he changed his family name from Magadesi to Barbaro<[8]: 161 in recognition of the incident and to honor the heroism of his fallen enemies, who he considered barbarians.[4]: 11
The Barbaro coat of arms are depicted on the façade of the church of Santa Maria Zobenigo.[22]: 307 It is also displayed on the pediment of the Villa Barbaro and the family crypt in the San Francesco della Vigna.[11]: 10 [23]
In 1432, Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor granted Ambassador Francesco Barbaro the title of Knight of the Holy Roman Empire and the right to quarter his arms with the Imperial Eagles.[3]: 275 In 1560, Queen Elizabeth I of England granted Ambassador Daniele Barbaro right to use the Tudor Rose in his personal arms.[3]: 275
Notable members
The brothers Daniele Barbaro and Marcantonio Barbaro, were patrons of the architect Andrea Palladio and the painter Paolo Veronese.[24] Barbaro-family members acted as deans and professors of the University of Padua. Several members were also Patriarchs of Aquileia.[3]: 275 [11]: 11 [25]


- Paolo Magadesi (c.836?) The first recorded member of the family and Procurator of San Marco.[4]: 14 [11]: 8
- Antonio Magadesi (c.968) Procurator of San Marco.[12]: 346
- Johannes Magadesi (c.982) Presbyter at the Church of San Zorzi.[3]: 274
- Marco Barbaro née Magadezzi/Maghadesi (c.1121) Provveditore d'Armata, Naval victor against the forces of the Sultan of Egypt, creator of the modern Barbaro coat of arms.[3]: 275 The Barbaro family arms were officially recognized in 1123 by the Venetian Senate.[3]: 275 A painting of the victory by Sante Peranda hung in the Palazzo Ducale of Venice.[3]: 275 [11]: 8
- Marco Barbaro (c.1229) Son of Pietro, cavalry captain in forces that defeated Ezzelino III da Romano tyrant of Padua[3]: 275 [4]: 346
- Donato Barbaro (c.1259) Son of Pietro, captain of 40 galleys, defeated the Genoese and the forces of the Byzantine Emperor Manuel at the Island of Seven Wells (Isola dei Sette Pozzi).[3]: 275 [4]: 346 [26]
- Pietro Barbaro (c.1270) Son of Jacopo. Served in the cavalry of Charles of Anjou in the conquest of Naples. Recognized by Charles for his actions in the Battle of Benevento; appointed Signore of the Castle of Pietramala.[3]: 275
- Nicolo Barbaro (c.1361) Son of Bertucci. Provveditore d'Armata, defeated the Genoese at Rhodes.[3]: 275
- Donato Barbaro (c.1364) Son of Giovanni. Distinguished himself in the suppression of a rebellion in Candia[3]: 275
- Marco Barbaro was Auditor of Grado in 1366[27]: 191 and Podestà of Oderzo in 1367.[28]: 253
- Bernardo Barbaro (c.1370) Son of Donato. Ambassador for the Doge to the Sultan of Egypt.[3]: 275
- Giovanni Barbaro (c.1380) Son of Adamo. Provveditore of the army that fought against Padua.[3]: 275

- Francesco Barbaro (c.1398) Son of Marco. One of the founders of the Congregazione dei Canonici Secolari (Secular Canons) of San Giorgio in Alga.[3]: 275
- Francesco Barbaro (1398–1454) Son of Candiano,[29]: 135 uncle to Ermolao Barbaro[29]: 136 Author, diplomat, politician, and military commander. Honored for his defense of Brescia from 1432 to 1435 against the Milanese under Niccolò Piccinino.[3]: 275 A painting on this subject by Tintoretto, La difesa di Brescia, hung in the Palazzo Ducale of Venice. .[3]: 276 Ambassador to Emperor Sigismund of the Holy Roman Empire. Made Knight of the Holy Roman Empire in 1448. Elected Procurator of San Marco. Noted scholar with many works. Subject of a 1932 biography by Percy Gothein.[3]: 276
- Almoro Barbaro (c.1403) Son of Adamo. Captain of a galley in the victory of Carlo Zeno against the Genoese.[3]: 275
- Ermolao Barbaro (1410-1471/1474), Son of Zaccaria and nephew to Francesco Barbaro.[29]: 136 Bishop of Treviso(1443–1453). Bishop of Verona(1453-?).[30] Governor of Perugia.[3]: 276
- Pietro Barbaro (c.1413) Son of Donato. Ambassador to the Duke of Savoy.[3]: 275
- Nicolo Barbaro was Auditor of Pola from 1413 to 1414.[31]: 194
- Marco Barbaro, son of Jacopo, was Podestà of Pirano from 1419 to 1421,[32]: 199 and Ambassador to Byzantium in 1423,[3]: 275 Podestà of Pirano from 1430 to 1431,[32]: 199 and Captain of Grisignana from 1431 to 1437.[33]: 178
- Giosafat Barbaro (1413–1494) Son of Antonio. Traveled to Tana in 1436.[34] In 1473, he was one of several Venetian ambassadors to Persia.[35] Barbaro also served as Provveditore of the Army in Albania fighting with Skanderbeg against the Turks.[3]: 276 [29]: 137 Barbaro served as Captain of Rovigo and Provveditore of all Polesine from 1482 to 1483.[36]: 16 Barbaro wrote about his travels[3]: 276 [29]: 137
- Nicolo Barbaro (1420–1494) Son of Marco. Wrote an eyewitness account of the Fall of Constantinople.[3]: 276 [11]: 11
- Andréa Barbaro was Castellan of Modon and Corone from 1421 to 1423.[37]: 380
- Zaccaria Barbaro. (1422–1492) He was the only son of Francesco Barbaro[38][39]: 201 [40]: 91 and the father of Ermolao Barbaro.[39]: 201 [40]: 91 and Alvise Barbaro, Cavalier, Procurator, and Provveditore al Sal[39]: 201 Zaccaria served as ambassador to the Courts of Naples and Milan,[3]: 276 [41] and served as Procurator of San Marco.[42]: 90 [43][44][45] In 1465, Zaccaria purchased the Palazzo Barbaro in San Vitale on the Grand Canal which remained in the family's possession until 1864.[3]: 276 [12]: 278 [42]: 90 In 1480, Zaccaria served as ambassador to the Papal court of Pope Sixtus I.[46] During the War of Ferrara Zaccaria served as an army commander.[11]: 7 [42]: 90
- Benedetto Barbaro was Captain of Grisignana in 1423.[33]: 178 and Auditor of Pola from 1433 to 1435.[31]: 194
- Matteo Barbaro was Auditor of Pola from 1423 to 1424.[31]: 194
- Vittore Barbaro, son of Maffeo, was Provveditore of the Army against Milan in 1426[3]: 276 and Captain of Rovigo and Polesine in 1428.[36]: 15
- Matteo Barbaro, son of Antonio was Rector of Nauplia and Argos from 1438 to 1441[37]: 383 and Bailo and Captain of Negroponte (the Greek island of Euboea, from 1444 to 1446.[37]: 372
- Dona Barbaro was Auditor of Trau from 1440 to 1443.[47]
- Bernabo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado in 1446.[27]: 192
- Ermolao Barbaro (c.1448) Son of Candiano. Ambassador to the Duke of Burgundy.[3]: 276
- Donato Barbaro, son of Andréa, was Captain of Zara from 1450 to 1451,[48]: 293 and Castellan and Provveditore of Modon in 1455,[37]: 380 and Captain of Zara from 1462 to 1465.[48]: 293

- Ermolao Barbaro (1455–1497) Son of Zaccaria Barbaro, and the grandson of Francesco Barbaro.[40]: 91 [49] He was also the uncle of Daniele Barbaro and Marcantonio Barbaro[29]: 137 Ambassador to Maximillian, King of the Romans. Patriarch of Aquileia 1491-1493[3]: 276 [25]
- Marco Barbaro was Auditor of Pola in 1458.[31]: 195
- Francesco Barbaro was Luogotenente of Friuli from 1458 to 1459.[50]: 126
- Leonardo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado in 1464.[27]: 192
- Bartolommeo Barbaro, son of Stefano, was Rector of Stalimene (Lemnos) from 1467 to 1471.[37]: 372
- Zaccaria Barbaro was Podestà and Captain of Ravenna from 1468 to 1470.[51]: 337
- Jacopo Barbaro, son of Maffio was Provveditore of Lepanto.from 1468 to 1472.[37]: 392
- Antonio Barbaro. (c.1470) Son of Matteo. Governor of Scutari. Sustained a long siege against the Turks.[3]: 276
- Alvise Barbaro. (c.1470) Son of Zaccaria. Provveditore of the Army, died in the War of Ferrara.[3]: 276
- Pietro Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1472 to 1473.[52]: 133 and Podestà and Captain of Ravenna in 1475.[51]: 337
- Zaccaria Barbaro, son of Matteo was Rector of Nauplia and Argos from 1473 to 1477[37]: 384 and Provveditore General of Cyprus in 1479. Captain against the Turks.[3]: 276
- Andrea Barbaro was Auditor of Grado in 1487.[27]: 193
- Francesco Barbaro (1488–1568) Grandson of Francesco Barbaro, son of Daniele Barbaro and Elena Pisani, father of Daniele Barbaro, Marcantonio Barbaro, and Alvise Barbaro. He was a Senator by 1530, Provveditore alle biave in 1533, Savio di Terrafirma in 1539, Provveditore al Sal in 1541, and Provveditore general of Corfu in 1555, and Provveditore general of Cyprus in 1566. Established the family chapel at the Church of San Francesco della Vigna.[11]: 11 [53]: 738
- Matteo Barbaro was Captain of Cyprus from 1488 to 1489.[54]
- Giacomo Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1489.[55]: 343
- Paolo Barbaro was Podestà of Brescia in 1485 [51]: 145 and Luogotenente of Friuli from 1490 to 1492.[50]: 126
- Ermolao Barbaro (1493–1556) Son of Alvise Barbaro and nephew of Ermolao Barbaro. After holding a series of junior naval and diplomatic posts, he became Governor of Verona from 1544–55 and governor of Padua from 1548-50.[40]: 92 [56]: 244
- Daniele Barbaro was Auditor of Grado in 1499.[27]: 193
- Lunardo Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1504.[55]: 344
- Girolamo Barbaro was Auditor of Zara from 1504 to 1507.[48]: 290
- Giorgio Barbaro, son of Stefano, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1506 to 1508.[57]: 313
- Giovanni Barbaro (c.1508) Ambassador to Pope Julius II.[3]: 276
- Giovanni Antonio Barbaro, son of Giosafat Barbaro was Captain and Provveditore of Piove di Sacco in 1509[58]: 322 and Rector of Nauplia and Argos from 1512 to 1514.[37]: 384 He also served as Provveditore General in Dalmatia and Albania.[59]
- Francesco Barbaro, son of Antonio, was Auditor of Grado in 1511,[27]: 193 Rector of Nauplia and Argos from 1516 to 1519,[37]: 384 Podestà of Monselice in 1527,[56]: 262 Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1528 to 1529,[58]: 322 and Bailo at Constantinople in 1530,[3]: 276
- Alvise Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1511[55]: 358 and Provveditore alle biave in 1512.[53]: 736
- Jacopo Barbaro (d.1511) Naval commander against the Turks. Buried in the Church of Frari.[11]: 11
- Marco Barbaro. (1511–1570) Son of Marco. Genealogist of the families of Venice. His work is preserved in the British Museum in London.[3]: 276 [11]: 7

- Daniele Barbaro (1514–1574) Son of Francesco. Historian, humanist, and diplomat.[60] Mathematician, philosopher, and theologian. Owner of Villa Barbaro. Founded the Botanical Gardens of Padua. Served on the Council of Trent. Created Cardinal in pectore in 1561, revealed as Cardinal in 1571, Patriarch of Aquileia 1550-1570.[25][61]: 72 Ambassador to England. Allowed by Queen Elizabeth to quarter the red and white Tudor roses in his arms. Historian of Venice. Patron of Paolo Veronese. A portrait of him by Veronese hangs in the Pitti Gallery of Florence, another in the Dresden Gallery, and one by Titian in the National Gallery of Canada.[3]: 276

- Marcantonio Barbaro (1518–1595) Son of Francesco, Brother of Patriarch Daniele. Co-owner of Villa Barbaro Diplomat, ambassador to Charles IX of France.[61]: 72 Bailo of Constantinople, imprisoned during the Battle of Lepanto.[61]: 72 Procurator of San Marco. Inquisitor in Corfu. Regent of the University of Padua. President of the construction of the Rialto Bridge. A portrait by Paolo Veronese hung in the Belvedere Gallery in Vienna, but was returned to Italy after World War I. With his brother Daniele, built the Villa Barbaro in Maser (Treviso), with work by Palladio and Vittoria and frescoes by Veronese.[3]: 276 Subject of the work ’'La vie d'un patricien de Venise au XVI siècle " by French academic Charles Yriarte in 1874 in Paris.[3]: 277
- Pietro Barbaro was Podestà of Pirano from 1516 to 1518,[32]: 201 Podestà of Portole from 1523 to 1528,[62]: 260 and Podestà of Pirano again from 1530 to 1532.[32]: 201
- Matteo Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1518 to 1520.[52]: 135
- Cornelio Barbaro was Podestà of Asolo in 1527.[56]: 262
- Alvise Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1528.[55]: 359
- Luigi Barbaro was Lieutenant of Udine in 1530.[56]: 244
- Bernardo Barbaro. (c.1532) Son of Galzerando. Condotierre in the army of Charles V in Italy.[3]: 276
- Zuanne Barbaro. (c.1534) Uncle of Daniele Barbaro and Marcantonio Barbaro. Supervised the rebuilding of the San Francesco della Vigna.[1]: 112
- Francesco Barbaro, son of Luigi, was Podestà of Castelfranco in 1532[56]: 263 and Rector of Nauplia and Argos in 1539[37]: 384 and Provveditore of Zante from 1552 to 1554.[37]: 407
- Bortolomio Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1535.[55]: 359
- Bernardo Barbaro, son of Girolamo, was Podestà of Oderzo from 1540 to 1541.[28]: 255
- Zaccaria Barbaro was Auditor of Trau in 1537.[63]: 365
- Marco Vincenzo Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1541 to 1542.[58]: 322
- Cornelio Barbaro, son of Luigi, was Podestà of Bergamo in 1543,[56]: 265 Provveditore of Zante from 1547 to 1549,[37]: 407 and Captain of Cyprus from 1554 to 1556.[54]
- Ermolao Barbaro was Podestà of Verona in 1545.[56]: 244
- Francesco Barbaro (1546–1616) Son of Marcantonio Barbaro.[13]: 113 Bishop of Aquileia(1585–1593), Patriarch of Aquileia(1593–1616).[25] Ambassador to the Court of Savoy. Archbishop of Tyre. Shown celebrating a Provincial Synod in the choir of the Udine Cathedral.[3]: 277
- Ermolao Barbaro (1548–1622) son of Marc'Antonio. Bishop of Aquileia (1596–1616), Patriarch of Aquileia(1616–1622)[25] Ambassador to Pope Paul V, Archbishop of Tarsus.[3]: 277
- Zaccaria Barbaro, son of Daniele, was Provveditore of Cefalonia from 1554 to 1556.[37]: 399
- Giovanni Barbaro was Luogotenente of Cyprus from 1559 to 1561.[54]
- Giovanni Battista Barbaro. (c.1560) Son of Francesco. Fought against the pirates of the Adriatic.[3]: 276
- Giovanni Nicolo Barbaro, son of Francesco, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1564 to 1567.[57]: 314
- Nicolo Barbaro (c.1569) Son of Bertucci. Captain in Lake Garda, defended the Castle of Lazise against the troops of Georg von Frundsberg during the Sack of Rome. His arms are visible in the Palace dei Capitani de Malcesine.[3]: 276
- Francesco Barbaro. (c.1569) Son of Alvise. Provveditore general in Dalmatia.[3]: 276
- Zaccaria Barbaro was Rector of Belluno in 1571.[52]: 136
- Alvise Barbaro was Auditor of Zara from 1580 to 1581[48]: 291 and Auditor of Trau from 1585 to 1587.[63]: 365
- Francesco Barbaro was Ambassador to Savoy from 1581 to 1582.[64]
- Giacomo Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1589 to 1590.[52]: 137
- Cornelio Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1591.[55]: 361
- Zaccaria Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1593.[55]: 361
- Marco Barbaro, son of Francesco, was Captain of Rovigo and Provveditore of all Polesine from 1598 to 1599[36]: 25 and Provveditore of Cefalonia from 1606 to 1609.[37]: 400
- Luigi Barbaro, son of Giovanni, was Captain and Provveditore of Corfu from 1598 to 1600.[37]: 397
- Aurelio Barbaro was Rector of Fiume in 1602, 1612, and 1624.[65]
- Cornelio Barbaro, son of Giovanni, was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1606[55]: 362 and Castellan and Provveditore of Cerigo from 1612 to 1614.[37]: 412
- Pietro Alvise Barbaro was Podestà of Albona and Fianona from 1612 to 1614.[66]: 234
- Almoro Barbaro, son of Luigi, was Provveditore of Zante from 1615 to 1617.[37]: 408 [67]: 81 Plague struck Zante in 1617.[67]: 580
- Antonio Barbaro was Provedditore General in Istria during the War of Gradisca.[67]: 241 He was relieved on the grounds of illness in 1616, but reappointed in 1617.[68]
- Marin Barbaro was Podestà of Capodistria from 1618 to 1621.[33]: 166

- Piero Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1618.[55]: 362
- Cornelio Barbaro, son of Zaccaria, was Provveditore of Zante from 1619 to 1620.[37]: 408
- Antonio Barbaro was Provveditore general of Zara from 1620 to 1623.[48]: 286
- Giovanni Barbaro, son of Jacopo, was Provveditore of Zante in 1624.[37]: 408
- Bartolomeo Barbaro, son of Giuseppe, was Podestà of Oderzo from 1624 to 1626.[28]: 257
- Alvise Barbaro was Podestà of Capodistria from 1626 to 1627.[33]: 167
- Antonio Barbaro (1627–1678)[22]: 307 [69]: 464 Son of Marc'Antonio. Provveditore general of the army against the Uscocchi. Captain of the Gulf in 1654.[69]: 182 Provveditore d’Armata from 1658-1661.[69]: 182 Provveditore general of Crete in 1667.[69]: 193 Captain in the Battle of the Dardanelles. Provveditore general of Dalmatia. Conquered Zara. There are statues of him and his brothers in the Church of Santa Maria Zobenigo. Praised by Gabriele d'Annunzio during his declaration in Zara in 1918.[3]: 277
- Francesco Barbaro (c.1632) Son of Orazio. Knight of Malta.[3]: 277
- Giacomo Barbaro, son of Pietro Alvise, was Podestà of Oderzo in 1634 .[28]: 257
- Marcantonio Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1636 to 1638.[27]: 195
- Francesco Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1642 to 1643[27]: 195 and Podestà of Portole from 1643 to 1646.[62]: 261
- Alvise Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1644 to 1645[27]: 195 and Podestà of Portole in 1648.[62]: 261
- Daniele Barbaro, son of Alvise was Provveditore alle biave in 1646.[53]: 748
- Giacomo Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Doge of Crete in 1648,[70]: 57 Rector of Belluno in 1654,[52]: 139 Podestà of Oderzo from 1661 to 1662,[28]: 258 and Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1665 to 1667.[58]: 322
- Antonio Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1648 to 1649.[27]: 195
- Lorenzo Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1648 to 1652.[57]: 315
- Luca Francesco Barbaro was Doge of Crete in 1649[70]: 57 and Captain of the Navy in 1651.[69]: 163
- Angelo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1651 to 1653.[27]: 195
- Zambattista Barbaro, son of Zuanne was Provveditore alle biave in 1655.[53]: 749
- Leonardo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1656 to 1657.[27]: 195
- Almoro Barbaro, son of Daniele, was Auditor of Pola from 1658 to 1659.[31]: 198 and Bailo of Corfu from 1666 to 1667.[37]: 395
- Bernardo Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà of Oderzo in 1663.[28]: 258
- Lorenzo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1664 to 1665.[27]: 195
- Sante Barbaro (c.1668) Son of Alberto. Died victorious at Candia. Death is depicted in an album by Gatteri.[3]: 277
- Pietro Alvise Barbaro, son of Giaco, was Podestà of Oderzo from 1669 to 1670.[28]: 258
- Almoro Barbaro, son of Piero was Provveditore alle biave in 1670.[53]: 750
- Giuseppe Barbaro was Podestà of Portole from 1670 to 1674.[62]: 262
- Luigi Barbaro, son of Pietro, was Provveditore of Zante from 1671 to 1674.[37]: 408
- Valentino Barbaro, son of Marc’Antonio, was Podestà of Oderzo from in 1675.[28]: 258
- Stefano Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1677.[55]: 364
- Bernardo Barbaro was Auditor of Trau in 1676.[63]: 365
- Almoro Barbaro. (1681–1758) Son of Alvise. Savior of Terraferma. Procurator of San Marco. Elected Doge of Venice, but refused the position.[3]: 277
- Giorgio Barbaro, son of Alberto, was Rector of Tinos and Mykonos from 1684 to 1689[37]: 375 and again from 1696 to 1700.[37]: 376
- Alvise Barbaro, son of Piero was Provveditore alle biave in 1686[53]: 751 and Podestà of Albona and Fianona from 1690 until his death in 1691.[66]: 234
- Giacomo Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà of Oderzo from 1688 to 1689.[28]: 258
- Angelo Maria Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1692 to 1693.[58]: 323
- Alessandro Barbaro, son of Antonio, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1692 to 1694.[57]: 315
- Alberto Barbaro was Podestà of Portole from 1697 to 1700.[62]: 262
- Girolamo Barbaro was Auditor of Pola from 1698 to 1699[31]: 199 and Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1699.[55]: 365
- Giacomo Barbaro was Podestà of Pirano from 1703 to 1704[32]: 203 and Auditor of Pola from 1704 to 1706.[31]: 199
- Camillo Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1705 to 1707.[58]: 323
- Lorenzo Barbaro, son of Antonio, was Auditor of Grado from 1706 to 1707[27]: 196 and Provveditore of Zarnata from 1711 to 1713.[37]: 390
- Giuseppe Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1708 to 1709[58]: 323 and Rector of Belluno from 1710 to 1711.[52]: 140
- Lorenzo Barbaro established a school in 1711 for the education of poor women in the San Andrea district, which was run by the Sisters of San Dorotea.[26]
- Pietro Barbaro, son of Alberto, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1712 to 1714[57]: 316 and Podestà of Oderzo in 1721.[28]: 259
- Iseppo Barbaro, son of Antonio, was Bailo of Corfu from 1713 to 1716.[37]: 395 [71]
- Marino Barbaro son of Gianfrancesco, was Captain of Zara from 1718 to 1720,[48]: 295 and Provveditore of Vonizza from 1728 to 1730.[37]: 406 [71]
- Marco Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1719.[55]: 352
- Angelo Barbaro, son of Giuseppe, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1721 to 1724[57]: 316 and Auditor of Zara from 1726 to 1728.[48]: 292
- Alessandro Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1725 to 1726.[27]: 196
- Marco Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1727 to 1729.[57]: 316
- Bernardo Barbaro, son of Angelo Maria, was Podestà of Oderzo from 1729 to 1730[28]: 259 and Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1733 to 1735.[58]: 323
- Francesco Barbaro was Captain of Grisignana from 1731 to 1732.[33]: 183
- Agostino Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1732 to 1733.[52]: 141
- Giorgio Barbaro, son of Giuseppe, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1732 to 1735 and from 1745 to 1748.[57]: 316
- Triffon Barbaro was Captain of Grisignana from 1735 to 1736.[33]: 183
- Giuseppe Barbaro, son of Alessandro was Castellan and Provveditore of Cerigo from 1737 to 1739.[37]: 413 [71]
- Girolamo Bernardo Barbaro, son of Nicolo, was Provveditore of Vonizza from 1738 to 1740.[37]: 406 [71]
- Francesco Barbaro was Podestà of Pirano in 1740.[32]: 203
- Antonio Barbaro was Auditor of Zara from 1740 to 1742.[48]: 292
- Marchio Barbaro, son of Alessandro, was Provveditore of Asso and Cefalonia from 1743 to 1745.[37]: 403
- Bernardo Barbaro was Podestà of Albona and Fianona from 1744 to 1747.[66]: 234
- Giuseppe Barbaro was Auditor of Zara from 1746 to 1748.[48]: 292 and Captain of Zara from 1749 to 1752.[48]: 295
- Vicenzo Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1748.[55]: 353
- Andrea Lauro Barbaro was Captain of Grisignana from 1748 to 1750.[33]: 184
- Zuanne Alvise Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1751.[55]: 367
- Stefano Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1753.[55]: 367
- Antonio Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1752 to 1754,[52]: 141 Auditor of Grado from 1754 to 1755,[27]: 197 and Auditor of Zara from 1756 to 1758.[48]: 292
- Giuseppe Maria Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1755 to 1756.[58]: 323
- Zorzi Barbaro was Podestà of Pirano from 1755 to 1756.[32]: 204
- Francesco Antonio Barbaro, son of Marino, was Bailo of Corfu from 1755 to 1758.[37]: 396 [71]
- Simeone Barbaro was Podestà of Pirano from 1758 to 1759.[32]: 204
- Triffon Barbaro was Auditor of Trau from 1759 to 1760.[63]: 367
- Agostino Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà and Provveditore of Romano di Lombardia from 1759 to 1762.[57]: 316
- Pietro Girolamo Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1762 to 1763.[27]: 197
- Bernardo Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1763 to 1765.[58]: 323
- Giacomo Antonio Barbaro was Rector of Belluno from 1765 to 1766.[52]: 142
- Piero Alvise Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1766.[55]: 368
- Girolamo Alberto Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1766 to 1767.[58]: 323
- Marco Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1766 to 1767.[27]: 197
- Giuseppe Maria Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1767 to 1769.[58]: 323
- Federico Barbaro, son of Giacomo, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1775 to 1777[58]: 323 and Podestà of Oderzo in 1778.[28]: 260
- Giovanni Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1777 to 1778.[27]: 197
- Giovanni Barbaro, was Podestà of Piove di Sacco from 1777 to 1778.[58]: 323
- Antonio Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1778 to 1780.[27]: 197
- Angelo Barbaro, son of Agostino, was Provveditore of Santa Maura from 1784 to 1786.[37]: 404 [71]
- Agostino Barbaro, son of Angelo, was Podestà of Oderzo in 1786.[28]: 260
- Antonio Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1792[55]: 354 and Rector of Belluno from 1795 to 1796.[52]: 143
- Giorgio Barbaro was Auditor of Grado from 1793 to 1794.[27]: 198
- Marco Barbaro was Massaro all’oro at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1794.[55]: 354
- Francesco Barbaro was Massaro all’argento at the Zecca (the Venetian Mint) in 1796.[55]: 369
Patronage
The Barbaro family commissioned works from and actively supported the careers of several men. This list includes:
- Flavio Biondo.[72]
- Josse Le Court.[22]: 307
- Andrea Palladio[1]: 113
- Giuseppe Sardi.[22]: 267 [73]
- Vincenzo Scamozzi[1]: 114
- Titian
- Giovanni Battista Tiepolo[11]: 11
- Tintoretto
- Titian
- George of Trebizond[74]
- Paolo Veronese[1]: 113 [75]
- Alessandro Vittoria[1]: 113
Architecture
The Barbaro family was connected to several buildings in and near Venice, some of which include:
- The Palazzi Barbaro, located near the Ponte dell'Accademia, was the family's principal residence in Venice.[1]: 112 until 1864.[12]: 282 "The buildings are also known as the Palazzo Barbaro-Curtis.[12]: 282 It is one of the least altered of the Gothic palaces of Venice.[1]: 112
- Another Palazzo Barbaro owned by a Daniele Barbaro and in 1797 by a Marco Barbaro.[12]: 58
- Yet another Palazzo Barbaro, near the Palazzo Barbarigo. It was owned in 1661 by a Lorenzo Barbaro and in 1712 by a Francesco Antonio Barbaro, but by 1740 it belonged to the Barbarigo family.[12]: 298
- The Palazzo Dario was built about 1450 by Zuanne Dario. After the death of diplomat Giovanni Dario in 1494, his daughter inherited. She was married to Vincenzo Barbaro, the son of Giacomo Barbaro and owner of the neighboring Palazzo Barbaro.[12]: 329
- Another Palazzo Barbaro, now known as the Palazzo Barbaro-Volkoff or Barbaro-Wolkoff. This 14th-century Gothic palace was owned by an Antonio Barbaro in 1797. Eleonora Duse later lived there.[12]: 330
- Marcantonio Barbaro supported Vincenzo Scamozzi’s design for a triple-arched Rialto Bridge, though Antonio da Ponte’s design for a single-arched bridge was chosen instead,[1]: 114 and was one of three Venetian noblemen appointed to oversee the rebuilding of the bridge.[13]: 113
- Starting in 1534, Fra Zuanne Barbaro was one of two friars who were responsible for rebuilding the Church of San Francesco della Vigna according to the design of Jacopo Sansovino. Zuanne's brother Francisco was the first Venetian noble to purchase a family chapel there.[1]: 112 Daniele Barbaro commissioned the church's altarpiece of' 'The Baptism of Christ (c.1555) by Battista Franco and was buried in an unmarked grave in behind the church instead of in the family chapel.[1]: 113
- The church of Santa Maria Zobenigo, also known as the Santa Maria de Giglio was built around 900 by the Zubenigo family, who died out in 1124. It was rebuilt between 1680 and 1700 by Giuseppe Sardi. The Barbaro family funded the rebuilding and the church contains statues of four members of the family. The façade shows plans for Rome, Corfu, Padua, Candia, Spalatro, and Pavia.[12]: 54
- Villa Barbaro at Maser. One of the best known of Andrea Palladio's villas, which he built for Daniele and Marcantonio Barbaro.[1]: 113
- The family also owned a property in the San Giovanni district. Ermolao Barbaro established an academy of philosophy there in 1484.[26]
- In 1593-4 Marcantonio Barbaro was one of the Venetian nobles in charge of the building of the star-shaped fortress town of Palmanova in Friuli.[1]: 114 Marcantonio headed the group, Marcantonio Martinego was in charge of construction, and Giulio Savorgnan acted as an adviser.[76]
- Daniele Barbaro may have designed the Palazzo Trevisan in Murano, alone or in collaboration with Palladio. Like the Villa Barbaro, Paolo Veronese and Alessandro Vittoria probably also worked on the project, which was completed in 1557.[1]: 113
-
Palais Barbaro Wolkoff
-
Palais Barbaro-Curtis
-
Palazzo Barbaro a Santo Stefano
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Encyclopedia of Italian Renaissance & Mannerist art, Volume 1, Jane Turner, New York, 2000 ISBN 0-333-76094-8
- ^ a b c The City of Falling Angels, John Berendt, Penguin Books, 2006, ISBN 1-59420-058-0
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi Enciclopedia storico-nobiliare italiana, Volume 7, Vittorio Spreti, Arnaldo Forni, 1981
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Francesco Barbaro: Früh-Humanismus und Staatskunst in Venedig, Percy Gothein, Berlin, 1932
- ^ Virgil and the myth of Venice, Craig Kallendorf, Oxford University Press, 1999, pg. 17
- ^ Venice, Pure City, Peter Ackroyd, Doubleday, New York, 2009, p.96
- ^ "Palazzo Barbaro-Curtis website"..
- ^ a b c d e f g Das Schiff aus Stein: Venedig u.d. Venezianer, Hermann Schreiber, München, 1979
- ^ a b c The life of Poggio Bracciolini, William Shepherd, Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown, Green & Longman, London, 1837
- ^ a b Una famiglia veneziana nella storia: i Barbaro, Michela Marangoni, Manlio Pastore Stocchi, Istituto Veneto di Scienze, Lettere ed Arti, 1996, ISBN 88-86166-34-6
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o La vie d'un patricien de Venise au seizième siècle, Charles Yriarte, Paris, 1874
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Venice on foot, with the itinerary of the Grand Canal and several direct routes to useful places, Hugh A Douglas, C. Scribner's Sons, 1907
- ^ a b c d Venice and the Renaissance, Manfredo Tafuri, trans. Jessica Levine, 1989, MIT Press, ISBN 0-262-70054-9
- ^ a b Views of Venice, Antonio Canaletto, Antonio Visentini, J. G. Links, Dover Publications, 1971, ISBN 0-486-22627-1
- ^ "Armorial de J.B. RIETSTAP". Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- ^ a b Armorial universel, précédé d'un traité complet de la science du blason, et suivi d'un Supplément:, Jouffroy d'Eschavannes, Paris : L. Curmer, 1845-1848
- ^ Armorial général: précédé d'un Dictionnaire des termes du blason, Volume 1, Johannes Baptist Rietstap, 1884, pg. 1
- ^ Venice, Augustus John Cuthbert Hare, Ballantyne Press, 1896, pg. 149
- ^ Delle inscrizioni veneziane, Volume 4, Emmanuele Antonio Cicogna, Fonni, 1969, pg. 520
- ^ A literary companion to Venice, Ian Littlewood, Ballantyne Press, 1995, pg. 150
- ^ Guida per la città di Venezia all'amico delle belle arti, Volume 1, Giannantonio Moschini, Giovanni Antonio Moschini, Tip. di Alvisopoli, 1815, pg. 468
- ^ a b c d The Baroque in central Europe: places, architecture and art, Manlio Brusatin; Gilberto Pizzamiglio; Gottfried Biedermann; Mark Smith; et al, Venice, Marsillio, 1992
- ^ The Rough Guide to Venice & the Veneto, Jonathan Buckley, Rough Guides, 2004, pg.165
- ^ Hobson, Anthony, "Villa Barbaro", in ’'Great Houses of Europe", ed. Sacheverell Sitwell (London: Weidenfeld, 1961), pp. 89-97. ISBN 0-600-33843-6
- ^ a b c d e "The Patriarchate of Aquileia". Retrieved 2010-10-05.
- ^ a b c "Origini della Toponomastica Veneziana". Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u L'Archeografo triestino: raccolta di opuscoli notizie per Trieste e per l'Istria?, Società di Minerva.; Deputazione di storia patria per le Venezie. Sezione di Trieste, Trieste, 1890
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Museo opitergino, Gaetano Mantovanii, 1874
- ^ a b c d e f A new general biographical dictionary, Volume 3, Hugh James Rose, Henry John Rose, 1857 ISBN 0-333-76094-8
- ^ "The Diocese of Treviso". Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- ^ a b c d e f g Notizie storiche di Pola, Parenzo, 1876
- ^ a b c d e f g h Atti e memorie della Società istriana di archeologia e storia patria, Volume 4, Trieste : Società Istriana di Archeologia e Storia Patria, 1996
- ^ a b c d e f g Pagine istriane, Associazione istriana di studi e storia patria, Centro di cultura Giuliano Dalmata, Societa istriana di archeology, Trieste, 1905
- ^ Biographie universelle, ancienne et moderne, J Fr Michaud; Louis Gabriel Michaud, Paris, Michaud, 1811-28., pg. 327
- ^ Mehmed the Conqueror & His Time, Franz Babinger, Trans. Ralph Manheim, Princeton University Press; 1992, p.305 ISBN 0-691-01078-1
- ^ a b c Dei rettori veneziani in Rovigo: illustrazione storica con documenti, Giovanni Durazzo, Venezia, Tip. del Commercio, 1865
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae Chroniques gréco-romanes inédites ou peu connues, pub. avec notes et tables généalogiques, Carl Hermann Friedrich Johann Hopf, Weidmann, 1873
- ^ Scorsa di un lombardo negli archivj di Venezia, Cesare Cantů, Civelli, 1856, pg.128
- ^ a b c Venice: A Documentary History, 1450-1630, Brian Pullan, 2001, University of Toronto Press
- ^ a b c d Contemporaries of Erasmus a biographical register of the Renaissance and Reformation, v.1-3, A-Z, Peter G Bietenholz; niv. of Toronto Press 2003, ISBN 0-8020-8577-6
- ^ Shell games: studies in scams, frauds, and deceits (1300-1650), Margaret Reeves, Richard Raiswell, Mark Crane, Toronto Centre for Reformation and Renaissance Studies, 2004, pg. 92 ISBN 0-7727-2023-1
- ^ a b c Magnificent Italian villas and palaces, Massimo Listri, Cesare M. Cunaccia, New York, NY, 2003, ISBN 0-8478-2591-4
- ^ Rivista di storia della Chiesa in Italia, Volume 16, Istituto grafico tiberino, Rome, 1962, pg. 107
- ^ Bibliothéque curieuse historique et critique ou catalogue raisonné des livres difficiles a` trouver : Tome 1-9, David Clément, Hannover, 1751, pg. 409
- ^ Dissertazioni Vossiane di Apostolo Zeno, Apostolo Zeno, 1753, pg. 360
- ^ Papacy and the Levant, 1204-1571, Kenneth M. Setton, American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pa. 1976, pg. 340 ISBN 0-87169-114-0
- ^ Storia dell citta di Trau, Paolo Andreis, Marko Perojević, Spljet : Hrvatska stamparija Trumbići drug, 1908, pg. 364
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Istoria della insigne reliquia di San Simeone profeta che si venera in Zara, Lorenzo Fondra, Venezia, 1855
- ^ Pierio Valeriano On the ill fortune of learned men : a Renaissance humanist and his world, Pierio Valeriano; Julia Haig Gaisser, University of Michigan Press, 1999, pg.288, ISBN 0-472-11055-1
- ^ a b Strenna cronologica per l'antica storia del Friuli, Gius. Dom. Della Bona, Gorizia 1856
- ^ a b c Archivio storico italiano, Deputazione toscana di storia patria, 1874
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Compendio storico della regia citta di Belluno e sua antica provincia, Florio Miari, 1830
- ^ a b c d e f Atti del Regio Istituto veneto di scienze, lettere ed arti, Venezia, 1870
- ^ a b c "World Statesmen of Cyprus". Archived from the original on 25 March 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Archivio veneto, Volume 14, Deputazione di storia patria per le Venezie, 1877
- ^ a b c d e f g Renaissance book collecting, Anthony Hobson, New York : Cambridge University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-521-65129-8
- ^ a b c d e f g h i L'antico stato di Romano di Lombardia, Damiano Muoni, Milano, C. Brigola, 1871
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Codice diplomatico Saccense, Pietro Pinton, Roma, 1892
- ^ Vjesnik za arheologiju i historiju dalmatinsku, Volume 12, Frane Bulić, Mihovil Abramić, Arheološki muzej u Splitu., 1889, p.42
- ^ Renaissance vision from spectacles to telescopes, Vincent Ilardi, Philadelphia, PA : American Philosophical Society, 2007, pg. 220 ISBN 978-0-87169-259-7
- ^ a b c Renaissance education between religion and politics, Paul F. Grendler, Aldershot: Ashgate, 2006, ISBN 0-86078-989-6
- ^ a b c d e Archeografo triestino, Volume 11, Domenico Rossetti, 1884
- ^ a b c d Storia dell città di Traù, Paolo Andreis, Marko Perojević, Spljet : Hrvatska stamparija Trumbići drug, 1908
- ^ La diplomatie vénitienne: Les princes de l'Europe au XVIe sičcle, Armand Baschet, Paris, H. Plon, 1862, pg. 158
- ^ Memorie per la storia della liburnica città di Fiume, Giovanni Kobler, 1896, pg. 148, 149
- ^ a b c L' Istria, Volume 1, 1846
- ^ a b c Calendar of state papers and manuscripts, relating to English affairs, A B Hinds, London, 1908
- ^ The Military Organisation of a Renaissance State: Venice C. 1400 to 1617, M.E. Mallett and J.R. Hale, New York : Cambridge University Press, 1984, pg. 279 ISBN 0-521-24842-6
- ^ a b c d e Venice, Austria, and the Turks in the seventeenth century, Kenneth Meyer Setton, Philadelphia : American Philosophical Society, 1991
- ^ a b Venezia e il Turco nella seconda meta del secolo XVII : con documenti inediti e con prefazione di Pasquale Villar, Amy A Bernardy, Florence, 1902
- ^ a b c d e f "World Statesmen of Greece". Archived from the original on 18 April 2010. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Possible lives: authors and saints in Renaissance Italy, Alison Knowles Frazier, New York : Columbia University Press, 2005, pg. 224 ISBN 0-231-12976-9
- ^ The companion guide to Venice, Hugh Honour, New York, Harper & Row, 1966, pg. 182
- ^ Venice, a maritime republic, Frederic Chapin Lane, JHU Press, 1973, pg.219, ISBN 0-8018-1445-6
- ^ The Gentleman's magazine, Volume 223, London, 1867, pg. 737 ISBN 0-521-65129-8
- ^ Renaissance war studies, John Rigby Hale, London Hambledon Press, 1983, pg. 185 ISBN 0-907628-02-8



