Burgundian Netherlands
The Burgundian Netherlands | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1384–1482 | |||||||
| Status | Imperial and French fiefs | ||||||
| Capital | Brussels | ||||||
| Common languages | Dutch, Low Saxon, Frisian, Walloon, Luxembourgish, French | ||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholic | ||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||
• Established | 1384 | ||||||
• Disestablished | 1482 | ||||||
| ISO 3166 code | NL | ||||||
| |||||||
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (French: Pays-Bas Bourguignons, Dutch: Bourgondische Nederlanden, Luxembourgish: Burgundeschen Nidderlanden) refers to a number of Imperial and French fiefs ruled in personal union by the House of Valois-Burgundy and their Habsburg heirs in the period from 1384 to 1482. The area comprised large parts of present-day Belgium and the Netherlands, as well as Luxembourg and parts of northern France.
Dynastic
A fair share (but not most) of these territories were inherited by the Burgundian dukes, a younger branch of the French royal House of Valois in 1384, upon the death of Count Louis II of Flanders. His heiress, Margaret III of Flanders in 1369 had married Philip the Bold, youngest son of King John II of France and the first of the Valois dukes of Burgundy at Dijon, who thus inherited the County of Flanders. The Flemish comital House of Dampierre had been French vassals, who held territory around the affluent cities of Bruges and Ghent, but also adjacent lands in former Lower Lorraine east of the Scheldt river ("Imperial Flanders") including the exclave of Mechelen, which were a fief of the Holy Roman Empire, and furthermore the neighbouring French County of Artois. Together they initiated an era of Burgundian governance in the Low Countries.
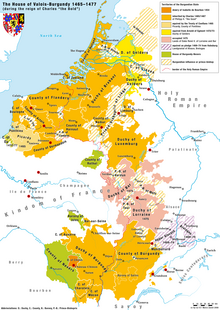
The Dampierre legacy further comprised the French counties of Rethel in northern Champagne and Nevers west of Burgundy proper, both held by Philip's younger son Philip II from 1407, as well as the County of Burgundy (Franche-Comté) east of it, an Imperial fief which had been part of the former Kingdom of Arles.
In the following decades, the Burgundian dukes expanded their territories in the Low Countries by the acquisition of several Imperial States: Duke Philip the Good purchased the County of Namur in 1421, inherited the Duchies of Brabant and Limburg in 1430, and seized the Counties of Hainaut, Holland and Zeeland in 1432, and the Duchy of Luxembourg in 1441. His son, the last Burgundian duke Charles the Bold, in 1473 annexed the Duchy of Guelders, which had been pawned by late Arnold of Egmond.
The Valois era would last until 1477, when Duke Charles the Bold died at the Battle of Nancy leaving no male heir. The territorial Duchy of Burgundy reverted to the French crown according to Salic law, and King Louis XI of France also seized the French portion of the Burgundian possessions in the Low Countries. The Imperial fiefs passed to the Austrian House of Habsburg through Charles' daughter Mary of Burgundy and her husband Archduke Maximilian of Habsburg, son of Emperor Frederick III. Maximilian however regarded the Burgundian Netherlands including Flanders and Artois as the undivided domains of his wife and himself and marched against the French. The conflict culminated at the Battle of Guinegate in 1479. Though Maximilian was victorious, he was only able to gain the County of Flanders according to the 1482 Treaty of Arras after his wife Mary had suddenly died, while France retained Artois.
In her testament, Mary of Burgundy had bequested the Burgundian heritage to her and Maximilian's son, Philip the Handsome. His father, dissatisfied with the terms of the Arras agreement, continued to campaign the seized French territories. In 1493, King Charles VIII of France according to the Treaty of Senlis finally renounced Artois, which together with Flanders was incorporated into the Imperial Seventeen Provinces under the rule of Philip.
Rulers
The Burgundian dukes who ruled the Netherlandish territories were:
House of Valois, territorial Dukes of Burgundy
- Philip the Bold (1384–1405), son of King John II of France, by his wife Margaret III of Flanders
- John the Fearless (1405–1419), son
- Philip the Good (1419–1467), son
- Charles the Bold (1467–1477), son
House of Valois, titular Duchess of Burgundy
- Mary of Burgundy (1477–1482), Charles' daughter, married Maximilian I of Habsburg in 1477
House of Habsburg, titular Dukes of Burgundy (see Habsburg Netherlands)
- Philip the Handsome (1482–1506), Mary's son; Maximilian I, his father, as regent (1482–1493)
- Charles V (1506–1555), Philip's son; Margaret of Austria, regent (1507–1515) and (1519–1530)
Political
The sheer burden of variety of bishoprics and independent cities, the intensely local partisanship, the various taxation systems, weights and measures, internal customs barriers, fiercely defended local rights were all hindrances to a "good Valois". Attempts at enlarging personal control by the dukes resulted in revolts among the independent towns (sometimes supported by independent local nobles) and bloody military suppression in response. An increasingly modernized central government, with a bureaucracy of clerks, allowed the dukes to become celebrated art patrons and establish a glamorous court life that gave rise to conventions of behavior that lasted for centuries. Philip the Good (1419–1467) extended his personal control to the southeast; bringing Brussels, Namur, and Liège under his control. He channeled the traditional independence of the cities through such mechanisms as the first Estates-General, and consolidating of the region's economy.
The Estates-General met for the first time in the City Hall of Bruges on 9 January 1464. It consisted of delegates of the Estates of Brabant, Flanders, Lille, Douai, Orchies, Artois, Hainaut, Holland, Zeeland, Namur, Mechelen and Boulonnais. Up to 1464, the Duke only maintained ties with each of the provincial States separately. In principle, the provincial Estates were composed of representatives of the three traditional estates: clergy, nobility and the Third Estate, but the exact composition and influence of each estate (within the provincial Estates) could differ. Convening an Estates-General in which all provincial Estates were represented was part of Philip the Good's policy of centralisation.
Ducal patronage
From 1441, Philip based his ducal court in Brussels, but Bruges was the center of commerce, though by the 1480s the inevitable silting of its harbor was bringing its economic hegemony to a close. Philip was a great patron of illuminated manuscripts and court painting reached new highs: Robert Campin, the van Eyck brothers, and Rogier van der Weyden
Social and economic
In 1491 and 1492, the Netherlands was afflicted by revolts by the Dutch peasantry. These revolts were suppressed by an army under the command of Duke Albert III of Saxony at the Battle of Heemskerk.[1]
External links
- Metropolitan Museum: "Burgundian Netherlands: Court Life
- Metropolitan Museum: "Burgundian Netherlands: Private Life
References
- ^ Frederick Engels, "The Peasant War of Germany" contained in the Collected Works of Karl Marx and Frederick Engels: Volume 10 (International Publishers: New York, 1978) p. 431.
Sources
- Panofsky, Erwin, Early Netherlandish Painting
- Prevenier, W. and Blockmans W., The Burgundian Netherlands Cambridge University Press 1986

