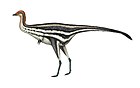
Caudipteryx
| Caudipteryx Temporal range: Early Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Mounted C. zoui skeleton restoration | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Caudipteridae |
| Genus: | †Caudipteryx Ji et al., 1998 |
| Type species | |
| †Caudipteryx zoui Ji et al., 1998
| |
| Species | |
| |
Caudipteryx (which means "tail feather") is a genus of peacock-sized theropod dinosaurs that lived in the Barremian age of the early Cretaceous (about 124.6 million years ago). They were feathered and extremely birdlike in their overall appearance, to the point that some paleontologists think it was a bird. Two species have been described: C. zoui (the type species), in 1998,[1] and C. dongi, in 2000.[2]
Caudipteryx fossils were first discovered in the Yixian Formation of the Sihetun area of Liaoning Province, northeastern China in 1997.
Description

Caudipteryx, like many other maniraptorans, has a mix of reptile- and bird-like anatomical features.[3]
It had a short, boxy skull with a beak-like snout that retained only a few tapered teeth in the front of the upper jaw. It had a stout trunk, long legs and was probably a swift runner.[citation needed]
Its short tail was stiffened toward the tip, with few vertebrae, like in birds and other oviraptorosaurs. It has a primitive pelvis and shoulder, and primitive skull details in the quadratojugal, squamosal, quadrate, jugal, and mandibular fenestra (in the cheek, jaw, and jaw joint). It has a hand skeleton with a reduced third finger, like that of early birds and the oviraptorid Heyuannia.[4]
Caudipteryx had uncinate processes on the ribs, birdlike teeth, a first toe which may or may not be partially reversed and overall body proportions that are comparable to those of modern flightless birds.[1][2][3][5][6] The size of C. zoui is estimated at 65 cm (2.1 ft) in length and 2.2 kg (4.8 lbs) in body mass, while C. dongi is thought to have been slightly larger at 80 cm (2.6 ft) in length and 2.3 kg (5 lbs) in body mass.[7][8]
Paleobiology
Feathers


The hands of Caudipteryx supported symmetrical, pennaceous feathers that had vanes and barbs, measuring between 15–20 centimetres (5.9–7.9 inches) long. The primary feathers were arranged in a wing-like fan along the second finger, just like primary feathers of birds and other maniraptorans. No fossil of Caudipteryx zoui preserves any secondary feathers attached to the forearms, as found in dromaeosaurids, Archaeopteryx, and modern birds.[3] Either these arm feathers are not preserved, or they were not present on Caudipteryx in life. An additional fan of feathers existed on its tail. The shortness and symmetry of the feathers, and the shortness of the arms relative to the body size, indicate that Caudipteryx was flightless.[citation needed]
Its body was covered in black feathers, with a visible banding pattern preserved on tail feathers.[9]
Diet

Caudipteryx is thought to have been an omnivore. In at least two specimens of Caudipteryx (NGMC 97 4 A and NGMC 97 9 A), gastroliths are preserved. As in some herbivorous dinosaurs, the avialan Sapeornis, and modern birds, these gastroliths remain in the position where the animals' gizzards would have been.[1]
Paleoecology
All Caudipteryx fossils were recovered from the Yixian Formation in Liaoning, China. Specifically, they come from a small area of the Jianshangou bed, near the town of Zhangjiakou. They appear to have been fairly common, though isolated to this small region. The specific region in which Caudipteryx lived was home to the other feathered dinosaurs Dilong and Sinornithosaurus.[10]
Implications

The discovery of Caudipteryx has led to many intensive studies and debate over the relationship of birds and dinosaurs. The possible positions in the debate can be summarized as follows: Caudipteryx is either a member of the Oviraptorosauria, or a bird, or both, and birds are either dinosaurs or they are not. (See the rest of this section and Phylogeny, below).[This paragraph needs citation(s)]
Because Caudipteryx has clear and unambiguously pennaceous feathers, like modern birds, and because several cladistic analyses have consistently recovered it as a non-avian oviraptorid dinosaur, it provided, at the time of its description, the clearest and most succinct evidence that birds evolved from dinosaurs. Lawrence Witmer stated: “The presence of unambiguous feathers in an unambiguously non-avian theropod has the rhetorical impact of an atomic bomb, rendering any doubt about the theropod relationships of birds ludicrous.”[3]
However, not all scientists agreed that Caudipteryx was unambiguously non-avian, and some of them continued to doubt that general consensus. Paleornithologist Alan Feduccia sees Caudipteryx as a flightless bird evolving from earlier archosaurian dinosaurs rather than from late theropods.[11] Jones et al. (2000) found that Caudipteryx was a bird based on a mathematical comparison of the body proportions of flightless birds and non-avian theropods. Dyke and Norell (2005) criticized this result for flaws in their mathematical methods, and produced results of their own which supported the opposite conclusion.[6][12]
Other researchers not normally involved in the debate over bird origins, such as Zhou, acknowledged that the true affinities of Caudipteryx were debatable.[5]
Classification

The consensus view, based on several cladistic analyses, is that Caudipteryx is a basal (primitive) member of the Oviraptorosauria, and the oviraptorosaurians are non-avian theropod dinosaurs.[12] Incisivosaurus is the only oviraptorosaur that is more primitive.[13]
Halszka Osmólska et al. (2004) ran a cladistic analysis that came to a different conclusion. They found that the most birdlike features of oviraptorids actually place the whole clade within Aves itself, meaning that Caudipteryx is both an oviraptorid and a bird. In their analysis, birds evolved from more primitive theropods, and one lineage of birds became flightless, re-evolved some primitive features, and gave rise to the oviraptorids. This analysis was persuasive enough to be included in paleontological textbooks like Benton's Vertebrate Paleontology (2005).[14] The view that Caudipteryx was secondarily flightless is also preferred by Gregory S. Paul,[15] Lü et al.,[16] and Maryańska et al.[17]
Others, such as Stephen Czerkas and Larry Martin have concluded that Caudipteryx is not a theropod dinosaur at all.[18] They believe that Caudipteryx, like all maniraptorans, is a flightless bird, and that birds evolved from non-dinosaurian archosaurs.[19]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Ji, Q.; Currie, P.J.; Norell, M.A.; Ji, S. (1998). "Two feathered dinosaurs from northeastern China" (PDF). Nature. 393 (6687): 753–761. Bibcode:1998Natur.393..753Q. doi:10.1038/31635. S2CID 205001388. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-12-17.
- ^ a b Zhou, Z.; Wang, X. (2000). "A new species of Caudipteryx from the Yixian Formation of Liaoning, northeast China" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 38 (2): 113–130. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-10-07.
- ^ a b c d Witmer, L.M. (2005). “The Debate on Avian Ancestry; Phylogeny, Function and Fossils”, Mesozoic Birds: Above the Heads of Dinosaurs : 3–30. ISBN 0-520-20094-2
- ^ Osmolska, H., Currie, P.J., and Barsbold, R. (2004). "Oviraptorosauria." In Weishampel, Dodson, Osmolska (eds.) The Dinosauria, second edition. University of California Press, 2004.
- ^ a b Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X. (2000). "Important features of Caudipteryx - Evidence from two nearly complete new specimens" (PDF). Vertebrata PalAsiatica. 38 (4): 241–254.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Jones, T.D.; Farlow, J.O.; Ruben, J.A.; Henderson, D.M.; Hillenius, W.J. (2000). "Cursoriality in bipedal archosaurs". Nature. 406 (6797): 716–718. Bibcode:2000Natur.406..716J. doi:10.1038/35021041. PMID 10963594. S2CID 4395244. PDF Supplementary information
- ^ Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs. Princeton University Press. p. 173. ISBN 978-1-78684-190-2. OCLC 985402380.
- ^ Molina-Pérez & Larramendi (2016). Récords y curiosidades de los dinosaurios Terópodos y otros dinosauromorfos. Spain: Larousse. p. 271.
- ^ Roy, Arindam; Pittman, Michael; Saitta, Evan T.; Kaye, Thomas G.; Xu, Xing (2020). "Recent advances in amniote palaeocolour reconstruction and a framework for future research". Biological Reviews. 95: 22–50. doi:10.1111/brv.12552.
- ^ Xu, X.; Norell, M.A. (2006). "Non-Avian dinosaur fossils from the Lower Cretaceous Jehol Group of western Liaoning, China". Geological Journal. 41 (3–4): 419–437. doi:10.1002/gj.1044. S2CID 32369205.
- ^ Feduccia, A. (1999). The Origin and Evolution of Birds. 420 pp. Yale University Press, New Haven. ISBN 0-300-07861-7.
- ^ a b Dyke, Gareth J.; Norell, Mark A. (2005). "Caudipteryx as a non-avialan theropod rather than a flightless bird" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 50 (1): 101–116.
- ^ Turner, Alan H.; Pol, Diego; Clarke, Julia A.; Erickson, Gregory M.; Norell, Mark (2007). "A basal dromaeosaurid and size evolution preceding avian flight" (PDF). Science. 317 (5843): 1378–1381. Bibcode:2007Sci...317.1378T. doi:10.1126/science.1144066. PMID 17823350.
- ^ Osmólska, Halszka, Currie, Philip J., Barsbold, Rinchen (2004) The Dinosauria Weishampel, Dodson, Osmolska. "Chapter 8 Oviraptorosauria" University of California Press.
- ^ Paul, G.S. (2002). Dinosaurs of the Air: The Evolution and Loss of Flight in Dinosaurs and Birds. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore. ISBN 0-8018-6763-0
- ^ Lü, J., Dong, Z., Azuma, Y., Barsbold, R., and Tomida, Y. (2002). "Oviraptorosaurs compared to birds." In Zhou, Z., and Zhang, F. (eds.), Proceedings of the 5th Symposium of the Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, 175–189. Beijing Science Press.
- ^ Maryańska, T.; Osmólska, H.; Wolsan, M. (2002). "Avialan status for Oviraptorosauria" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 47 (1): 97–116.
- ^ Martin, Larry D. (2004). "A basal archosaurian origin for birds". Acta Zoologica Sinica. 50 (6): 978–990.
- ^ Martin, L.D.; Czerkas, S.A. (2000). "The Fossil Record of Feather Evolution in the Mesozoic". American Zoologist. 40 (4): 687–694. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.505.6483. doi:10.1668/0003-1569(2000)040[0687:TFROFE]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 85701665.
External links
- Australian Museum: Chinese Dinosaurs: Caudipteryx zoui. Retrieved 2007-FEB-19.
- Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County: From Dinosaurs to Birds: Caudipteryx. Retrieved 2007-FEB-19.
- Research Casting International: Life-size model of Caudipteryx zoui. Retrieved 2007-FEB-19.
- CNN: Scientists: Fossils prove that birds evolved from dinosaurs. Retrieved 2007-AUG-10