Cibao
El Cibao | |
|---|---|
 The main Cibao region in dark blue. | |
| Country | Dominican Republic |
| Area | |
| • Total | 19,058.62 km2 (7,358.57 sq mi) |
| Population (2009) | |
| • Total | 5,622,378. |
| • Density | 295/km2 (760/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Cibaenian; Cibaine (Template:Lang-es) |
Cibao (from Taíno Ciba-o 'rocky land'; from ciba 'rock" or "stone' and o 'land" or "place'), usually referred as "El Cibao", is a region of the Dominican Republic located at the northern part of the country. As of 2009 the Cibao has a population of 5,622,378 making it the most populous region in the country.[1]
The word Cibao, meaning "place where rocks abound", was a native name for the island, although the Spanish used it during the Spanish conquest to refer to the rich and fertile valley between the Central and Septentrional mountain ranges.
Geography and Economy

Cibao occupies the central and northern part of the Dominican territory. To the north and east of the region lies the Atlantic Ocean; to its west lies the Republic of Haiti and to the south the Central Range, which separates Cibao from the other natural regions.
The Cordilla Central mountain range is located within Cibao, containing the highest peak in all of the Caribbean, Pico Duarte. Two of the largest rivers of the country are also located inside this region: the Yaque del Norte, the largest river of the Dominican Republic, and the Yuna river. Both of these rivers contain several chains of dams used to provide the region with water for irrigation (since agriculture is the main activity of the area) and hydroelectric energy. Rice, coffee and cacao are the most important crops grown in the area.
The central mountain range also has important mining activity. Its main mineral resources include gold, iron and nickel, among others. The internationally known Falconbridge is the company in charge of the extraction of these ores.
Culture

The valley is not only a geographical unit, but also a cultural and linguistic unit. The Cibao region is considered to be the cultural heartland of the Dominican Republic. The local dialect of Spanish spoken in the area, has a number of innovative syntactic, semantic, and phonological features [2], none of which appear to be the product of language contact with either English or French.
Merengue music, played using the güira, tambora and accordion, was originated in Cibao. The folk type of merengue is played by the perico ripiao, which are typical local musical groups. This latter name is also often used to refer to the folk genre itself.

During Late January and through February, several carnivals are held within the region. The most popular of these festivals belongs to the province of La Vega, and dates back to the first European settlements. It began as a religious activity celebrating the pre-Lent season, and the carnival's theme revolves around the victory of good over evil.
Many important Dominican patriots were of Cibaine origin. Among the most important are local generals José Desiderio Valverde and José Antonio Salcedo, who were responsible for the restoration of the Republic in the later decades of the 1800s. During the Trujillo dictatorship, the Mirabal sisters arranged clandestine organizations to rebel against the anarchy. The sisters were brutally murdered in 1960, and remain today as some of the biggest martyrs on behalf of the Dominican nation.
The bulk of the population is mainly concentrated in the center of the region. The city of Santiago de los Caballeros constitutes the regional center and main focus of development of the area.
Provinces
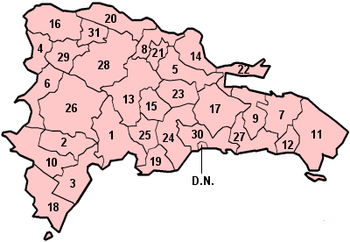
| Province | Capital | Area (km²)[3] | Population[3] | Density[3] | Map region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dajabón | Dajabón | 1,020.73 | 62,046 | 61 | 4 |
| Duarte | San Francisco de Macorís | 1,605.35 | 283,805 | 177 | 5 |
| Espaillat | Moca | 838.62 | 225,091 | 268 | 8 |
| Hermanas Mirabal | Salcedo | 440.43 | 96,356 | 219 | 21 |
| La Vega | Concepción de la Vega | 2,287.24 | 385,101 | 168 | 13 |
| María Trinidad Sánchez | Nagua | 1,271.71 | 135,727 | 119 | 14 |
| Monseñor Nouel | Bonao | 992.39 | 167,618 | 169 | 15 |
| Monte Cristi | San Fernando de Monte Cristi | 1,924.35 | 111,014 | 58 | 16 |
| Puerto Plata | San Felipe de Puerto Plata | 1,852.90 | 312,706 | 168 | 20 |
| Samaná | Santa Bárbara de Samaná | 853.74 | 91,875 | 108 | 22 |
| Sánchez Ramírez | Cotuí | 1,196.13 | 151,179 | 126 | 23 |
| Santiago | Santiago de los Caballeros | 2,836.51 | 908,250 | 320 | 28 |
| Santiago Rodríguez | San Ignacio de Sabaneta | 1,111.14 | 59,629 | 54 | 29 |
| Valverde | Santa Cruz de Mao | 823.38 | 158,293 | 192 | 31 |
| Total | 19,058.62 | 3,148,690 | 165 | - |
References
- ^ Santo Domingo: A Country with a Future.
- ^ Bullock, B. & J. Toribio. 2009. Reconsidering Dominican Spanish: Data from the rural Cibao. RILI 7, 2: 49-73.
- ^ a b c Oficina Nacional de Estadística. "República Dominicana en Cifras 2006" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 2007-03-27. Archived October 9, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
