Diocese of Asia
Appearance
| Diocese of Asia Dioecesis Asiana Διοίκησις Ασίας | |
|---|---|
| Diocese of the Roman Empire | |
| 314 – 535 | |
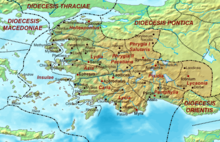 The Diocese of Asia c. 400. | |
| Capital | Ephesus |
| Historical era | Late Antiquity |
• Established | 314 |
• Diocese abolished by Justinian I | 535 |
| Today part of | |
The Diocese of Asia (Latin: Dioecesis Asiana, Greek: Διοίκησις Ασίας/Ασιανής) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of western Asia Minor and the islands of the eastern Aegean Sea. The diocese was established after the reforms of Diocletian, was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of the East, and was abolished during the reforms of Justinian I in 535.
It was one of the most populous and wealthy dioceses of the Empire, and included 11 provinces:[1] Asia, Hellespontus, Pamphylia, Caria, Lydia, Lycia, Lycaonia, Pisidia, Phrygia Pacatiana, Phrygia Salutaria and Insulae.
List of known Vicarii Asiae
- Flavius Ablabius (324-326)
- Tertullianus (c. 330)
- Veronicianus (334-335)
- Scylacius (c. 343)
- Anatolius (c. 352)
- Araxius (353-354)
- Germanus (360)
- Italicianus (361)
- Caesarius (362-363)
- Clearchus (363-366)
- Auxonius (366-367)
- Musonius (367-368)
References
- ^ Alexander Demandt, Geschichte der Spätantike, Monachii 1998, p. 216.
Categories:
- States and territories established in the 310s
- States and territories disestablished in the 530s
- Civil dioceses of the Roman Empire
- Roman provinces in Anatolia
- Roman Greece
- Civil dioceses of the Byzantine Empire
- Praetorian prefecture of the East
- Roman Anatolia
- States and territories disestablished in 535
- Ancient Rome stubs
- Byzantine Empire stubs
