External sphincter muscle of male urethra
Appearance
It has been suggested that this article be merged with External sphincter muscle of female urethra. (Discuss) Proposed since July 2014. |
| Sphincter urethrae membranaceae muscle | |
|---|---|
 The male urethra laid open on its anterior (upper) surface. (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.) | |
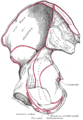
 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Junction of the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium to the extent of 1.25 to 2 cm. |
| Insertion | Ischiopubic rami |
| Nerve | Deep branch of Perineal Nerve |
| Actions | Constricts urethra, maintain urinary continence |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter urethrae externus urethrae masculinae, musculus sphincter urethrae membranaceae |
| TA98 | A09.4.02.016M |
| TA2 | 2421 |
| FMA | 19733 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The external sphincter muscle of urethra (or sphincter urethrae membranaceae) surrounds the whole length of the membranous portion of the urethra, and is enclosed in the fasciæ of the urogenital diaphragm.
Its external fibers arise from the junction of the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium to the extent of 1.25 to 2 cm., and from the neighboring fasciae.
They arch across the front of the urethra and bulbourethral glands, pass around the urethra, and behind it unite with the muscle of the opposite side, by means of a tendinous raphe.
Its innermost fibers form a continuous circular investment for the membranous urethra.
Additional images
-
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy figure: 41:06-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Muscles of the female urogenital diaphragm (deep perineal pouch) and structures located inferior to it."