Golden triangle (mathematics)

A golden triangle, also known as the sublime triangle,[1] is an isosceles triangle in which the duplicated side is in the golden ratio to the distinct side:
Golden triangles are found in the nets of several stellations of dodecahedrons and icosahedrons.
Also, it is the shape of the triangles found in the points of pentagrams. The vertex angle is equal to
Since the angles of a triangle sum to 180°, base angles are therefore 72° each.[1] The golden triangle can also be found in a decagon, or a ten-sided polygon, by connecting any two adjacent vertices to the center. This will form a golden triangle. This is because: 180(10-2)/2=144 degrees is the interior angle and bisecting it through the vertex to the center, 144/2=72.[1]
The golden triangle is also uniquely identified as the only triangle to have its three angles in 2:2:1 proportions.[2]
Logarithmic spiral

The golden triangle is used to form a logarithmic spiral. By bisecting the base angles, a new point is created that in turn, makes another golden triangle.[3] The bisection process can be continued infinitely, creating an infinite number of golden triangles. A logarithmic spiral can be drawn through the vertices. This spiral is also known as an equiangular spiral, a term coined by René Descartes. "If a straight line is drawn from the pole to any point on the curve, it cuts the curve at precisely the same angle," hence equiangular.[4]
Golden gnomon
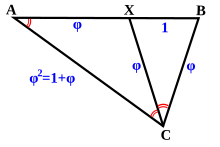

Closely related to the golden triangle is the golden gnomon, which is the obtuse isosceles triangle in which the ratio of the length of the equal (shorter) sides to the length of the third side is the reciprocal of the golden ratio. The golden gnomon is also uniquely identified as a triangle having its three angles in 1:1:3 proportion. The acute angle is 36 degrees, which is the same as the apex of the golden triangle.
The distance of AD and BD are both equal to φ, as seen in the figure. "The golden triangle has a ratio of base length to side length equal to the golden section φ, whereas the golden gnomon has the ratio of side length to base length equal to the golden section φ."[5]
A golden triangle can be bisected into a golden triangle and a golden gnomon. The same is true for a golden gnomon. A golden gnomon and a golden triangle with their equal sides matching each other in length, are also referred to as the obtuse and acute Robinson triangles.[2] These isosceles triangles can be used to produce Penrose tilings. Penrose tiles are made from kites and darts. A kite is made from the golden triangle, and a dart is made from two gnomons.
See also
- Golden ratio
- Golden rectangle
- Golden rhombus
- Kepler triangle
- Lute of Pythagoras
- Penrose tiling
- Pentagram
References
- ^ a b c Elam, Kimberly (2001). Geometry of Design. New York: Princeton Architectural Press. ISBN 1-56898-249-6. Cite error: The named reference "elam" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b Tilings Encyclopedia. 1970. Cite error: The named reference "tilings" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ Huntley, H.E. (1970). The Divine Proportion: A Study In Mathematical Beauty. New York: Dover Publications Inc. ISBN 0-486-22254-3.
- ^ Livio, Mario (2002). The Golden Ratio: The Story of Phi, The World's Most Astonishing Number. New York: Broadway Books. ISBN 0-7679-0815-5.
- ^ Livio, Arthur (1992). Concepts and Images: Visual Mathematics. Boston: Birkhäuser Boston. ISBN 0-8176-3620-X.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Golden triangle". MathWorld.
- Robinson triangles at Tilings Encyclopedia



