HIST3H2BB
Appearance
| H2BU1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | H2BU1, H2Bb, histone cluster 3, H2bb, histone cluster 3 H2B family member b, H2B.U histone 1, HIST3H2BB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 615046; MGI: 1922442; HomoloGene: 75941; GeneCards: H2BU1; OMA:H2BU1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Histone H2B type 3-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST3H2BB gene.[5][6]
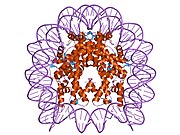
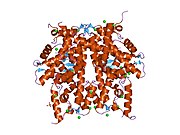
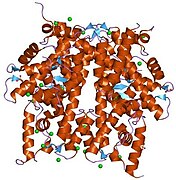
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 base pairs (bp) of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H2B family. Transcripts from this gene contain a palindromic termination element.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c ENSG00000285449 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000196890, ENSG00000285449 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000080712 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Marzluff WF, Gongidi P, Woods KR, Jin J, Maltais LJ (Oct 2002). "The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes". Genomics. 80 (5): 487–98. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(02)96850-3. PMID 12408966.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: HIST3H2BB histone cluster 3, H2bb".
Further reading
[edit]- Borowski P, Heiland M, Oehlmann K, et al. (1996). "Non-structural protein 3 of hepatitis C virus inhibits phosphorylation mediated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase". Eur. J. Biochem. 237 (3): 611–8. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0611p.x. PMID 8647104.
- El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional activation of the integrated chromatin-associated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2535–44. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.5.2535. PMC 110633. PMID 9566873.
- Borowski P, Kühl R, Laufs R, et al. (1999). "Identification and characterization of a histone binding site of the non-structural protein 3 of hepatitis C virus". J. Clin. Virol. 13 (1–2): 61–9. doi:10.1016/S1386-6532(99)00007-4. PMID 10405893.
- Thomson S, Clayton AL, Hazzalin CA, et al. (1999). "The nucleosomal response associated with immediate-early gene induction is mediated via alternative MAP kinase cascades: MSK1 as a potential histone H3/HMG-14 kinase". EMBO J. 18 (17): 4779–93. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.17.4779. PMC 1171550. PMID 10469656.
- Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, et al. (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones". Virology. 277 (2): 278–95. doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0593. PMID 11080476.
- Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, et al. (2001). "Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA". Virology. 289 (2): 312–26. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1129. PMID 11689053.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Cheung WL, Ajiro K, Samejima K, et al. (2003). "Apoptotic phosphorylation of histone H2B is mediated by mammalian sterile twenty kinase". Cell. 113 (4): 507–17. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00355-6. PMID 12757711. S2CID 21854.
- Coleman MA, Miller KA, Beernink PT, et al. (2004). "Identification of chromatin-related protein interactions using protein microarrays". Proteomics. 3 (11): 2101–7. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300593. PMID 14595808. S2CID 23471253.
- Lusic M, Marcello A, Cereseto A, Giacca M (2004). "Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression by histone acetylation and factor recruitment at the LTR promoter". EMBO J. 22 (24): 6550–61. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg631. PMC 291826. PMID 14657027.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Kanno T, Kanno Y, Siegel RM, et al. (2004). "Selective recognition of acetylated histones by bromodomain proteins visualized in living cells". Mol. Cell. 13 (1): 33–43. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00482-9. PMID 14731392.
- Zhang Y, Griffin K, Mondal N, Parvin JD (2004). "Phosphorylation of histone H2A inhibits transcription on chromatin templates". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (21): 21866–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400099200. PMID 15010469.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Golebiowski F, Kasprzak KS (2007). "Inhibition of core histones acetylation by carcinogenic nickel(II)". Mol. Cell. Biochem. 279 (1–2): 133–9. doi:10.1007/s11010-005-8285-1. PMID 16283522. S2CID 25071586.
- Zhu B, Zheng Y, Pham AD, et al. (2006). "Monoubiquitination of human histone H2B: the factors involved and their roles in HOX gene regulation". Mol. Cell. 20 (4): 601–11. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.09.025. PMID 16307923.
- Bonenfant D, Coulot M, Towbin H, et al. (2006). "Characterization of histone H2A and H2B variants and their post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 5 (3): 541–52. doi:10.1074/mcp.M500288-MCP200. PMID 16319397.
- Beck HC, Nielsen EC, Matthiesen R, et al. (2006). "Quantitative proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications of human histones". Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 5 (7): 1314–25. doi:10.1074/mcp.M600007-MCP200. PMID 16627869.
- Gregory SG, Barlow KF, McLay KE, et al. (2006). "The DNA sequence and biological annotation of human chromosome 1". Nature. 441 (7091): 315–21. Bibcode:2006Natur.441..315G. doi:10.1038/nature04727. PMID 16710414.