Hernando de Soto: Difference between revisions
Neurolysis (talk | contribs) m Reverted edits by 208.25.97.242 to last version by 216.79.181.106 (HG) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Hernando de Soto''' ([[Jerez de los Caballeros]], [[Badajoz (province)|Badajoz]], [[Spain]], c.1496/1497<ref>[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9068780/Hernando-de-Soto "Hernando de Soto"], from ''[[Encyclopedia Britannica]]'', Online edition. Full article freely available (3 pages: keep clicking "Next page" links).</ref>–[[May 21]], [[1542]]) was a [[Spanish people|Spanish]] [[Exploration|explorer]] and [[conquistador]] who, while leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day [[United States]], was the first European to discover the [[Mississippi River]]. |
'''Hernando de Soto''im gay wanna f me' ([[Jerez de los Caballeros]], [[Badajoz (province)|Badajoz]], [[Spain]], c.1496/1497<ref>[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9068780/Hernando-de-Soto "Hernando de Soto"], from ''[[Encyclopedia Britannica]]'', Online edition. Full article freely available (3 pages: keep clicking "Next page" links).</ref>–[[May 21]], [[1542]]) was a [[Spanish people|Spanish]] [[Exploration|explorer]] and [[conquistador]] who, while leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day [[United States]], was the first European to discover the [[Mississippi River]]. |
||
A vast undertaking, de Soto's expedition ranged throughout the [[southeastern United States]] searching for gold and a passage to China. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the [[Mississippi River]] at present-day [[Lake Village, Arkansas]]. Hernando de Soto was born to parents who were [[Hidalgo (Spanish nobility)|hidalgos]] of modest means in Extremadura, a region of poverty and hardship from which many young people looked for ways to seek their fortune elsewhere. Two towns—[[Badajoz]] and [[Jerez de los Caballeros]]—claim to be his birthplace. All that is known with certainty is that he spent time as a child at both places and he stipulated in his will that his body be interred at Jerez de los Caballeros, where other members of his family were also interred.<ref>Charles Hudson (1997). Page 39.</ref> The age of the Conquerors came on the heels of the Spanish reconquest of the Iberian peninsula from Islamic forces. Spain and Portugal were filled with young men begging for a chance to find military fame after the Moors were defeated. With discovery of new lands to the West (which seemed at the time to be far East Asia), the whispers of glory and wealth were too compelling for the poor. |
A vast undertaking, de Soto's expedition ranged throughout the [[southeastern United States]] searching for gold and a passage to China. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the [[Mississippi River]] at present-day [[Lake Village, Arkansas]]. Hernando de Soto was born to parents who were [[Hidalgo (Spanish nobility)|hidalgos]] of modest means in Extremadura, a region of poverty and hardship from which many young people looked for ways to seek their fortune elsewhere. Two towns—[[Badajoz]] and [[Jerez de los Caballeros]]—claim to be his birthplace. All that is known with certainty is that he spent time as a child at both places and he stipulated in his will that his body be interred at Jerez de los Caballeros, where other members of his family were also interred.<ref>Charles Hudson (1997). Page 39.</ref> The age of the Conquerors came on the heels of the Spanish reconquest of the Iberian peninsula from Islamic forces. Spain and Portugal were filled with young men begging for a chance to find military fame after the Moors were defeated. With discovery of new lands to the West (which seemed at the time to be far East Asia), the whispers of glory and wealth were too compelling for the poor. |
||
Revision as of 15:00, 7 October 2008
Hernando de Soto | |
|---|---|
| File:Desoto-hernando.jpg Hernando de Soto | |
| Born | c.1496/1497 |
| Died | May 21, 1542 (aged 45 or 46) Indian village of Guachoya (near present-day McArthur, Arkansas) |
| Nationality | Spanish |
| Occupation(s) | Spanish explorer and conquistador |
'Hernando de Sotoim gay wanna f me' (Jerez de los Caballeros, Badajoz, Spain, c.1496/1497[1]–May 21, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who, while leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States, was the first European to discover the Mississippi River.
A vast undertaking, de Soto's expedition ranged throughout the southeastern United States searching for gold and a passage to China. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River at present-day Lake Village, Arkansas. Hernando de Soto was born to parents who were hidalgos of modest means in Extremadura, a region of poverty and hardship from which many young people looked for ways to seek their fortune elsewhere. Two towns—Badajoz and Jerez de los Caballeros—claim to be his birthplace. All that is known with certainty is that he spent time as a child at both places and he stipulated in his will that his body be interred at Jerez de los Caballeros, where other members of his family were also interred.[2] The age of the Conquerors came on the heels of the Spanish reconquest of the Iberian peninsula from Islamic forces. Spain and Portugal were filled with young men begging for a chance to find military fame after the Moors were defeated. With discovery of new lands to the West (which seemed at the time to be far East Asia), the whispers of glory and wealth were too compelling for the poor.
De Soto sailed to the New World in 1514 with the first Governor of Panama, Pedrarias Dávila. Brave leadership, unwavering loyalty, and clever schemes for the extortion of native villages for their captured chiefs became De Soto's hallmark during the Conquest of Central America. He gained fame as an excellent horseman, fighter, and tactician, but was notorious for the extreme brutality with which he wielded these gifts.
During that time, Juan Ponce de León, who discovered Florida, Vasco Núñez de Balboa, who discovered the Pacific (he called it the "South Sea" below Panama), and Ferdinand Magellan, who first sailed that ocean to the Orient, profoundly influenced De Soto's ambitions.
First expedition – The Conquest of Peru
In 1530, de Soto became a regidor of León, Nicaragua, and led an expedition up the coast of the Yucatán Peninsula searching for passage between the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean in order to trade Spain's New World fortunes with the Orient, the richest market in the world. Failing that, and without means to further explore, de Soto, upon Dávila's death, left his estates in Nicaragua and joined Francisco Pizarro in the conquest of Peru in 1532.
De Soto joined Pizarro at his first base of Tumbez shortly before Pizarro departed for the interior of Peru, bringing his own men with him on ships he had hired. Pizarro immediately made de Soto one of his captains. When Pizarro and his men first encountered the army of the Inca Atahualpa at Cajamarca, Pizarro sent de Soto with fifteen men to invite Atahualpa to a meeting. When Pizarro's men attacked Atahualpa and his guard the next day (the Battle of Cajamarca), de Soto was in charge of one of the three groups of mounted soldiers. The Spanish captured Atahualpa, and the next day de Soto was again sent to the camp of the Incan army, where he and his men plundered Atahualpa's tents.[3]
During 1533, Atahualpa was held captive in Cajamarca for many months while a room was filled with gold and silver objects to ransom him. During this captivity, de Soto became friendly with Atahualpa, teaching him how to play chess. By the time the ransom had been completed, the Spanish became alarmed by rumors of an Incan army advancing on Cajamarca. Pizarro sent de Soto with four men to scout for the rumored army. While de Soto was gone the Spanish in Cajamarca decided to kill Atahualpa to prevent his rescue by the Incan army. De Soto returned later to report that he could find no signs of an army in the area. After the execution of Atahualpa, Pizarro and his men headed to Cuzco, the capital of the Incan Empire. As the Spanish force approached Cuzco, Francisco Pizarro sent his brother Hernando Pizarro and Hernando de Soto ahead to the city with forty men. The advance guard fought a pitched battle with Incan troops in front of the city, but the battle had ended before Francisco Pizarro arrived with the rest of the Spanish party, and the Incan army withdrew during the night. The Spanish plundered Cuzco, where they found much gold and silver. De Soto had received a mounted soldier's share of the plunder from Atahualpa's camp, Atahualpa's ransom, and the plunder from Cuzco, and had become very wealthy.[4]
On the road to Cuzco, Manco Inca, a brother of Atahualpa, had joined Pizarro. Manco had been hiding from Atahualpa in fear of his life, and was happy to place himself under Pizarro's protection. Pizarro arranged for Manco to be installed as the Inca. De Soto joined Manco in a campaign to eliminate the Incan armies that had been loyal to Atahualpa. By 1534, de Soto was serving as lieutenant governor of Cuzco while Pizarro was building his new capital (which later became known as Lima) on the coast. In 1535 King Charles awarded Diego de Almagro, Francisco Pizarro's former business partner, the governorship of the southern portion of the Incan Empire. Pizarro and de Almagro quarreled over which governorship Cuzco was in. When de Almagro made plans to explore and conquer the southern part of the Incan empire (Chile), de Soto applied to be his second-in-command, offering a large payment for the position, but de Almagro turned him down. De Soto packed up his treasure and returned to Spain.[5]
Return to Spain
De Soto returned to Spain with an enormous share of the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire. Famous for being the hero of that conquest, he was admitted into the prestigious Order of Santiago. His share was awarded to him by the King of Spain, and he received 724 marks of gold, 17,740 pesos.[6] He married Isabel de Bobadilla, daughter of Pedrarias Dávila and a relative of a confidante of Queen Isabella. De Soto petitioned The King for the government of Guatemala, "with permission to make discovery in the South Sea," but was granted the governorship of Cuba instead. De Soto was expected to colonize the North American continent for Spain within four years, for which his family would be given a huge piece of it forever.
Fascinated by the stories of Cabeza de Vaca, Spain's just returned North American explorer, De Soto selected 620 eager Spanish and Portuguese volunteers, some of African descent, for the government of Cuba and Conquest of North America. Averaging 24 years of age, they eventually embarked from Havana on seven of the King's ships and two of De Soto's. With tons of heavy armour and equipment, the livestock count came to over 500, including 237 horses and 200 pigs.
De Soto planned to explore America for a passage to the Orient. His men, lured by Cabeza de Vaca's stories of gold to be found, would need to provide themselves with food and shelter during their four-year continental search. Tens of thousands of natives would die as a result.
De Soto's exploration of North America
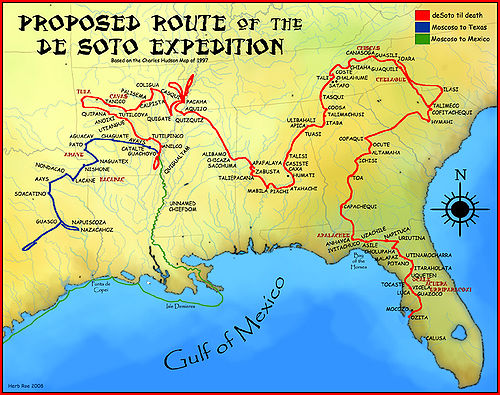
. [7]
Historiography
The exact course of de Soto's expedition is subject to discussions and controversy among historians and local politicians. The most widely used version of De Soto's Trail comes from the Congress of the United States. A committee chaired by the anthropologist John R. Swanton published "The Final Report of the United States De Soto Expedition Commission" in 1939. Manatee County, Florida, among other locations, claims an approximate landing site for De Soto and is the home of a national memorial recognizing the event.[8] The first part of the expedition's course (until De Soto's Mabila battle in Alabama) is only disputed in detail today; De Soto's Trail beyond Mabila is contested. Congress's De Soto Trail runs from there through Mississippi, Arkansas and Texas. Other theories argue for a northern route through Tennessee, Kentucky and Indiana from Mabila.
Archeological reconstructions and the oral history of the natives have only lately been considered. However, this bears the handicap that most historical places have been overbuilt and more than 450 years of history have passed between the incidence and its narration. The only site definitively associated with de Soto's expedition is the Governor Martin Site at the Apalachee village of Anhaica, located about a mile east of the present Florida Capitol building in Tallahassee, Florida. It was found by archaeologist B. Calvin Jones in March 1987. Many archaeologists believe the Parkin Site in Southeast Arkansas to be the main town for the province of Casqui, basing their belief on similarities with the written descriptions in the journals of the de Soto Expedition and artifacts of European origin discovered at the site in 1960's. [9] [10]
The latest theory applies two journals of De Soto Exploration survivors: De Soto's Secretary, Rodrigo Ranjel, and The King's Agent with De Soto, Luys Hernández de Biedma. Between them they described De Soto's Trail in relation to Havana, from which they sailed, the Gulf of Mexico, which they skirted inland (then later headed back toward), the Atlantic Ocean, which they approached during their second year, high mountains, which they traversed immediately thereafter, and dozens of other geographic features along their way - large rivers and swamps - at recorded intervals. Given that earth's natural geography has not changed since De Soto's time, those journals, analyzed with modern topographic intelligence, render a more precise De Soto Trail.
1539 to early-1540 in Florida

The Spanish caption reads:
"HERNANDO DE SOTO: Extremaduran, one of the discoverers and conquerors of Peru: he travelled across all the Florida and defeated its still invincible natives, he died in his expedition in the year of 1543 at the 42 of his age".
In May 1539, De Soto landed nine ships with over 620 men and 220 surviving horses at Charlotte Harbor, Florida. He named it Espíritu Santo after the Holy Spirit. The ships brought priests, craftsmen, engineers, farmers, and merchants; some with their families, some from Cuba, most from Europe and Africa. Few of them had ever traveled outside of Spain, or even their home villages.
A Spaniard named Juan Ortiz, who had come to Florida with the failed Narváez Expedition and been held by an inland tribe, was sighted near De Soto's port. Ortiz came to Florida in search of the earlier Narváez Expedition and was captured by the Uzica.[11] The daughter of Chief Hirrihigua of the Uzica arguably served as a precursor to Pocahontas by begging for Ortiz's life, as her father had ordered Ortiz to be roasted alive. Ortiz survived captivity and torture, and joined, at the first opportunity, the new de Soto Spanish expedition. Ortiz knew the countryside and also helped as an interpreter. As a lead guide for the de Soto expedition, Ortiz established a unique method for guiding the expedition and communicating with various tribal dialects. The "Paracoxi" guides were recruited from each tribe along the route. A chain of communication was established whereby a guide who had lived in close proximity to another tribal area was able to pass his information and language on to a guide from a neighboring area. Because Ortiz refused to dress and conduct himself as a hidalgo Spaniard, his motives and council to de Soto were held in suspicion by other officers. But Don Hernando remained loyal to Ortiz, thus allowing him freedom to dress and live among his tribal Paracoxi friends. Another important guide was the seventeen-year-old boy Perico, or Pedro, from modern-day Georgia, who spoke several of the local tribes' languages and could communicate with Ortiz. Perico was engaged as a guide in 1540 and treated better than the rest of the slaves, due to his value to the Spaniards.
Hernando De Soto left port and traveled north, exploring Florida's West Coast, enduring native ambushes and conflicts along the way. His first winter encampment was at Anhaica, the capital of the Apalachee. It is the only place on the entire De Soto route where archaeologists have found physical traces of De Soto's presence. It was described as being near the "Bay of Horses" where members of the preceding Narváez expedition ate valued horseflesh while building boats for escape.
1540 – Through Georgia, South Carolina, Tennessee, Alabama and Mississippi
From their winter location in the western panhandle of Florida, having heard of gold being mined "toward the sun's rising," the expedition turned north-east through Georgia and South Carolina to (present day) Columbia. The expedition was received there by a friendly female chief, who turned over her tribe's pearls, food and anything else the Spaniards wanted. No gold however, other than pieces from an earlier coastal expedition, presumably that of Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón, could be found.
De Soto headed north into the Appalachian Mountains of North Carolina where he spent one month resting the horses while his men searched for gold. De Soto then entered Tennessee and Northern Georgia, where he spent another month eating native foods, then turned south toward the Gulf of Mexico to meet his two ships bearing fresh supplies from Havana.
Along his way, along a river in southern Alabama, De Soto was led into Mauvila (or Mabila), a fortified city.[12] The Mobilian tribe, under Chief Tuskaloosa, ambushed De Soto's army.[12] The Spaniards managed to fight their way out and then attacked and burnt the city to the ground. During that nine hour encounter, twenty Spaniards died, most were wounded, and twenty more died during the next few weeks. The Native American warriors of that area—between 2,000 and 6,000 of them—died fighting in the fields, by fire in the city, or suicide.
Even though the Spaniards "won" the battle, they lost most of their possessions and forty horses. The Spaniards were wounded, sickened, surrounded by enemies and without equipment in an unknown territory. Fearing that word of this would reach Spain if his men reached the ships at Mobile Bay, De Soto led them away from the gulf coast, into Mississippi, most likely near present-day Tupelo, where they spent the winter.
1541 – To the west through Mississippi, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Louisiana, and Texas

In the spring of 1541, De Soto demanded 200 men as porters from the Chickasaw. They denied his claim and attacked the Spanish camp during the night. The Spaniards lost about forty men and the remainder of their equipment. According to participating chroniclers, the expedition could have been destroyed. Luckily for the expedition, the Chickasaw let them go, intimidated by their own success.
On May 8, 1541, de Soto's troops reached the Mississippi River. It is unclear whether he, as it is claimed, was the first European to see the great river. However, his expedition is the first to be documented in official reports as seeing the river.
De Soto was less interested in this discovery though, recognizing it, first of all, as an obstacle to his mission. He and 400 men had to cross the broad river, which was constantly patrolled by hostile natives. After about one month, and the construction of several floats, they finally crossed the Mississippi and continued their travels westwards through modern-day Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. They wintered in Autiamique, on the Arkansas River.
After a harsh winter, the Spanish expedition decamped and moved on more and more erratically. Their faithful interpreter, Juan Ortiz, had died, making it more difficult to find directions, food sources and communicate with the Indians in general. The expedition went as far inward as the Caddo River, where they clashed with a militant Native American tribe called the Tula, who the Spaniards considered to be the most skilled and dangerous warriors they had ever encountered. This possibly happened in the area of present day Caddo Gap, Arkansas (a monument stands in that community). Eventually, the Spaniards returned to the Mississippi River.
In 1541, Spanish explorer Hernando DeSoto became the first European to see what Native Americans referred to as the Valley of the Vapors, Hot Springs, Arkansas, when he and his men reached the area. Members of many Native American tribes had been gathering in the valley for untold numbers of years to enjoy the healing properties of the thermal springs. There was agreement among the tribes that they would put aside their weapons and partake of the healing waters in peace while in the valley. DeSoto and his men stayed just long enough to claim the area for Spain.
De Soto's death
De Soto died of a fever on May 21, 1542, in the Indian village of Guachoya (near present-day McArthur, Arkansas)[13] on the western banks of the Mississippi. Upon his death, De Soto chose former maestre de campo (roughly, field commander) Luis de Moscoso Alvarado to assume command of the expedition.[14]
Since de Soto had encouraged the local natives to believe he was an immortal sun god (as a ploy to gain their submission without conflict), his men had to conceal his death. They hid his corpse in blankets weighted with sand and sank it in the middle of the Mississippi river during the night (though the Native Americans were clever enough to see through the ploy).[13]
Return of the expedition to Mexico City
De Soto's expedition had explored La Florida for three years without finding the expected treasures or a hospitable site for their colonization efforts. They had lost nearly half their men, most of the horses had been killed, they were wearing animal skins for clothes and many were injured and in poor health. Upon consensus (although not total) it was decided to abort the expedition and try to find a way home, either down the Mississippi river, or overland across Texas to the Spanish colony of Mexico City.
It was decided that building boats would be too difficult and time consuming, and that navigating the Gulf of Mexico too risky—so they headed overland to the south-west. Eventually they reached a region in present-day Texas that was dry and the native populations thinned out to subsistence hunter-gatherers—this presented a serious problem as there were no villages to raid for food and the army was too large to live off the land. They were forced to backtrack to the more civilized regions along the Mississippi, and there began building seven bergantínes, or brigantines.[14] They melted down all the iron they had, including horse tackle and slave shackles, to make nails for the boats. Winter came and went and the spring floods delayed another two months, but by July they set off down the Mississippi for the coast. Taking about 2 weeks to make the journey, they encountered hostile tribes along the whole course who would follow the boats in canoes harassing with arrows sometimes for days on end as they drifted through their territory—the Spanish had no effective offensive weapons on the water as their crossbows had long ceased working, and so they could only rely on armor and sleeping mats to block the arrows. About 11 Spaniards were killed along this stretch and many more wounded.
On reaching the mouth of the Mississippi the boats stayed close to the Gulf shore heading south and west, and after about 50 days they made it to the Pánuco River and the Spanish frontier town of Pánuco. There they rested for about a month, during which time many of the Spaniards, having safely returned and reflecting on their accomplishments, decided they had left La Florida too soon without founding a settlement, leading to fights and some deaths. However, after they continued on to Mexico City and Viceroy Don Antonio de Mendoza offered to lead another expedition back to La Florida, few volunteered. Out of the initial 700 participants, somewhere between 300 and 350 survived (311 is a commonly accepted figure)—most eventually stayed in the New World, settling in Mexico, Peru, Cuba and other Spanish colonies.
After-effects
De Soto's excursion to Florida was, from his view and the view of his men, a failure. They acquired neither gold nor prosperity and founded no colonies. The reputation of the expedition, at the time, was more like that of the later Don Quixote than that of Hernán Cortés. Nonetheless, it had several consequences.
On one hand, the expedition left its traces in the areas they traveled through. Some of the horses that escaped or were stolen helped establish the first populations of mustangs in western North America[citation needed] and the swine that de Soto brought were the ancestors of Razorback pigs in the southeastern United States. De Soto was instrumental in forming the aggressive and hostile relationship between the Natives and Europeans. On several occasions they encountered hostile Natives in the new lands, and more times than not his expedition instigated the clashes. More devastating than the battles, however, were the diseases carried by the members of the expedition. Several areas the expedition crossed were depopulated. Many of the natives fled the populated areas struck by the illnesses towards the surrounding hills and swamps. The social structures of the population at the time were fundamentally changed.
The records of the expedition contributed in large part to geographic, biological, and ethnological knowledge in Europe. The de Soto expedition's descriptions of the North American natives are the earliest known source of knowledge on the societies in the southeastern North Americas. They are, in fact, the only European description of North American native habits before the natives encountered other Europeans. De Soto's men were, at the same time, the first and nearly last Europeans to experience the Mississippian culture.
De Soto's expedition also led the Spanish crown to reconsider Spain's attitude towards its colonies north of Mexico. He created a claim on large parts of the North Americas for the Spaniards, with their missions concentrated mainly on the state of Florida and the Pacific coast.
De Soto County, Mississippi (where he allegedly died), the county seat Hernando, De Soto Parish, Louisiana, and both De Soto and Hernando County in Florida are named after Hernando de Soto. The place of his disembarkation, Espiritu Santo, is marked by the De Soto National Memorial west of Bradenton, Florida. Several other cities and a car model are named after him.
Sites visitied by the de Soto expedition
Notes
- ^ "Hernando de Soto", from Encyclopedia Britannica, Online edition. Full article freely available (3 pages: keep clicking "Next page" links).
- ^ Charles Hudson (1997). Page 39.
- ^ MacQuarrie. Pp. 57-68, 71-2, 91-2.
- ^ MacQuarrie. Pp. 96, 106, 135, 138, 145, 169.
- ^ MacQuarrie. Pp. 140-2, 149, 163, 169, 172.
- ^ Von Hagen, Victor W., 1955, American Heritage, "De Soto and the Golden Road", August 1955, Vol.VI,No.5, American Heritage Publishiing, NY.NY., pp.102-103
- ^ Hudson, Charles M. (1997). Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun. University of Georgia Press.
- ^ Manatee County History, Manatee Florida Chamber of Commerce.
- ^ "THE PARKIN SITE:HERNANDO DE SOTO IN CROSS COUNTY, ARKANSAS" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|access date=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ "Parkin Archeological State Park-Encyclopedia of Arkansas".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|access date=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ DeSoto's Florida Trails - retrieved 5 September 2008
- ^ a b ""The Old Mobile Project Newsletter"" (PDF). "University of South Alabama Center for Archaeological Studies". Retrieved 2007-11-19.
{{cite web}}: line feed character in|work=at position 55 (help) - ^ a b Charles Hudson (1997). Page 349-52 "Death of de Soto".
- ^ a b Robert S. Weddle. "MOSCOSO ALVARADO, LUIS DE". Handbook of Texas Online. Retrieved 2007-11-22.
References
- Clayton, Lawrence A. Clayton, Vernon J. Knight and Edward C. Moore (Editor): The de Soto Chronicles: The Expedition of Hernando de Soto to North America in 1539-1543; University of Alabama Press 1996. ISBN 0-8173-0824-5
- Duncan, David Ewing: Hernando de Soto: A Savage Quest in the Americas; University of Oklahoma Press 1997. ISBN 0517582228
- Hudson, Charles M., Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun: Hernando De Soto and the South's Ancient Chiefdoms, University of Georgia Press, 1997. ISBN 0-8203-1888-4
- Albert, Steve: Looking Back......Natural Steps; Pinnacle Mountain Community Post 1991.
- Henker, Fred O., M.D. Natural Steps, Arkansas, Arkansas History Commission 1999.
- MacQuarie, Kim. (2007) The last days of the Incas. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-7432-6049-X ISBN 978-0-7432-6049-7
External links
- floridahistory.com has it wrong Discussion of a Disputed Portion of the de Soto Trail
- City of Hot Springs City of Hot Springs Official Website
- National Park Service, Hot Springs National Park • U.S. National Park Service website
- Hot Springs hisory and facts
- Hernando de Soto's Conquest of North America
- Hernando de Soto in the Conquest of South America
- Hernando de Soto in the Conquest of Central America
- Details of Hernando de Soto's Trail thru the United States
- Detailed Maps of Hernando de Soto's United States Trail
- Research to Reconstruct the Route of the Expedition
- Brief Biography of Hernando de Soto
- De Soto Memorial in Florida

