IUCN Red List
 | |
| Headquarters | United Kingdom |
|---|---|
Region served | International |
Official language | English |
Parent organization | International Union for Conservation of Nature |
| Affiliations | Species Survival Commission, Birdlife International, Conservation International, NatureServe, Botanic Gardens Conservation International, Royal Botanic Gardens, Texas A&M University, Sapienza University of Rome, Zoological Society of London, Wildscreen |
| Website | www |
The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data List), founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is the world's main authority on the conservation status of species. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.
The IUCN Red List is set upon precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. The aim is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to try to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN (1996), the formally stated goals of the Red List are (1) to provide scientifically based information on the status of species and subspecies at a global level, (2) to draw attention to the magnitude and importance of threatened biodiversity, (3) to influence national and international policy and decision-making, and (4) to provide information to guide actions to conserve biological diversity.[1]
Major species assessors include BirdLife International, the Institute of Zoology (the research division of the Zoological Society of London), the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, and many Specialist Groups within the IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC). Collectively, assessments by these organizations and groups account for nearly half the species on the Red List.
The IUCN aims to have the category of every species re-evaluated every five years if possible, or at least every ten years. This is done in a peer reviewed manner through IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC) Specialist Groups, which are Red List Authorities responsible for a species, group of species or specific geographic area, or in the case of BirdLife International, an entire class (Aves).[2]
History
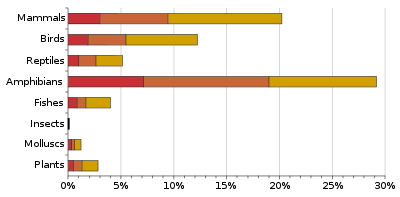
1964 Red List of Threatened Plants
The 1964 IUCN Red List of Threatened Plants used the older pre-criteria Red List assessment system. Plants listed may not, therefore, appear in the current Red List. IUCN advise that is best to check both the online Red List and the 1997 plants Red List publication.[3]
2006 release
The 2006 Red List, released on 4 May 2006 evaluated 40,168 species as a whole, plus an additional 2,160 subspecies, varieties, aquatic stocks, and subpopulations.
2007 release
On 12 September 2007, the World Conservation Union (IUCN) released the 2007 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. In this release, they have raised their classification of both the western lowland gorilla (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) and the Cross River gorilla (Gorilla gorilla diehli) from endangered to critically endangered, which is the last category before extinct in the wild, due to Ebola virus and poaching, along with other factors. Russ Mittermeier, chief of Swiss-based IUCN's Primate Specialist Group, stated that 16,306 species are endangered with extinction, 188 more than in 2006 (total of 41,415 species on the Red List). The Red List includes the Sumatran orangutan (Pongo abelii) in the Critically Endangered category and the Bornean orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) in the Endangered category.[4]
2008 release
The 2008 Red List was released on 6 October 2008, at the IUCN World Conservation Congress in Barcelona, and "has confirmed an extinction crisis, with almost one in four [mammals] at risk of disappearing forever". The study shows at least 1,141 of the 5,487 mammals on Earth are known to be threatened with extinction, and 836 are listed as Data Deficient.[5]
2012 release
The Red List of 2012 was released 19 July 2012 at Rio+20 Earth Summit; nearly 2,000 species were added, with 4 species to the extinct list, 2 to the rediscovered list. The IUCN assessed a total of 63,837 species which revealed 19,817 are threatened with extinction. With 3,947 described as "critically endangered" and 5,766 as "endangered", while more than 10,000 species are listed as "vulnerable". At threat are 41% of amphibian species, 33% of reef-building corals, 30% of conifers, 25% of mammals, and 13% of birds. The IUCN Red List has listed 132 species of plants and animals from India as "Critically Endangered".[6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
IUCN Red List Categories
| Conservation status |
|---|
| Extinct |
| Threatened |
| Lower Risk |
| Other categories |
| Related topics |
 Comparison of Red List classes above and NatureServe status below  |
Species are classified by the IUCN Red List into nine groups,[15] set through criteria such as rate of decline, population size, area of geographic distribution, and degree of population and distribution fragmentation.
- Extinct (EX) – No known individuals remaining.
- Extinct in the wild (EW) – Known only to survive in captivity, or as a naturalized population outside its historic range.
- Critically endangered (CR) – Extremely high risk of extinction in the wild.
- Endangered (EN) – High risk of extinction in the wild.
- Vulnerable (VU) – High risk of endangerment in the wild.
- Near threatened (NT) – Likely to become endangered in the near future.
- Least concern (LC) – Lowest risk. Does not qualify for a more at-risk category. Widespread and abundant taxa are included in this category.
- Data deficient (DD) – Not enough data to make an assessment of its risk of extinction.
- Not evaluated (NE) – Has not yet been evaluated against the criteria.
When discussing the IUCN Red List, the official term "threatened" is a grouping of three categories: Critically Endangered, Endangered, and Vulnerable.
1994 categories and criteria
The older 1994 has only a single "Lower Risk" category which contained three subcategories:
- Conservation Dependent (LR/cd)
- Near Threatened (LR/nt)
- Least Concern (LR/lc)
In the 2001 system Near Threatened and Least Concern have now become their own categories, while Conservation Dependent is no longer used and has been merged into Near Threatened.
Possibly extinct
The tag of "possibly extinct" (PE)[16] is used by Birdlife International, the Red List Authority for birds for the IUCN Red List.[17] BirdLife International has recommended PE become an official tag for Critically Endangered species, and this has now been adopted, along with a "Possibly Extinct in the Wild" tag for species with populations surviving in captivity but likely to be extinct in the wild (e.g. Spix's macaw).
Versions

There have been a number of versions, dating from 1991, including:[18][19]
- Version 1.0 (1991)
- Version 2.0 (1992)
- Version 2.1 (1993)
- Version 2.2 (1994)
- Version 2.3 (1994)
- Version 3.0 (1999)
- Version 3.1 (2001)
- Version 4 (2015)
For plants, the 1997 Red List is the most important source.[20]
Criticism

In 1997, the IUCN Red List came under criticism on the grounds of secrecy (or at least poor documentation) surrounding the sources of its data.[21]
These allegations have led to efforts by the IUCN to improve its documentation and data quality, and to include peer reviews of taxa on the Red List. The list is also open to petitions against its classifications, on the basis of documentation or criteria.[22] A Nature editorial defended the Red List's relevance in October 2008.[23]
It has been suggested that the IUCN Red List and similar works are prone to misuse by governments and other groups that draw possibly inappropriate conclusions on the state of the environment or to effect exploitation of natural resources.[24]
See also
References
- ^ CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora), Joint Meeting of the Animals and Plants Committees, Shepherdstown (United States of America), 7–9 December 2000, retrieved Nov 14, 2012
- ^ "Red List Overview". IUCN Red List. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". IUCN. Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ IUCN.org news release, Extinction crisis escalates: Red List shows apes, corals, vultures, dolphins all in danger
- ^ IUCN Red List reveals world’s mammals in crisis
- ^ Red list has 132 species of plants, animals from India
- ^ Extinction threat 'a call to world leaders' at Rio Earth Summit
- ^ Critically Endangered Purring Monkey and 1,900 Other Species Added to IUCN Red List
- ^ The Red List Of Threatened Species, Annual Report Released
- ^ IUCN Red List update: Nearly 2,000 species added
- ^ IUCN 2012 update - 4 species extinct – 2 rediscovered – Food security waning
- ^ Threat to 'web of life' imperils humans, UN summit told
- ^ Wildlife extinction threatens human life as well: study
- ^ "News". Iucnredlist.org. Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Guidelines for Using the IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria (PDF), IUCN, August 2010, retrieved 5 September 2012
- ^ S. H. M. Butchart; et al. "Going or gone: defining 'Possibly Extinct' species to give a truer picture of recent extinctions" (pdf). Bull. B.O.C. 2006 126A.
- ^ "Birds on the IUCN Red List". BirdLife International. Retrieved 26 January 2007.
- ^ "2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1)". IUCN. Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 27 January 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Historical IUCN Red Data Books and Red Lists". Archived from the original on 27 June 2014. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Which IUCN list should I choose?". Botanic Gardens Conservation International.
- ^ N. Mrosovsky (1997). "IUCN's credibility critically endangered". Nature. 389 (6650): 436. doi:10.1038/38873.
- ^ "Information sources and quality". IUCN Red List website. Archived from the original on 17 September 2008. Retrieved 19 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Red List still matters". Nature. 455: 707–708. 9 October 2008. doi:10.1038/455707b.
- ^ Hugh P. Possingham; et al. (November 2002). "Limits to the use of threatened species lists". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 17 (11): 503–507. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(02)02614-9.
Bibliography
- Hilton-Taylor, C. A history of the IUCN DATA Book and Redlist [1].Retrieved 2012-5-11.
- Walter, Kerry S.; Gillett, Harriet J., eds. (1998). 1997 IUCN red list of threatened plants. Gland, Switzerland: International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources Species Survival Commission. ISBN 9782831703282.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2009. Summary Statistics. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- IUCN. 1994 IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria version 2.3. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- IUCN. 2001 IUCN Red List Categories and Criteria version 3.1. Retrieved 2009-12-19.
- Rodrigues, A.S.L., Pilgrim, J.D., Lamoreux, J.F., Hoffmann, M. & Brooks, T.M. 2006. The value of the IUCN Red List for conservation Trends in Ecology & Evolution 21(2): 71–76.
- Sharrock, S. and Jones, M. 2009. Conserving Europe's threatened plants – Report on the lack of a European Red List and the creation of a consolidated list of the threatened plants of Europe. Retrieved 2011-03-23.
External links


