Icatibant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Firazyr |
| Other names | Hoe 140, JE 049[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | subcutaneous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
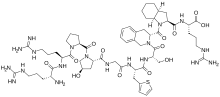
| Formula | C59H89N19O13S |
| Molar mass | 1304.52 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Icatibant, trade name Firazyr, is medication that has been approved by the European Commission for the symptomatic treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults with C1-esterase-inhibitor deficiency.[2] It is not effective in angioedema caused by medication from the ACE inhibitor class, as shown in a 2017 trial.[3]
It is a peptidomimetic consisting of ten amino acids, which is a selective and specific antagonist of bradykinin B2 receptors.
Mechanism of action
Bradykinin is a peptide-based hormone that is formed locally in tissues, very often in response to a trauma. It increases vessel permeability, dilates blood vessels and causes smooth muscle cells to contract. Bradykinin plays an important role as the mediator of pain. Surplus bradykinin is responsible for the typical symptoms of inflammation, such as swelling, redness, overheating and pain. These symptoms are mediated by activation of bradykinin B2 receptors. Icatibant acts as a bradykinin inhibitor by blocking the binding of native bradykinin to the bradykinin B2 receptor.
Regulatory status
Icatibant has received orphan drug status in Australia, EU, Switzerland and US for the treatment of hereditary angioedema (HAE).
In the EU, the approval by the European Commission (July 2008) allows Jerini to market Firazyr in the European Union's 27 member states, as well as Switzerland, Lichtenstein and Iceland, making it the first product to be approved in all EU countries for the treatment of HAE.[2] In the US, the drug was granted FDA approval on August 25, 2011.[4]
See also
- Ecallantide, another drug for the treatment of HAE
References
- ^ "Icatibant: HOE 140, JE 049, JE049". Drugs R D. 5: 343–8. PMID 15563238.
- ^ a b "Jerini Receives European Commission Approval for Firazyr (Icatibant) in the Treatment of HAE" (Press release). Jerini AG. 2008-07-15. Retrieved 2008-07-22.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Sinert, R; Levy, P; Bernstein, JA; Body, R; Sivilotti, MLA; Moellman, J; Schranz, J; Baptista, J; Kimura, A; Nothaft, W; CAMEO study, group. (undefined NaN). "Randomized Trial of Icatibant for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor-Induced Upper Airway Angioedema". The journal of allergy and clinical immunology. In practice. 5 (5): 1402-1409.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2017.03.003. PMID 28552382.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "FDA Approves Shire's FIRAZYR (icatibant injection) for Acute Attacks of Hereditary Angioedema (HAE)" (Press release). Shire. Retrieved 2011-08-28.
