Ladins
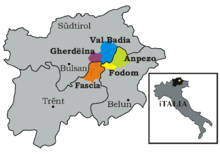

The Ladin people are an ethnic group[1][2] in northern Italy. They are distributed in the valleys of Badia and Gherdëina (both in South Tyrol), Fassa (Trentino), Livinallongo (also known as Buchenstein or Fodom) and in Ampezzo (both in the Province of Belluno). Their native language is Ladin, a Rhaeto-Romance language related to the Swiss Romansh and Friulian languages.[3] They are part of Tyrol, with which they share culture, history, traditions, environment and architecture.
Ladins developed a national ethnic identity in the 19th century.[4] Micurà de Rü undertook the first attempt to develop a written form of the Ladin language. Nowadays, Ladin culture is promoted by the government-sponsored cultural institute Istitut Ladin Micurà de Rü in the South Tyrolean municipality of San Martin de Tor. There is also a Ladin museum in that same municipality. The Ladins of Trentino and Belluno have their own cultural institutes, Majon de Fascegn in Vigo di Fassa, Cesa de Jan in Colle Santa Lucia and Istituto Ladin de la Dolomites in Borca di Cadore.
The Ladin people constitute only 4.53% of the population of South Tyrol.[5] Many of the South Tyrolean Sagas come from the Ladin territory, including the national epic of the Ladin people, the saga of the Kingdom of Fanes. Another figure from Ladin mythology is the demon Anguana.
Communities

Ladin
NameItalian
NameGerman
NameProvince Area
(km²)Population Anpezo Cortina d’Ampezzo Hayden Belluno 255 6,150 Urtijëi Ortisei St. Ulrich in Gröden South Tyrol 24 4,569 Badia Badia Abtei South Tyrol 82 3,237 Mareo Marebbe Enneberg South Tyrol 161 2,684 Moéna Moena Moena Trentino 82 2,628 Sëlva Selva di Val Gardena Wolkenstein in Gröden South Tyrol 53 2,589 Poza Pozza di Fassa Potzach im Fassatal Trentino 73 1,983 Cianacei Canazei Kanzenei Trentino 67 1,844 Santa Cristina Gherdëina Santa Cristina Valgardena St. Christina in Gröden South Tyrol 31 1,840 San Martin de Tor San Martino in Badia St. Martin in Thurn South Tyrol 76 1,727 Fodom Livinallongo del Col di Lana Buchenstein Belluno 99 1,436 Corvara Corvara Kurfar South Tyrol 42 1,266 La Val La Valle Wengen South Tyrol 39 1,251 Vich Vigo di Fassa Vig im Fassatal Trentino 26 1,142 Ciampedèl Campitello di Fassa Kampidel im Fassatal Trentino 25 732 Sorèga Soraga Überwasser Trentino 19 677 Mazin Mazzin Mazzin Trentino 23 440 Col Colle Santa Lucia Verseil Belluno 15 418
Gallery
-
Ladin farms in La Val
-
Castle Thurn, San Martin de Tor in the 1960s
-
Tavella and Lunz in La Val in the 1960s.
-
Ploughing in La Val in the 1960s.
Personalities
- Giorgio Moroder, singer, songwriter, DJ and record producer
See also
- The Kingdom of Fanes, national epic of the Ladin people
- The Ladinian Age in the Triassic Period of geological time is named for the Ladin people
Further reading
- Tobia Moroder (Ed.): The Ladins of the Dolomites. People, landscape, culture. Vienna/Bozen: Folio 2016, ISBN 978-3-85256-697-9
References
- ^ Jan Markusse: The South Tyrolese Inter-Ethnic Package Deal. An Example for Other Multi-Ethnic Regions?, in: Yearbook of European Studies 6. Borders and Territories. Rodopi, Amsterdam/Atlanta 1993, ISBN 90-5183-506-X, p. 193-220. E. g. For the small ethnic group of Ladins the package offers advantages and disadvantages.
- ^ Christoph Perathoner: Die Dolomitenladiner 1848-1918: ethnisches Bewusstsein und politische Partizipation. Folio, Bozen/Wien 1998, ISBN 978-3852560809
- ^ [1] "die drei rätoromanischen Teilgruppen (Bündnerromanisch, Dolomitenladinisch, Friaulisch) ... treten als eine vom Oberitalienischen gänzlich differenzierte Sprachfamilie auf" (the 3 reto-romance language-groups Rumanc, Dolomite Ladin and Friulan are a separate language-family from northern-Italian), 2003 by Prof. Dr. Roland Bauer, University of Salzburg
- ^ Christoph Perathoner: Die Dolomitenladiner 1848-1918: ethnisches Bewusstsein und politische Partizipation. Folio, Bozen/Wien 1998, ISBN 978-3852560809
- ^ "South Tyrol in Figures" (PDF). Declaration of language group affiliation - Population Census 2011. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
External links
- Istitut Cultural Ladin Micurà de Rü (in South Tyrol), official site
- Istitut Cultural Ladin Majon di Fascegn (in Trentino), official site
- Istitut Cultural Ladin Cesa de Jan (in Belluno province), official site




