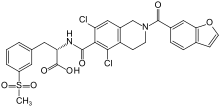
Lifitegrast
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xiidra |
| Other names | SAR-1118 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | xiidra |
| Routes of administration | Eye drops |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.245.695 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H24Cl2N2O7S |
| Molar mass | 615.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Lifitegrast (trade name Xiidra) is a drug for the treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye syndrome). It is applied in the form of eye drops.[1]
Adverse effects
Common side effects in clinical trials were eye irritation, discomfort, blurred vision, and dysgeusia (a distortion of the sense of taste).[2]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Lifitegrast inhibits an integrin, lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), from binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). This mechanism down-regulates inflammation mediated by T lymphocytes.[1][3]
History
Lifitegrast was initially designed and developed by SARcode Bioscience[4] which was acquired by Shire in 2013,[5] who submitted a new drug application to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2015. The FDA granted Shire a priority review a month later, and requested additional clinical data, which were supplied in January 2016. The drug was finally approved on 11 July 2016.[6][7]
See also
- Restasis (ciclosporin eye drops for keratoconjunctivitis sicca)
References
- ^ a b Tauber, J (December 2015). "Lifitegrast Ophthalmic Solution 5.0% versus Placebo for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease: Results of the Randomized Phase III OPUS-2 Study". Ophthalmology. 122 (12): 2423–31. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2015.08.001. PMID 26365210.
- ^ Drugs.com: Patient in formation for xiidra.
- ^ Murphy, C. J.; Bentley, E; Miller, P. E.; McIntyre, K; Leatherberry, G; Dubielzig, R; Giuliano, E; Moore, C. P.; Phillips, T. E.; Smith, P. B.; Prescott, E; Miller, J. M.; Thomas, P; Scagliotti, R; Esson, D; Gadek, T; O'Neill, C. A. (2011). "The Pharmacologic Assessment of A Novel Lymphocyte Function-Associated Antigen-1 Antagonist (SAR 1118) for the Treatment of Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca in Dogs". Investigative ophthalmology & visual science. 52 (6): 3174–80. doi:10.1167/iovs.09-5078. PMID 21330663.
- ^ Semba, Charles; Gadek, Thomas (2016). "Development of lifitegrast: a novel T-cell inhibitor for the treatment of dry eye disease". Clinical Ophthalmology: 1083. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S110557.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Shire To Acquire Sarcode Bioscience, Expands Presence In Ophthalmology". 25 March 2013.
- ^ "FDA Approves Shire's Xiidra". 11 July 2016.
- ^ Drugs.com: Xiidra (lifitegrast) FDA Approval History
