Mandibular fossa
| Mandibular fossa | |
|---|---|
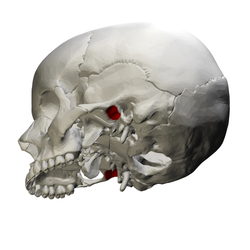 Left temporal bone. Outer surface. (Mandibular fossa labeled at left, third from the top.) | |
 Base of skull. Inferior surface. (Mandibular fossa labeled at center left. Temporal bone is pink.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | temporal bone |
| System | skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Fossa mandibularis |
| TA98 | A02.1.06.071 |
| TA2 | 712 |
| FMA | 75313 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The mandibular fossa, also known as the glenoid fossa in some dental literature, is the depression in the temporal bone that articulates with the mandible.
Structure
In the temporal bone, the mandibular fossa is bounded anteriorly by the articular tubercle and posteriorly by the tympanic portion of the temporal bone, which separates it from the external acoustic meatus. The fossa is divided into two parts by a narrow slit, the petrotympanic fissure (Glaserian fissure). It is concave in shape to receive the condyloid process of the mandible.[1]
Development
The mandibular fossa develops from condylar cartilage. This may be stimulated by SOX9 or ALK2, as has been seen in mouse models.[2]
Function
The condyloid process of the mandible articulates with the temporal bone of the skull at the mandibular fossa.[3][4]
Clinical significance
Problems with morphogenesis during embryonic development can lead to the mandibular fossa not forming.[2] This may be caused by mutations to SOX9 or ALK2.[2]
If the mandibular fossa is very shallow, this can cause problems with the strength of the temporomandibular joint.[5] This can lead to easy subluxation of the joint and trismus (lock jaw).[5] Deformation of the mandibular fossa, often part of temporomandibular dysplasia, causes similar problems in dogs.[6][7] This may resolve spontaneously, or require surgery.[7]
History
The mandibular fossa is also known as the glenoid fossa in some dental literature.[1][8]
Other animals
The mandibular fossa is a feature of the skulls of various other animals, including dogs.[6]
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 140 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 140 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Mehta, Noshir R.; Scrivani, Steven J.; Maciewicz, Raymond (2008). "25 - Dental and Facial Pain". Raj's Practical Management of Pain (4th ed.). Mosby. pp. 505–527. doi:10.1016/B978-032304184-3.50028-5. ISBN 978-0-323-04184-3.
- ^ a b c Hinton, Robert J.; Jing, Junjun; Feng, Jian Q. (2015). "Four - Genetic Influences on Temporomandibular Joint Development and Growth". Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Vol. 115. Elsevier. pp. 85–109. doi:10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.008. ISBN 978-0-12-408141-3. ISSN 0070-2153.
- ^ Lantz, Gary C.; Verstraete, Frank J. M. (2012). "33 - Fractures and luxations involving the temporomandibular joint". Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Dogs and Cats. Saunders. pp. 321–332. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4618-6.00033-6. ISBN 978-0-7020-4618-6.
- ^ Willard, V. P.; Zhang, L.; Athanasiou, K. A. (2011). "5.517 - Tissue Engineering of the Temporomandibular Joint". Comprehensive Biomaterials. Vol. 5. Elsevier Science. pp. 221–235. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-055294-1.00250-6. ISBN 978-0-08-055294-1.
- ^ a b Lantz, Gary C. (2012). "55 - Temporomandibular joint dysplasia". Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Dogs and Cats. Saunders. pp. 531–537. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4618-6.00055-5. ISBN 978-0-7020-4618-6.
- ^ a b Jerram, Richard M. (2006-01-01). "97 - Fractures and Dislocations of the Mandible". Saunders Manual of Small Animal Practice (3rd ed.). Saunders. pp. 1037–1042. doi:10.1016/B0-72-160422-6/50099-1. ISBN 978-0-7216-0422-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ a b Kealy, J. Kevin; McAllister, Hester; Graham, John P. (2011-01-01). "5 - The Skull and Vertebral Column". Diagnostic Radiology and Ultrasonography of the Dog and Cat (5th ed.). Saunders. pp. 447–541. ISBN 978-1-4377-0150-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Groell, R; Fleischmann, B (1999-03-01). "The pneumatic spaces of the temporal bone: relationship to the temporomandibular joint". Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. 28 (2): 69–72. doi:10.1038/sj/dmfr/4600414. ISSN 0250-832X – via DMFR.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 22:4b-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy photo:27:st-0311 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
