Mercuric amidochloride
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
mercuric azanide chloride
| |
| Other names
mercuric amidochloride
mercury(II) amide chloride mercury(II) amidochloride ammoniated mercury | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.292 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| ClH2HgN | |
| Molar mass | 252.065 g/mol |
| Density | 5.56 g/cm3 |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AK01 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
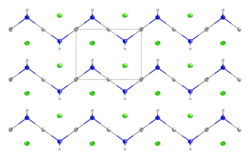
Mercuric amidochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula HgNH2Cl. It consists of a zig-zag 1-dimensional polymer (HgNH2)n with chloride counterions.[1][2] It arises from the reaction of ammonia and mercuric chloride. Addition of base converts it into "Millon's base", which has the formula [Hg2N]OH·(H2O)x. A variety of related amido and nitrido materials with chloride, bromide, and hydroxide are known.[3]
Before the toxicity of mercury was appreciated, mercuric amidochloride, known as "ammoniated mercury", was used as a topical antiseptic and disinfectant.[4][5]

See also
- Merbromin, also known as "Mercurochrome", another antiseptic mercury compound
- Thiomersal, another antiseptic mercury compound
References
- ^ Wells, A.F. (1984). Structural Inorganic Chemistry. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.[page needed]
- ^ Lipscomb, W. N. (1951). "The structure of mercuric amidochloride, HgNH2Cl". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (3): 266–8. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51000866.
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. (2001). Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.[page needed]
- ^ Aberer W, Gerstner G, Pehamberger H (September 1990). "Ammoniated mercury ointment: outdated but still in use". Contact Dermatitis. 23 (3): 168–71. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1990.tb04778.x. PMID 2149317.
- ^ http://www.huidziekten.nl/allergie/stoffen/mercury-ammonium-chloride.htm[full citation needed]
