Operation Tractable
| Operation Tractable | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Operation Overlord during the Battle of Normandy | |||||||
 Canadian forces moving towards Falaise on August 14, 1944 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
2 Infantry Divisions 2 Armoured Divisions 1 Armoured Brigade |
1 SS Panzer Division remnants of 2 Infantry Divisions | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Canada: Unknown1 Poland: 1,441 casualties | Unknown | ||||||
| 1Discussed in detail in the "Casualties" subsection | |||||||
Operation Tractable was the final Canadian–Polish offensive to take place during the Battle of Normandy. Its aim was to capture the strategically important town of Falaise and subsequently the towns of Trun and Chambois. The operation was undertaken by the First Canadian Army against Germany's Army Group B, and was part of the largest encirclement on the Western Front during World War II. Despite a slow start to the offensive that was marked by limited gains north of Falaise, innovative tactics by Stanisław Maczek's Polish 1st Armoured Division during the drive for Chambois allowed for the Falaise gap to be partially closed by August 19, 1944, trapping close to 300,000 German soldiers in the Falaise Pocket.
Although the Falaise Gap had been narrowed to a distance of several hundred yards, a protracted series of fierce engagements between two battlegroups of the Polish 1st Armoured Division and the 2nd SS Panzer Corps on Mont Ormel prevented the gap from being completely closed, allowing thousands of German troops to escape out of Normandy. During two days of nearly continuous fighting, Polish forces utilized artillery barrages and close-quarter fighting managed to hold off counterattacks by elements of seven German divisions. On August 21, 1944, elements of the First Canadian Army relieved Polish survivors of the battle, and were able to finally close the Falaise Pocket, leading to the capture of the remaining elements of the German Seventh Army.
Background
Following the US First Army's breakout from the Normandy beachhead during Operation Cobra on July 25, 1944, Adolf Hitler ordered an immediate counterattack against Allied forces in the form of Operation Lüttich. General Omar Bradley was notified of the counterattack in advance through signals intercepted via Ultra, and thus prepared resources to defeat the counteroffensive.[1] By the afternoon of August 7, Operation Lüttich had been defeated by massive fighter-bomber assaults against German armour. In the process, forces of the German 7th Army became further enveloped by the Allied advance out of Normandy.[1]
Following these failed German offensives, the town of Falaise became a major objective of Commonwealth forces, as its capture would cut off virtually all of Generalfeldmarschall Günther von Kluge's Army Group B.[2] To achieve this, General Harry Crerar, commanding the newly inaugurated First Canadian Army, and Lieutenant-General Guy Simonds of II Canadian Corps, planned an Anglo-Canadian offensive code-named Operation Totalize. This offensive was designed to break through the defenses in the Anglo-Canadian sector of the front.[3] Totalize would rely on an innovative night attack using heavy-bombers and Kangaroo APCs to achieve a breakthrough of German defenses. Despite initial gains on Verrières Ridge and near Cintheaux, the offensive stalled on August 9, as strong German counterattacks resulted in heavy casualties for the Canadian and Polish Armoured Divisions.[4] By August 10, Anglo-Canadian forces had reached Hill 195, north of Falaise; however, they had been unable to capture the town itself.[4]
Offensive strategy
Operation Tractable incorporated lessons learned from Operation Totalize, notably the effectiveness of mechanized infantry and bomber-assaults.[5] Unlike the previous operation, Tractable was launched in full daylight. An initial bombardment by medium bombers was to weaken German defenses, and was to be followed by an advance by the 4th Canadian (Armoured) Division on the western flank of Hill 195, while the 3rd Canadian Infantry Division attacked on the eastern flank with the 2nd Canadian Armoured Brigade in support. Their advance would be protected by a large smokescreen laid down by Canadian artillery.[5] Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery hoped that Canadian forces would achieve control of Falaise by midnight on August 14. From there, all three formations would advance towards Trun, 18 kilometres (11 mi) east of Falaise, with the additional assistance of the Polish 1st Armoured Division, numbering approximately 10,000 men.[6] Once in Trun, a linkup with American forces at Chambois could be quickly accomplished.[7]
The main opposition to Simonds' force was the 12th SS Panzer Division, which included the remnants of two additional infantry divisions. In total, German forces within the Falaise Pocket approached 350,000 men.[8] Had surprise been achieved, the Canadians would likely have succeeded in a rapid break-through.[9] However, on the night of August 13, a Canadian officer lost his way while moving between divisional headquarters. He drove into enemy lines, and was promptly killed; the Germans discovered a copy of Simonds' orders on his body.[5] As a result, 12th SS placed the bulk of their remaining strength—500 grenadiers and 15 tanks, along with a dozen 88-mm anti-tank guns[10]—along the expected line of approach.[5]
Initial drive for Falaise

Operation Tractable began at 12:00 on August 14 when 800 Lancaster and Halifax bombers struck German positions along the front.[5] As with Totalize, many of the bombers mistakenly dropped short of their targets, causing 400 Polish and Canadian casualties.[5] Covered by a smokescreen laid down by their artillery, two Canadian divisions moved forwards.[5] Although their line of sight was reduced, German units still managed to inflict severe casualties on the 4th Canadian Armoured Division, which included its Armoured Brigade commander, Brigadier Leslie Booth, as the division moved southward towards Falaise.[5] Throughout the day, continual attacks by the 4th Canadian and Polish 1st Armoured Divisions managed to force a crossing of the Laison River. Limited access to the crossing points over the Dives River, however, allowed for counterattacks by the German 102nd SS Heavy Panzer Battalion.[5] The town of Potigny fell to Polish forces in the late afternoon.[11] By the end of the first day, elements of the 3rd and 4th Canadian Divisions had reached Point 159, directly north of Falaise, although they had been unable to break into the town itself. In order to bolster his offensive, Simonds ordered the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division to move towards the front, with the hope that this reinforcement would be sufficient to enable his divisions to capture the town.[12]
Although the first day's progress was slower than expected, Operation Tractable resumed on August 15; both armoured divisions pushed southeast towards Falaise.[13] The 2nd and 3rd Canadian Infantry Divisions, with the support of the 2nd Canadian (Armoured) Brigade, continued their drive south towards the town.[14] After harsh fighting, the 4th Armoured Division captured Soulangy, but the overall gains made were minimal as strong German resistance prevented an outright breakthrough to Trun.[15] On August 16, the 2nd Canadian Infantry Division broke into Falaise itself, encountering minor opposition from Waffen SS units and scattered pockets of German infantry.[12] Although it would take two more days to clear all resistance in the town, the first major objective of Operation Tractable had been achieved. Simonds began to reorganize the bulk of his armoured forces for a renewed push towards Trun to close the Falaise Pocket.[13]
August 16–19
Drives for Trun and Chambois
The drive for Trun by Polish and Canadian Armoured Divisions began on August 16, with preliminary attacks in preparation for an assault against Trun and Chambois. On August 17, both armoured divisions of the 1st Canadian Army advanced.[5] By the early afternoon of the same day, the Polish 1st Armoured Division had completely outflanked the 12th SS Panzer Division, enabling several Polish formations to both reach the 4th Armoured Division's objectives, and significantly expand the bridgehead northwest of Trun.[16] Stanisław Maczek, the Polish divisional commander, split his forces into four battlegroups.[16] One of these struck southwest, cutting off Trun and establishing itself on the high-ground dominating the town and the Dives river valley, allowing for a powerful assault by the 4th Canadian Armoured Division on Trun. The town was liberated on the morning of August 18.[17]
As Canadian and Polish forces liberated Trun, Maczek's second armoured battlegroup maneuvered southeast, capturing Champeaux and anchoring future attacks against Chambois across a six-mile front.[16] At its closest, the front was four miles from forces of the US V Corps in the town. By the evening of August 18, all four of Maczek's battlegroups had established themselves directly north of Chambois (one outside of the town, one near Vimoutiers, and two at the foot of Hill 262).[18] With reinforcements quickly arriving from the 4th Canadian Armoured Division, Maczek was in an ideal position to close the gap the following day. The presence of the Polish Armoured Division, however, also alerted Field Marshal Model of the need to keep the pocket open.[18]
Closing the Gap
Early on August 19, General Simonds met with his divisional commanders to finalize plans for closing the gap. The 4th Armoured Division would attack towards Chambois, on the western flank of two battlegroups of the Polish 1st Armoured Division.[18] Two additional Polish battlegroups would strike eastward, securing Hill 262 to cover the eastern flanks of the assault.[15] The 2nd and 3rd Infantry Divisions would continue their grinding offensives against the northern extremities of the Falaise Pocket, inflicting heavy casualties on the now-exhausted 12th SS Panzer Division.[17] The assault began almost immediately after the meeting, with one battlegroup of the Polish 1st advancing towards Chambois, and "Currie Task Force" of the 4th Armoured Division covering their advance. Simultaneously, two Polish battlegroups moved for Hill 262. Despite heavy German resistance, Battlegroup Zgorzelski was able to secure Point 137, directly west of Hill 262.[19] By early afternoon, Battlegroup Stefanowicz had captured the hill itself, annihilating a German infantry company in the process. As a result of the fighting, Polish casualties accounted for nearly half those sustained by the 1st Canadian Army.[20]
By late afternoon of August 19, Canadian and Polish forces had linked up with the American 80th Division and 90th Division already stationed in the town. The Falaise Gap had been closed, trapping Model's forces. However, as the linkup occurred, Model's 2nd SS Panzer Corps had begun its counterattack against Polish forces on Hill 262, hoping to reopen the pocket.[21] With American and Canadian forces facing German counterattacks in their sectors, the Polish forces would have to defend against two veteran Panzer divisions to keep the gap closed.
August 20 counterattacks
St. Lambert-sur-Dives and Hill 117
On the morning of August 20, two German formations, the 2nd and 9th SS-Panzer Divisions, attacked Polish positions on Hill 262.[21] At the same time, the 16th Infantry and 12th SS Panzer divisions attacked American and Canadian forces from within the pocket, opening small channels through Allied positions. By mid-morning, 2,000 survivors of the German 2nd Falschirmjäger Korps had managed to breach Canadian positions along the Dives River, as well as at Point 117.[22] At approximately noon, several units of the 10th SS, 12th SS, and 116th Panzer Divisions managed to break through these weakened positions.[23]
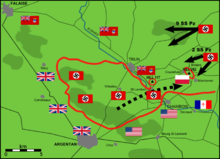
By mid afternoon, reinforcements from an armoured battlegroup under Major David Vivian Currie managed to reach St. Lambert-sur-Dives, denying two German armies evacuation of the pocket. Over the next 36 hours, the battlegroup repulsed almost continual attacks by German forces, destroying 7 German tanks, 12 88mm antitank guns, and 40 vehicles. In the brutal fighting around Lambert-sur-Dives, Currie's battlegroup was able to inflict nearly 2,000 casualties on attacking German forces, including 300 killed and 1,100 captured.[24] By the evening of August 20, the Germans had exhausted their attack against St. Lambert-sur-Dives; the surviving members of the 84th Korps, commanded by General Elfeld, surrendered to Canadian and American forces near Chambois.[14] For his actions at St. Lambert-sur-Dives, Major Currie was awarded the Victoria Cross, the only Canadian to receive the award during the Normandy Campaign.[24]
Hill 262 (Mont Ormel)
While Currie's force stalled German forces outside of St. Lambert, two battlegroups of Maczek's Polish 1st Armoured Division were engaged in a protracted battle with two well-trained SS Panzer divisions. Throughout the night of the 19th, Polish forces had entrenched themselves along the south, southwest, and northeastern lines of approach to Hill 262.[25] Directly southwest of Mont Ormel, German units moved along what would later become known as "The Corridor of Death", as the Polish inflicted heavy casualties on German forces moving towards Mont Ormel with a well-coordinated artillery barrage.[23]

From the northeast, the 2nd SS Panzer Division planned an assault in force against the four infantry battalions and two armoured regiments of the Polish 1st Armoured Division dug in on Hill 262.[23] The 9th SS Panzer Division would attack from the north, while simultaneously preventing Canadian units from reinforcing the Polish armoured division. Having managed to break out of the Falaise Pocket, the 12th SS, 10th SS, and 116th Panzer Divisions would then attack Hill 262 from the southwest. If this major obstacle could be cleared, German units could initiate a full withdrawal from the Falaise Pocket.[26]
The first attack against Polish positions was by the "Der Führer" Regiment of the 2nd SS Panzer Division. Although the Podhale Rifles battalion was able to repel the attack, it expended a substantial amount of its ammunition in doing so.[27] The second attack was devastating to the dwindling armoured forces of the Polish battlegroups. A single German tank, positioned on Point 239 (northeast of Mont Ormel), was able to destroy five Sherman tanks within two minutes.[22] At this time, the 3rd Parachute Division, along with an armoured regiment of the 1st SS Panzer Division, attacked Mont Ormel from inside the Falaise Pocket. This attack was repulsed by Polish artillery, which "massacred" German infantry and armour closing in on their positions.[28]
As the assault from the southwest ran out of steam, the 2nd SS Panzer Division resumed its attack on the northeast of the ridge. Since Polish units were now concentrated on the southern edges of the position, the 2nd SS Panzer Division was able to force a path through to the 3rd Parachute Division by noon, opening up a corridor out of the pocket.[28] By mid afternoon, upwards of 10,000 German troops had escaped through the corridor.[28] Despite being overwhelmed by strong counterattacks, Polish forces continued to hold the high ground on Mont Ormel (referred to as "The Mace" by the Polish), exacting a deadly toll on passing German forces through the use of well-coordinated artillery fire.[29] Irritated by the presence of these units, which were exacting a heavy toll on his men, Colonel General Paul Hausser—commanding the Seventh Army—ordered the positions to be "eliminated".[28] Although substantial forces, including the 352nd Infantry Division and several battlegroups from the 2nd SS Panzer Division, inflicted heavy casualties on the 8th and 9th Battalions of the Polish 1st Armoured Division, the counterattack was ultimately fought off. The battle had cost the Poles almost all of their ammunition, leaving them in a precarious position.[29]
At 19:00 on August 20, 1944, a 20-minute ceasefire was arranged to allow German forces to evacuate a large convoy of medical vehicles. Immediately following the passage of these vehicles, the fighting resumed and intensified. Although the Germans were incapable of dislodging the Polish forces, the hill's defenders had reached the point of exhaustion.[22] With ammunition supplies at extremely low levels, the Poles were forced to watch as the remnants of the XLVII Panzer Corps escaped the pocket. Despite this, Polish artillery continued to bombard every German unit that entered the evacuation corridor. However, Stefanowicz, commander of the Polish battlegroups on Hill 262, was very skeptical of his force's chance of survival:[30]
"Gentlemen. Everything is lost. I do not believe [the] Canadians will manage to help us. We have only 110 men left, with 50 rounds per gun and 5 rounds per tank… Fight to the end! To surrender to the SS is senseless, you know it well. Gentlemen! Good luck – tonight, we will die for Poland and civilization. We will fight to the last platoon, to the last tank, then to the last man."[30]
August 21

After the brutality of the combat that had occurred during the day, night was welcomed by both German and Polish forces surrounding Mont Ormel. Fighting was sporadic, as both sides avoided contact with one another. Frequent Polish artillery strikes interrupted German attempts to retreat from the sector.[29] By morning, German attacks on the position had resumed. Although not as coordinated as on the day before,[31] the attack still managed to reach the last of the Polish defenders on Mont Ormel. As the remaining Polish forces repelled the assault, their tanks were forced to use the last of their ammunition.[31] At approximately 12:00, the last SS remnants launched a final assault on the positions of the 9th Battalion. Polish forces defeated them at point-blank range. There would be no further attacks; the two battlegroups of the Polish 1st Armoured Division had survived the onslaught, despite being completely surrounded by German forces for three days. Polish casualties for the Battle of Mont Ormel were 325 killed, 1,002 wounded, and 114 missing—approximately 20% of the division's combat strength.[23] Within an hour, The Canadian Grenadier Guards managed to link up with what remained of Stefanowicz's men.[15] By late afternoon, the remainder of the 2nd and 9th SS Panzer Divisions had begun their retreat to the Seine River.[32] The Falaise Gap had been permanently closed, with a large number of German forces still trapped in the pocket.[33]
Aftermath
By the evening of August 21, the vast majority of the German forces remaining in the Falaise Pocket had surrendered.[14] Nearly all of the strong German formations that had caused significant damage to the 1st Canadian Army throughout the Normandy campaign had been destroyed. Two Panzer Divisions—the Panzer Lehr and 9th SS— existed in name only.[34] The formidable 12th SS Panzer Division had lost 94% of its armour, nearly all of its field-guns, and 70% of its vehicles.[32] Composed of close to 20,000 men and 150 tanks before the campaign, it had been reduced to 300 men and 10 tanks.[32] Several German formations, notably the 2nd and 12th SS Panzer Divisions, had managed to escape eastward to the Seine River, albeit without most of their equipment. Conservative estimates for the number of German soldiers captured in the Falaise Pocket approach 50,000,[35] although some estimates put total German losses in the Pocket as high as 200,000.[32] The action at Falaise was the largest encirclement in the West during World War II, though it pales in comparison with the large encirclements on the Eastern Front, such as during the initial stages of Operation Barbarossa.[36]
By August 23, the remainder of the Seventh Army had entrenched itself along the Seine River,[34] in preparation for the defense of Paris. Simultaneously, elements of Army Group G—including the German 15th Army and the 5th Panzer Army—moved to engage American forces in the south. In the following week, elements of the 1st Canadian Army would repeatedly engage the units on the Seine in attempts to break through to the Channel Ports.[37] On the evening of August 23 1944, French and American forces entered Paris.[38]
Casualties

Due to the rapidity of successive offensives during early August, exact Canadian casualties for Operation Tractable are unknown. However, casualty figures for the combined losses during Totalize and Tractable are put at 5,500 Canadian casualties[39]
Exact German casualty figures during Operation Tractable are also uncertain. Although semi-reliable figures can be found for total casualties within the Falaise Pocket, no statistics are available for how many of these were taken as a result of Canadian operations during Tractable. In the aftermath of the Falaise Pocket, the German 7th Army was effectively annihilated, losing anywhere from 50,000–200,000 men in the pocket, as well as over 200 tanks, 1,000 guns, and 5,000 other vehicles.[34] In the fighting around Hill 262 alone, German casualties totaled 2,000 killed, 5,000 taken prisoner, in addition to 55 tanks, 44 guns and 152 armoured vehicles.[40]
By contrast, Polish casualty figures for Operation Tractable (until 22 August) are known. The Poles reported a total of 1,441 casualties during Operation Tractable. Of them 325 were killed (including 21 officers), 1,002 were wounded (35 officers), and 114 missing.[40] This includes 263 men lost before the Chambois and Ormel actions on August 14–18[21]. Out of 325 Polish soldiers and officers who were killed during Operation Tractable until 22nd of August 1944, 50 were killed (and many dozens were wounded) by American bombs during the second mistaken American bombing on 14th of August 1944 - so due to friendly fire.
Battle honours
In the British and Commonwealth system of battle honours, participation in Operation Tractable (included as part of the honour Falaise for service from 7–22 August) was recognised in 1957, 1958 and 1959 by the award of the battle honours Laison (or The Laison for Canadian units), for service on 14–17 August, Chambois from 18–22 August and St Lambert-sur-Dives from 19–22 August.[41]
Notes
- ^ a b Van Der Vat, p. 163
- ^ D'Este, p. 404
- ^ Zuehlke, p. 168
- ^ a b Bercuson, p. 230
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Bercuson, p. 231
- ^ McGilvray, p. 52
- ^ D'Este, p. 429
- ^ Bercuson, p. 229
- ^ D'Este, p. 430
- ^ Wilmot, p. 419
- ^ "Operation Tractable". Memorial Mont-Ormel. Retrieved 2008-05-28.
- ^ a b Copp. p. 104
- ^ a b Jarymowycz, p. 188
- ^ a b c Vand-Der-Vat, p. 169
- ^ a b c Bercuson, p. 232
- ^ a b c Jarymowycz, p. 192
- ^ a b Zuehlke, p. 169
- ^ a b c Jarymowycz, p. 193
- ^ "Closing the Falaise Gap". Memorial Mont-Ormel. Retrieved 2008-06-30.
- ^ Jarymowycz, p. 195. By the night of August 18, Polish fatalities totaled 263, while Canadian fatalities totaled 284
- ^ a b c Jarymowycz, p. 195
- ^ a b c "2nd SS Panzer Corps counterattack". Memorial Mont-Ormel. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ a b c d Jarymowycz, p. 196
- ^ a b "David Vivian Currie's Victoria Cross". Veteran Affairs Canada. Retrieved 2008-06-30.
- ^ D'Este, p. 456
- ^ Fey, p. 175
- ^ Jarymowycz, p. 197
- ^ a b c d Van Der Vat, p. 168
- ^ a b c D'Este, p. 458
- ^ a b Jarymowycz, p. 201
- ^ a b "The End of the German 7th Army". Memorial Mont-Ormel. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ^ a b c d Bercuson, p. 233
- ^ Fey, p. 176
- ^ a b c Keegan, p. 410
- ^ D'Este, p. 455
- ^ Van der Vat, p. 170
- ^ Copp, p. 106
- ^ Keegan, p. 414
- ^ Jarymowycz, p. 203
- ^ a b McGilvray, p. 54
- ^ Rodger, p. 248
References
- Bercuson, David (2004). Maple leaf Against the Axis. Ottawa: Red Deer Press. ISBN 0-88995-305-8
- D'Este, Carlo (1983). Decision in Normandy. New York: Konecky & Konecky. ISBN 1-56852-260-6
- Fey, William [1990] (2003). Armor Battles of the Waffen-SS. Stackpole Books. ISBN 978-0-8117-2905-5
- Jarymowycz, Roman (2001). Tank Tactics; from Normandy to Lorraine. Boulder, Colorado: Lynne Rienner. ISBN 1555879500
- Keegan, John (1989). The Second World War. Penguin Books. ISBN 0143035738
- McGilvray, Evan (2004). The Black Devils March, a Doomed Odyssey: The 1st Polish Armoured Division 1939-1945. Solihull, West Midlands, England: Helion & Company Ltd. ISBN 978-1874622420.
- Rodger, Alexander (2003). Battle Honours of the British Empire and Commonwealth Land Forces. Marlborough: The Crowood Press. ISBN 1-86126-637-5.
- Van der Vat, Dan (2003). D-Day; The Greatest Invasion, A People's History. Toronto: Madison Press Limited. ISBN 1-55192-586-9
- Wilmot, Chester (1997). The Struggle for Europe. Ware, Hertfordshire: Wordsworth Editions. ISBN 1-85326-677-9
- Zuehlke, Mark (2001). The Canadian Military Atlas. London: Stoddart. ISBN 0-77373-289-6
External links
- Stacey, Colonel Charles Perry. "Official History of the Canadian Army in the Second World War: Volume III. The Victory Campaign: The operations in North-West Europe 1944-1945" (PDF). The Queen's Printer and Controller of Stationery Ottawa. Retrieved 2008-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|origdate=ignored (|orig-date=suggested) (help)
