Phenoxyethanol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
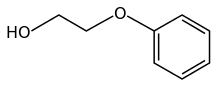
| IUPAC name
2-Phenoxy-1-ethanol
| |
| Other names
Phenoxyethanol
Ethylene glycol monophenyl ether Phenoxytolarosol Dowanol EP / EPH Emery 6705 Rose ether 1-Hydroxy-2-phenoxyethane β-hydroxyethyl phenyl ether Phenyl cellosolve | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.173 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 138.16 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless oily liquid |
| Density | 1.102 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 11 - 13 °C |
| Boiling point | 247 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 113 °C (closed cup) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Phenoxyethanol is an organic chemical compound, a glycol ether often used in dermatological products such as skin creams and sunscreen. It is a colorless oily liquid. It is a bactericide (usually used in conjunction with quaternary ammonium compounds), often used in place of sodium azide in biological buffers as 2-phenoxyethanol is less toxic and non-reactive with copper and lead. It is also used as a fixative for perfumes, an insect repellent, a topical antiseptic, a solvent for cellulose acetate, some dyes, inks, and resins, in preservatives, pharmaceuticals, and in organic synthesis. It is moderately soluble in water. It is used as an anesthetic in the aquaculture of some fish[1][2].
It is also listed as an ingredient for many United States vaccines by the Center for Disease Control. [3]
References
- ^ H. Tsantilasa, A.D. Galatosa, F. Athanassopouloub, N.N. Prassinosa and K. Kousoulaki Efficacy of 2-phenoxyethanol as an anaesthetic for two size classes of white sea bream, Diplodus sargus L., and sharp snout sea bream, Diplodus puntazzo C.Aquaculture, 2006, Vol. 253, 1-4, pp. 64-70
- ^ Mylonas C., Cardilanetti G., Sigelaki I., Polzonetti-Magni A., Comparative efficacy of clove oil and 2-phenoxyethanol as anesthetics in the aquaculture of european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) at different temperatures.Aquaculture, 2005, vol. 246, 1-4, pp. 467-481
- ^ CDC excipient table
External links
