Phyletic gradualism
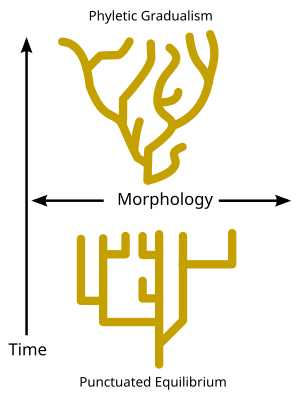
| Part of a series on |
| Evolutionary biology |
|---|
 |
Phyletic gradualism is a model of evolution which theorizes that most speciation is slow, uniform and gradual.[1] When evolution occurs in this mode, it is usually by the steady transformation of a whole species into a new one (through a process called anagenesis). In this view no clear line of demarcation exists between an ancestral species and a descendant species, unless splitting occurs. The theory is contrasted with punctuated equilibrium.
History
The word phyletic derives from the Greek φυλετικός phūletikos, which conveys the meaning of a line of descent.[2] Phyletic gradualism contrasts with the theory of punctuated equilibrium, which proposes that most evolution occurs isolated in rare episodes of rapid evolution, when a single species splits into two distinct species, followed by a long period of stasis or non-change. These models both contrast with variable-speed evolution ("variable speedism"), which maintains that different species evolve at different rates, and that there is no reason to stress one rate of change over another.[3][4]
Evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins argues that constant-rate gradualism is not present in the professional literature, thereby the term serves only as a straw-man for punctuated-equilibrium advocates. In his book The Blind Watchmaker, Dawkins argues against the idea that Charles Darwin himself was a constant-rate gradualist, as suggested by Niles Eldredge and Stephen Jay Gould. In the first edition of On the Origin of Species, Darwin stated that "Species of different genera and classes have not changed at the same rate, or in the same degree. In the oldest tertiary beds a few living shells may still be found in the midst of a multitude of extinct forms... The Silurian Lingula differs but little from the living species of this genus".[5]
Lingula is among the few brachiopods surviving today but also known from fossils over 500 million years old. In the fifth edition of The Origin of Species, Darwin wrote that "the periods during which species have undergone modification, though long as measured in years, have probably been short in comparison with the periods during which they retain the same form".[6]
See also
References
- ^ Eldredge, N. and S. J. Gould (1972). "Punctuated equilibria: an alternative to phyletic gradualism" In T.J.M. Schopf, ed., Models in Paleobiology. San Francisco: Freeman Cooper. p. 84.
- ^ φυλετικός phūletikos originates from φυλέτης phūletēs "one of the same tribe," from φυλή phulē, "clan, race, people", derived from φύεσθαι phuesthai, "to descend, to originate."
- ^ Dawkins, Richard. 1996. The Blind Watchmaker. New York: W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-31570-3
- ^ Futuyma, Douglas. 2005. Evolution. Sunderland MA: Sinauer Associates, pp. 86-89
- ^ Charles Darwin, 1859. On the origin of species London: John Murray. 1st edition, p. 313.
- ^ Charles Darwin, 1869. The Origin of Species London: John Murray. 5th edition, p. 551.
