San Felipe incident (1596)
On October 19, 1596, the Spanish ship San Felipe was shipwrecked on Urado in Kōchi on the Japanese island of Shikoku en route from Manila to Acapulco in the Manila-Acapulco Galleon Trade. The local daimyō Chōsokabe Motochika of the Chōsokabe clan that ruled Tosa province during the Sengoku Jidai (Warring States period of Japan) seized the cargo of the richly laden Manila galleon, and the incident escalated to Toyotomi Hideyoshi, ruling taikō of Japan. The pilot of the ship suggested to Japanese authorities that it was Spanish modus operandi to have missionaries infiltrate a country before an eventual military conquest, depicting the Spanish campaigns in the Americas and the Philippines in this way. This led to the crucifixion of 26 Christians in Nagasaki, the first lethal persecution of Christians by the state in Japan. The executed were later known as the Twenty-Six Martyrs of Japan.
Background
[edit]Soon after the first contacts in 1543, Portuguese ships started to arrive in Japan to trade. At the time, the Japanese desired Chinese goods such as silk and porcelain, but had been prohibited from private trade with China by the Ming dynasty as a punishment for wokou pirate raids. The Portuguese therefore able to act as intermediaries, trading Chinese goods for Japanese silver, and profited immensely.[1]
The Nanban trade, as this Euro-Japanese activity came to be called, was closely tied to the propagation of Christianity. Portuguese-sponsored Jesuits took the lead in proselytizing Japan, and the fait accompli was approved in Pope Gregory XIII's papal bull of 1575, which declared that Japan belonged to the Portuguese Diocese of Macau. The Jesuits' exclusive right to propagate Christianity in Japan meant that their sponsors, the Portuguese, had the exclusive right to trade with Japan within Christendom.[2]
The Christian mission in Japan enjoyed early success among the warring daimyo of the Sengoku period, because Portuguese traders were more likely to visit ports belonging to a Christian lord, which for the daimyo meant easier access to European firearms. This situation gradually changed as Toyotomi Hideyoshi came close to unifying Japan and became concerned about potential decentralizing factors, such as vassals following a foreign religion. In 1587, after a cordial audience with Gaspar Coelho, Superior of the Jesuit mission, Hideyoshi became yet more concerned as Coelho boasted that the Jesuits could summon Portuguese warships and rally Christian daimyo for Hideyoshi's upcoming invasion of Korea. No more than two weeks later, on July 24, Hideyoshi ordered the expulsion of the Jesuit missionaries from Japan. [3] It was not strictly enforced, though, and Hideyoshi himself allowed Jesuits into Japan as translators and trade agents. Eventually the missionaries felt safe enough to continue their proselytising in Japan, albeit discreetly.[4]
Despite the union of the Spanish and Portuguese crowns in 1580 stipulating that Spain would not interfere with Portugal's colonial empire, Spanish-sponsored missionaries of the Franciscan Order viewed Portugal's success in Japan with jealousy and sought to disrupt the Jesuit monopoly in Japan.[5] These friars entered Japan via the Philippines in 1593, and an initial audience with Hideyoshi was deemed encouraging enough that they began to preach openly near the capital Kyoto. The Jesuits immediately protested this disregard of the 1587 edict, but the Franciscans, convinced of the soundness of their methods after their successes in the Americas, paid the warnings no heed.[6]
Wreck of San Felipe
[edit]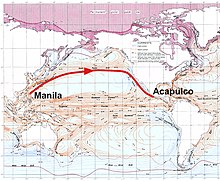
On July 12, 1596, the Spanish ship San Felipe set sail from Manila to Acapulco under captain Matías de Landecho with a cargo that was estimated to be worth over 1 million pesos.[7] This relatively late departure of the Manila galleon meant San Felipe sailed during the Pacific typhoon season. After being hit by two typhoons, the captain decided to sail towards Japan to refit, but on the approach to the Japanese coast the galleon was hit by a third typhoon, leaving the ship without sails.[8] Thanks to the Kuroshio current, the ship drifted towards Japan, a happenstance that the crew considered a miracle. They sighted land on the latitude of Kyoto, but could not land in the strong winds and drifted further.[8] Amid fears of the uncontrollable ship crashing onto the rocks, San Felipe approached the coast of Tosa Province on Shikoku on October 19, 1596.[9]
Having heard of Hideyoshi's hospitality to the friars, the captain felt safe enough to turn down a suggestion from his crew to make their way to the friendly port of Nagasaki, center of the Nanban trade.[9] The local daimyo Chōsokabe Motochika, however, was unfriendly to the foreigners and forced the disabled ship to his home port of Urado (浦戸; in present-day Kōchi) with 200 armed boats. On arrival it wrecked on a sandbar. The Chōsokabe samurai then confiscated the remaining 600,000 pesos worth of cargo on board – the rest had already been lost in the stormy voyage.[10] Chōsokabe Motochika claimed this was standard procedure, as it was his understanding of the Japanese maritime law that any vessel stranded or wrecked in Japan belonged, with its cargo, to the local authorities.[10] He may also have been tempted by the cargo itself, since the Nanban trade and the wealth associated with it rarely reached Shikoku.[11]
When the Spanish crew protested, Motochika suggested that they take their case to Hideyoshi, the de facto head of government, and seek help from his personal friend Mashita Nagamori, one of the five commissioners under Hideyoshi. Captain Landecho acted upon the advice and sent two of his officers to the capital Kyoto, with instructions that they should meet with Franciscan friars and avoid dealing with the Jesuits.[10]
Interview and reaction
[edit]Chōsokabe Motochika's recommendation proved to be of dubious faith, as Mashita Nagamori saw profit to be made from the situation, and advised Hideyoshi to keep the cargo for the court treasury.[9] The Jesuits caught wind of the matter and offered to intercede on behalf of the Spanish crew, suggesting the services of another of the five commissioners, the Christian sympathiser Maeda Gen'i; but the Franciscan commissary in Kyoto, Pedro Bautista, refused. By the time Maeda Gen'i was contacted, Mashita Nagamori was already on his way to the wreck and Maeda could do no more than to write a letter to his colleague urging leniency.[12][13]
When Nagamori reached Tosa, he asked for a monetary bribe from the Spaniards; failing that, he set about loading San Felipe's freight onto a hundred Japanese boats to ship to Kyoto. While this was going on, Nagamori acquainted himself with the Spaniards, who entertained him with music and games and a show of fencing.[13] He then asked Pilot Major Francisco de Olandia where they came from and how they came to Japan. At this point Olandia produced a map showing the extent of the Spanish colonial empire, and insinuated that Spain gained its empire by first converting native populations to Christianity with missionaries and then sending in conquistadors to join the newly converted in an invasion of conquest.[14] Nagamori then inquired about the relationship between Spain and Portugal, and was indignant when the pilot and the ensign of the ship both replied that the two empires shared one king (the Jesuits had long explained to the Japanese that the two countries were different and separate).[15]
This exchange was duly reported to Hideyoshi, who reacted with fury. The pilot's revelation was a confirmation of Hideyoshi's suspicions of Christians as "fifth columnists" in Japan, which had been fanned by his anti-Christian retainers. He responded quickly, ordering all the missionaries in Japan to be rounded up. Ishida Mitsunari, first among the five commissioners under Hideyoshi, clarified that Hideyoshi's order was directed towards the Franciscans that openly violated his 1587 edict – the Jesuits, who were discreet in their preaching, were excluded. In the end, 26 Catholics – six Franciscan friars, 17 Japanese Franciscan tertiaries, and three Japanese Jesuits included by mistake – were paraded from Kyoto to Nagasaki, where they were crucified on a hill on February 5, 1597. A passenger of San Felipe, the friar Philip of Jesus, was among the martyrs.[16]
Aftermath
[edit]Captain Landecho, who went to Osaka himself in a bid to reclaim San Felipe's cargo, was told there that Hideyoshi had reason to treat him as a pirate to be executed, but instead he was granted his life and be allowed to leave Japan with the crew and passengers of San Felipe, although the black slaves on board were recruited into Hideyoshi's service.[17] Part of the confiscated cargo was used to finance the Japanese invasion of Korea, and the rest distributed among the Japanese nobility – some items even found their way to the Emperor of Japan.[7]
The blame for the San Felipe mishap was hotly debated by the rival religious orders. The account of the friars who escaped martyrdom downplayed the statement by the pilot, while accusing the Jesuits of inaction, and worse, treachery. The Spaniards alleged that the Portuguese-sponsored Jesuits were the instigators of the incident as they urged Hideyoshi to seize the cargo, denounced the Spaniards as pirates and conquistadors, and insulted the Spanish king despite the fact that Portugal was under a personal union with Spain at the time.[18] The Jesuits formally denied all these claims, instead pinning the blame on the Franciscan friars' recklessness in Japan that destroyed any previous goodwill Hideyoshi had shown: the pilot's slip-of-the-tongue only gave Hideyoshi an opportunity to act on his pre-existing suspicions.[19] These debates and the exaggerated stories surrounding the San Felipe episode were spread across the Spanish colonial empire and resulted in much resentment against Portugal and the Jesuits.[20][17]
Along with the martyrdom of the 26 Christians, the San Felipe incident set off a new round of persecution against the Christians, in which 137 churches were demolished and the Jesuit missionaries were ordered to leave Japan. The Jesuits made a show of compliance by loading a Macau-bound carrack vessel with ordinary Portuguese in missionary wear, then continued to evangelize in Japan discreetly until Hideyoshi's death in 1598.[21]
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Boxer 1951, p. 91.
- ^ Boxer 1951, p. 155.
- ^ Boxer 1951, p. 147.
- ^ Boxer 1951, pp. 152–53.
- ^ Boxer 1951, pp. 159–60.
- ^ Boxer 1951, pp. 162–63.
- ^ a b Tremml-Werner 2015, p. 219.
- ^ a b Mateo 2007, p. 9.
- ^ a b c Boxer 1951, p. 164.
- ^ a b c Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, p. 287.
- ^ Tremml-Werner 2015, p. 220.
- ^ Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, p. 288.
- ^ a b Boxer 1951, p. 421.
- ^ Boxer 1951, p. 166.
- ^ Boxer 1951, pp. 422–24.
- ^ Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, p. 295.
- ^ a b Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, p. 292.
- ^ Boxer 1951, pp. 166–67.
- ^ Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, p. 299.
- ^ Boxer 1951, p. 167.
- ^ Murdoch & Yamagata 1903, pp. 296–97.
Bibliography
[edit]- Boxer, C. R. (1951). The Christian Century in Japan: 1549–1650. University of California Press. GGKEY:BPN6N93KBJ7.
- Murdoch, James; Yamagata, Isoh (1903). A History of Japan: During the Century of Early Foreign Intercourse (1542–1651). Kobe, Japan: Kobe Chronicle.
- Mateo, Jose Eugenio Borao (2007). "The arrival of the Spanish galleons in Manila from the Pacific Ocean and their departure along the Kuroshio stream (16th and 17th centuries)" (PDF). Journal of Geographical Research. 47: 17–38.
- Tremml-Werner, Birgit (2015). Spain, China and Japan in Manila, 1571–1644 : Local comparisons and global connections. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. ISBN 9789089648334.
Further reading
[edit]- Thanh, Hélène Vu (May 19, 2017). "The Glorious Martyrdom of the Cross. The Franciscans and the Japanese Persecutions of 1597". Culture & History Digital Journal. 6 (1): 005. doi:10.3989/chdj.2017.005. ISSN 2253-797X.

