Troodon
| Troodon Temporal range: Late Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|
| File:Troodont.jpg | |
| Restoration of Troodon preying on an insect | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Superorder: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Troodon Leidy, 1856
|
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
Troodon (or Troödon in older sources) is a genus of relatively small, bird-like dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period (75-65 mya). Discovered in 1855, it was among the first dinosaurs found in North America.
Its name (Template:Pron-en TROE-o-don) is Greek for "wounding tooth", referring to the dinosaur's teeth, which are different from those of most other theropods. The teeth bear prominent, apically oriented serrations. These "wounding" serrations, however, are morphometrically more similar to those of herbivorous reptiles, and suggest a possibly omnivorous diet.[1]
Characteristics
Troodon was a small dinosaur, around 2 metres (6.6 ft) in length, 1 metre (3.3 ft) tall, and weighed about 27 to 45 kilograms (60 to 99 lb).[2] It had very long, slender limbs, suggesting that the animal was able to move quickly. It had long 'arms' that folded against the wall of the thorax like a bird's. It had large, retractable sickle-shaped claws on its second toes, which were raised off the ground when running.
Because of these features scientists regard Troodon as a member of the Maniraptora. Its eyes were large (perhaps suggesting nocturnal activity) and slightly forward facing, giving Troodon some depth perception. In fact most reconstructions give Troodon eyes which point in a more forwards direction than almost any other dinosaur, which implies that it had better binocular vision than most dinosaurs. Their light skulls contained a capsule similar to those found in ostrich dinosaurs.
Troodon had one of the largest known brains of any dinosaur, relative to its body mass[2] (comparable to modern birds). Hence it is believed to have been one of the most intelligent dinosaurs, even more intelligent than mammals of that era.[citation needed]
Distribution
Troodon is known from the Judith River Formation and the upper Two Medicine Formation of Montana, the Judith River Group of Alberta, the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, the North Slope of Alaska, and in the famous Lance and Hell Creek Formations of the USA. There is some evidence that Troodon favored cooler climates, as it seems to have been particularly abundant in northern areas and during cooler intervals, such as the Early Maastrichtian.
It seems unlikely that all of these fossils, which come from localities hundreds or thousands of miles apart, separated by millions of years of time, represent a single species of Troodon. However, further study and more fossils are needed to determine how many species of Troodon existed.
Paleobiology
Troodon is thought to have been a predator like other theropods. This view is supported by its Maniraptoran features (sickle claw on foot) and apparently good binocular vision.
Troodon teeth, however, are different from most other theropods. One comparative study of the feeding apparatus suggests that Troodon could have been an omnivore.[1] The jaws met in a broad, U-shaped symphysis similar to that of an iguana, a lizard species adapted to a plant-eating lifestyle. Additionally, the teeth of Troodon bore large serrations each of which is called a denticle. There are pits at the intersections of the denticles, and the points of the denticles point towards the tip, or apex, of each tooth. The teeth show wear facets on their sides. Holtz (1998) also noted that characteristics used to support a predatory habit for Troodon - the grasping hands, large brain and stereoscopic vision, are all characteristics shared with the herbivorous/omnivorous primates and omnivorous Procyon (raccoon).
One study was based on the many Troodon teeth that have been collected from Late Cretaceous deposits from northern Alaska. These teeth are much larger than those collected from more southern sites, providing evidence that northern Alaskan populations of Troodon grew to larger average body size. The study suggests that the Alaskan Troodons may have had access to large animals as prey because there were no Tyrannosaurids in their habitat to provide competition for those resources. This study also provides an analysis of the proportions and wear patterns of a large sample of Troodon teeth. It proposes that the wear patterns of all Troodon teeth suggest a diet of soft foods - inconsistent with bone chewing, invertebrate exoskeletons, or tough plant items. This study hypothesizes a diet primarily consisting of meat[3]
Age determination studies performed on the fossilized remains of Troodon using growth ring counts suggest that the longevity of this dinosaur was around 3–5 years.[4]
Reproduction

Varriccho et al. (2002) have described eight Troodon nests. All of these nests are from the Two Medicine Formation of Montana. These are all in the collection of the Museum of the Rockies and their accession numbers are MOR 246, 299, 393, 675, 676, 750, 963, 1139. The first of these were discovered by John Horner in 1983. Horner (1984) found isolated bones and partial skeletons of the hypsilophodont Orodromeus very near the nests in the same horizon and described the eggs as those of Orodromeus.[5] Horner and Weishampel (1996) reexamined the embryos preserved in the eggs and determined that they were those of Troodon, not Orodromeus.[6]
Varricchio et al. (1997) made this determination with even more certainty when they described a partial skeleton of an adult Troodon (MOR 748) in contact with a clutch of at least five eggs (MOR 750), probably in a brooding position.[7]
Varricchio et al. (1997) described the exact structure of Troodon nests. They were built from sediments, they were dish shaped, about 100 cm in internal diameter, and with a pronounced raised rim encircling the eggs. The more complete nests had between 16 (minimum number in MOR 246) and 24 (MOR 963) eggs. The eggs are shaped like elongated teardrops, with the more tapered ends pointed downwards and imbedded about halfway in the sediment. The eggs are pitched at an angle so that, on average, the upper half is closer to the center of the nest. There is no evidence that plant matter was present in the nest.
Varricchio et al.(1997) were able to extract enough evidence from the nests to infer several characteristics of Troodon reproductive biology. The results are that Troodon appears to have a type of reproduction that is intermediate between crocodiles and birds, as phylogeny would predict. The eggs are statistically grouped in pairs, which suggests that the animal had two functional oviducts, like crocodiles, rather than one, as in birds. Crocodiles lay many eggs that are small proportional to adult body size. Birds lay fewer, larger, eggs. Troodon was intermediate, laying an egg of about 0.5 kg for a 50 kg adult. This is 10 times larger than reptiles of the same mass, but two Troodon eggs are roughly equivalent to the 1.1 kg egg predicted for a 50 kg bird.
Varricchio et al. also found evidence for iterative laying, where the adult might lay a pair of eggs every one or two days, and then ensured simultaneous hatching by delaying brooding until all eggs were laid. MOR 363 was found with 22 empty (hatched) eggs, and the embryos found in the eggs of MOR 246 were in very similar states of development, implying that all of the young hatched simultaneously. The embryos had an advanced degree of skeletal development, implying that they were precocial or even superprecocial. The authors estimated 45 to 65 total days of adult nest attendance for laying, brooding, and hatching. The authors found no evidence that the young remained in the nest after hatching and suggested that, instead, they dispersed like hatchling crocodiles or megapode birds.[8]
Varricchio et al. (2008) examined the bone histology of Troodon specimen MOR 748 and found that it lacked the bone resorption patterns that would indicate it was an egg-laying female. They also measured the ratio of the total volume of eggs in Troodon clutches to the body mass of the adult. They graphed correlations between this ratio and the type of parenting strategies used by extant birds and crocodiles and found that the ratio in Troodon was consistent with that in birds where only the adult male broods the eggs. From this they concluded that Troodon females likely did not brood eggs, that the males did, and this may be a character shared between maniraptoran dinosaurs and basal birds.[9]
History
Troodon was originally spelled Troödon (with a diaeresis) by Joseph Leidy in 1856, which was officially amended to its current status by Sauvage in 1876.
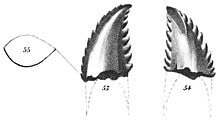
The Troodon tooth was originally classified as a "lacertian" (lizard) by Leidy, but re-assigned as a megalosaurid dinosaur by Nopsca in 1901 (Megalosauridae having historically been a wastebin taxon for most carnivorous dinosaurs). In 1924, Gilmore suggested that the tooth belonged to the herbivorous pachycephalosaur Stegoceras, and that Stegoceras was in fact a junior synonym of Troodon (the similarity of troodontid teeth to those of herbivorous dinosaurs continues to lead many paleontologists to believe that these animals were omnivores). In 1945, Charles Mortram Sternberg rejected the possibility that Troodon was a pachycephalosaur due to its stronger similarity to the teeth of other carnivorous dinosaurs.
The first specimen of Troodon that was not a tooth, then referred to its own genus (Stenonychosaurus), was named by Sternberg in 1932, based on a foot, fragments of a hand, and some caudal vertebrae from Alberta. A remarkable feature of these remains was the enlarged claw on the second toe, which is now recognized as characteristic of Deinonychosauria. Sternberg initially classified Stenonychosaurus as a member of the family Coeluridae. Later, Sternberg (1951) speculated that since Stenonychosaurus had a "very peculiar pes" and Troodon "equally unusual teeth", they may be closely related. Unfortunately, no comparable specimens were available at that time to test the idea.

A more complete skeleton of Stenonychosaurus was described by Dale Russell in 1969, which eventually formed the scientific foundation for a famous life-sized sculpture of Stenonychosaurus accompanied by its fictional, human-like descendant, the "dinosauroid". Stenonychosaurus became a well-known theropod in the 1980s, when the feet and braincase were described in more detail. Phil Currie, reviewing the known Troodontidae in 1987, reclassified Stenonychosaurus inequalis as a junior synonym of Troodon formosus. This synonymy has been widely adopted by other paleontologists, and therefore all of the specimens once called Stenonychosaurus are now referred to as Troodon in the recent scientific literature.
Classification
The type specimen of Troodon has caused problems with classification, as the entire genus is based only on a single tooth from the Judith River Formation. Since the discovery of the original tooth, postcranial material from a related animal were given the name Stenonychosaurus. More complete remains of Stenonychosaurus convinced most paleontologists that it in fact was the same animal as the original tooth, so the name Stenonychosaurus was replaced with its senior synonym, Troodon. Other genera, including Polyodontosaurus and Pectinodon, have also been assigned to Troodon based on the assumption that this particular tooth type is limited to only a single type of dinosaur. For this reason, the future of the name Troodon itself is dubious—in similar situations, genera based on teeth have been abandoned in favor of names based on better remains. Familiar names like Deinodon and Trachodon have been abandoned in this way, and further research may require Troodon be replaced with Stenonychosaurus. In a chapter of the 2005 book Dinosaur Provincial Park, Phil Currie (one of the leading experts on North American troodontids) resurrects the type species of Stenonychosaurus (S. inequalis) within the genus Troodon as Troodon inequalis (Currie, 2005).
The "Dinosauroid"

In 1982, paleontologist Dale Russell, curator of vertebrate fossils at the National Museum of Canada in Ottawa, speculated on how evolution would have proceeded if the troodonts had survived the extincton of the dinosaurs. Russell speculated that a species like Troodon would have grown smarter and taken on a human-like appearance. Russell partnered with taxidermist and artist Ron Sequin and together they made a model of what a derived, intelligent Troodon would look like, naming their fantasy creation a "Dinosauroid" (Russell & Séguin, 1982). While a few paleontologists, such as David Norman (1985) and Cristiano dal Sasso (2004) have regarded this as a plausible line of reasoning, others, such as Gregory S. Paul (1988) and Thomas R. Holtz Jr., consider it "suspiciously human" (Paul, 1988) and argue that a large-brained, highly intelligent troodontid would retain a more standard theropod body plan. Darren Naish has suggested the ground hornbill as a better model for a hominid-mimicking terrestrial theropod.[10][11]
In popular culture
Troodon is featured in ITV's Prehistoric Park in 2006, where it was portrayed as a highly intelligent scavenger. It was also shown in two episodes of Dinosaur Planet. In one, a pack of dwarf Troodon make "friends" with a Pyroraptor; in another, a pack of Troodon attack a flock of Orodromeus. Troodon was also featured in an episode of Animal Armageddon.
In fiction, Troodon feature prominently in the 1994 science-fiction novel End of an Era by Robert J. Sawyer, in which they are the preferred host vehicle for intelligent Martian viral invaders. Also, an intelligent saurian species very like the Troodon, called the saurs, appears in Ken MacLeod's "Engines of Light" series of books.
In the Star Trek novel First Frontier by Diane Carey and James Kirkland, several members of the Enterprise crew travel back in time and find that Troodon has rudimentary language and were well coordinated hunters. They also encounter evolved Troodons, called Clan Ru, from the future that were transplanted before the extinction by the Preservers and were sentient beings capable of warp travel.
The Troodon to "Dinosauroid" 'Thought Experiment', as proposed by Dr. Dale Russell, has also fueled conversation in the UFO community. John Rhodes, the original proponent for the potential for intelligence in "Dinosauroid" like cryptids, called Reptilian-Humanoids or Reptoids, has an entire web site dedicated to this subject.
In the children’s television show Dinosaur Train, the eponymous train is run by a Troodon.
References
- ^ a b Holtz, Thomas R., Brinkman, Daniel L., Chandler, Chistine L. (1998) Denticle Morphometrics and a Possibly Omnivorous Feeding Habit for the Theropod Dinosaur Troodon. Gaia number 15. December 1998. pp. 159-166.
- ^ a b Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. pp. 112–113. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ Fiorillo, Anthony R. (2008) "On the Occurrence of Exceptionally Large Teeth of Troodon (Dinosauria: Saurischia) from the Late Cretaceous of Northern Alaska" Palaios volume 23 pp.322-328
- ^ Varricchio, D. V. (1993). Bone microstructure of the Upper Cretaceous theropod dinosaur Troodon formosus. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 13, 99-104.
- ^ Horner, John R. (1984) "The nesting behavior of dinosaurs". "Scientific American", 250:130-137.
- ^ Horner, John R., Weishampel, David B. (1996) "A comparative embryological study of two ornithischian dinosaurs - a correction." "Nature" 383:256-257.
- ^ Varricchio, David J., Jackson, frankie, Borkowski, John J., Horner, John R. "Nest and egg clutches of the dinosaur Troodon formosus and the evolution of avian reproductive traits." "Nature" Vol. 385:247-250 16 January 1997.
- ^ Varricchio, David J., Horner, John J., Jackson, Frankie D. (2002) "Embryos and eggs for the Cretaceous theropod dinosaur Troodon formosus." "Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology" 22(3):564-576, September 2002,
- ^ Varrichio, David J. Moore, Jason R. Erickson, Gregory M., Norell, Mark A. Jackson, Frankie D. Borkowski, John J. (2008) Avian Paternal Care Had Dinosaur Origin. Science 19 December 2008 Vol 322, 1826-1828 DOI: 10.1126/science.1163245
- ^ "Darren Naish: Tetrapod Zoology: Bucorvids: post-Cretaceous maniraptorans on the savannah". Darrennaish.blogspot.com. 2006-08-11. Retrieved 2009-08-16.
- ^ "Darren Naish: Tetrapod Zoology: Dinosauroids revisited". Darrennaish.blogspot.com. 2006-11-02. Retrieved 2009-08-16.
- Currie, P. J. (1987). "Bird-like characteristics of the jaws and teeth of troodontid theropods (Dinosauria, Saurischia)." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 7: 72-81.
- Currie, P. J. (2005). "Theropods including birds." In: Currie & Koppelhus, Dinosaur Provincial Park, Indiana University Press, Bloomington. Pp 367–397.
- Norman, D. B. (1985). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. Salamander Books, London.
- Russell, D. A. and Séguin, R. (1982). "Reconstruction of the small Cretaceous theropod Stenonychosaurus inequalis and a hypothetical dinosauroid." Syllogeus, 37, 1-43.
- Russell, D. A. (1987). "Models and paintings of North American dinosaurs." In: Czerkas, S. J. & Olson, E. C. (eds) Dinosaurs Past and Present, Volume I. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County/University of Washington Press (Seattle and Washington), pp. 114–131.
