Truncated cube
Appearance
| Truncated cube | |
|---|---|
 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 14, E = 36, V = 24 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 8{3}+6{8} |
| Conway notation | tC |
| Schläfli symbols | t{4,3} |
| t0,1{4,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | 2 3 | 4 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | Oh, B3, [4,3], (*432), order 48 |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432), order 24 |
| Dihedral angle | 3-8: 125°15′51″ 8-8: 90° |
| References | U09, C21, W8 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex |
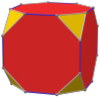 Colored faces |
 3.8.8 (Vertex figure) |
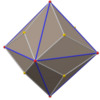 Triakis octahedron (dual polyhedron) |
 Net |


The truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 6 regular octagonal faces, 8 regular triangular faces, 24 vertices and 36 edges.
It shares the vertex arrangement with the uniform great rhombicuboctahedron.
Cartesian coordinates
The following Cartesian coordinates define the vertices of a truncated hexahedron centered at the origin:
- (±ξ, ±1, ±1),
- (±1, ±ξ, ±1)
- (±1, ±1, ±ξ)
where ξ = √2 − 1.
Related polyhedra
Compare:
 Cube |
 Truncated cube |
 cuboctahedron |
 Truncated octahedron |
 Octahedron |
See also
References
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
External links
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
