User:FelixKling/sandbox
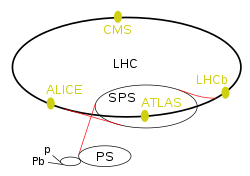 Plan of the LHC experiments and the preaccelerators. | |
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| FASER | ForwArd Search ExpeRiment |
| SND | Scattering and Neutrino Detector |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 4) and lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
FASER (ForwArd Search ExpeRiment) is one of the eight particle physics experiments at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN. It is designed to both search for new light and weakly coupled particles, and to study the interactions of high-energy neutrinos.
The experiment is located in the service tunnel TI12, which is 480 m downstream from the interaction point used by the ATLAS experiment. This tunnel was formerly used to inject the beam from the SPS into the LEP accelerator, but does currently not host any LHC infrastructure. In this location, the FASER experiment is placed into an intense and highly collimated beam of both neutrinos as well as possible new particles. Additionally, it is shielded from ATLAS by about 100 meters of rock and concrete, providing a low background environment. The FASER experiment was approved in 2019 and will start taking data in 2021[1][2].
New Physics Searches
[edit]The primary goal of the FASER experiment is to search for new light and weakly interacting particles, that have not been discovered yet, such as dark photons, axion-like particles and sterile neutrinos[3]. If these particles are sufficiently light, they can be produced in rare decays of hadrons. Such particles will therefore be dominantly produced in the forward direction along the collision axis, forming a highly collimated beam, and can inherit a large fraction of the LHC proton beam energy. Additionally, due to their small couplings to the standard model particles and large boosts, these particles are long-lived and can easily travel hundreds of meters without interacting before they decay to standard model particles. These decays lead to a spectacular signal, the appearance of highly energetic particles, which FASER aims to detect.
Neutrino Physics
[edit]The LHC is the highest energy particle collider built so far, and therefore also the source of the most energetic neutrinos created in a controlled laboratory environment. Collisions at the LHC lead to a large flux of high-energy neutrinos of all flavours, which are highly collimated around the beam collision axis and stream through the FASER location. The dedicated sub-detector FASERν is designed to detect these neutrinos[4]. It will record and study thousands of neutrino interactions, which allows to measure neutrino cross sections at TeV energies where they are currently unconstrained.
Detector
[edit]Located at the front end of FASER is the FASERν neutrino detector. It consists of many layers of emulsion films interleaved with tungsten plates as target material for neutrino interactions. Behind FASERν and at the entrance to the main detector is a charged particle veto consisting of plastic scintillators[5][6]. This is followed by a 1.5 meter long empty decay volume and a 2 meter long spectrometer, which are placed in a 0.55 T magnetic field. The spectrometer consists of three tracking stations, composed of layers of precision silicon strip detectors, to detect charged particles produced in the decay of long-lived particles. Located at the end is an electromagnetic calorimeter.
References
[edit]- ^ "FASER: CERN approves new experiment to look for long-lived, exotic particles". CERN. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- ^ "FASER's new detector expected to catch first collider neutrino". CERN. Retrieved 2019-12-19.
- ^ Ariga et al. (FASER Collaboration) (2019-05-15). "FASER's Physics Reach for Long-Lived Particles". Physical Review D. 99 (9): 095011. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.99.095011. ISSN 2470-0010.
- ^ Abreu et al. (FASER collaboration) (2019). "Detecting and Studying High-Energy Collider Neutrinos with FASER at the LHC".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Ariga et al. (FASER Collaboration) (2018-11-26). "Letter of Intent for FASER: ForwArd Search ExpeRiment at the LHC". arXiv:1811.10243 [hep-ex, physics:hep-ph, physics:physics].
- ^ Ariga et al. (FASER Collaboration) (2018-12-21). "Technical Proposal for FASER: ForwArd Search ExpeRiment at the LHC". arXiv:1812.09139 [hep-ex, physics:hep-ph, physics:physics].
External links
[edit]46°14′09″N 6°03′18″E / 46.23583°N 6.05500°E
Category:CERN experiments Category:Particle experiments Category:Large Hadron Collider
