User:Tomruen/List of Hanner polytopes
In geometry, a Hanner polytope is a convex polytope constructed recursively by Cartesian product and polar dual operations. Hanner polytopes are named after Olof Hanner, who introduced them in 1956.[1]
Construction[edit]
The Hanner polytopes are constructed recursively by the following rules:[2]
- A line segment is a one-dimensional Hanner polytope
- The Cartesian product of every two Hanner polytopes is another Hanner polytope, whose dimension is the sum of the dimensions of the two given polytopes
- The dual of a Hanner polytope is another Hanner polytope of the same dimension.
They are exactly the polytopes that can be constructed using only these rules: that is, every Hanner polytope can be formed from line segments by a sequence of product and dual operations.[2]
Alternatively and equivalently to the polar dual operation, the Hanner polytopes may be constructed by Cartesian products and direct sums, the dual of the Cartesian products. This direct sum operation combines two polytopes by placing them in two linearly independent subspaces of a larger space and then constructing the convex hull of their union.
Counts[edit]
Binary cases are complete up to n=5, and then new cases are added with cases more that doubling each new dimension.
| n | Count | Binary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 8 | 8 |
| 6 | 18 | 16 |
| 7 | 40 | 32 |
| 8 | 94 | 64 |
| 9 | 224 | 128 |
| 10 | 548 | 256 |
| 11 | 1,356 | 512 |
| 12 | 3,418 | 1,024 |
| 13 | 8,692 | 2,048 |
| 14 | 22,352 | 4,096 |
| 15 | 57,932 | 8,192 |
| 16 | 151,312 | 16,384 |
| 17 | 397,628 | 32,768 |
Lists[edit]
This article lists solutions up to dimension 7. There are 1, 1, 2, 4, 8, 18, and 40 Hanner polytopes in dimensions 1 to 7, respectively.
They exist in dual pairs and are listed below as n-polytopes in n-dimensions.[3]
Key:
- Cn=n-cube, coordinates, (±1,±1,±1...±1), 2n vertices
- CΔ
n=dual polytope=n-orthoplex, coordinates as permutations of (±1,0,0...,0), 2n vertices. - bip P := P ⊕ { } denotes a fusil, adding two vertices in an added dimension
- prism P := P × { } refers to a prism construction, doubling the vertices in an added dimension
Coordinates are assigned left to right in sets by the original polytope and the extending polytope, each set separated by a semicolon rather than comma. uniform polytopes here only require a single coordinate type.
The binary construction reads right to left, with 1 for prism, 0 for fusil, x is either, and xx is either, so ...000xx is an n-orthoplex, and ...111xx is an n-cube. There are powers of two binary expressions possible after the x's, while starting at 6D, some solutions can't be expressed this way.
For example, the binary construction 10010xx is interpreted right-to-left, with oxx as an octahedron, {3,4}, then 1 implying a prism, {3,4}×{}, next 00 (square) as a di-fusil, {3,4}×{}+{4}, and final 1 as a prism, ({3,4}×{}+{4})×{}. It can be called a octahedral-prism,square di-fusil prism.
For 7,8,9 dimensions the counts are 94, 224, 548, but are unlisted. The binary cases would be 64, 128, and 256, leaving 30, 96, and 292 special cases.
Hanner polytopes with ringed Coxeter–Dynkin diagram are (vertex-transitive) uniform polytopes. Their facet-transitive duals can be named by replacing rings with vertical lines through the nodes.
Line segment[edit]
The binary construction is named x because any value, 1-cube, or 1-orthoplex produce a line segment, { }.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | f0 | ||
| 1 | x=0 or 1 | CΔ 1 or C1 |
line segment | d{ } = { } |
2 | (±1) | |
Polygons[edit]
 1-orthoplex |
 1-cube |
There is only one Hanner polygon, a square, which can be in two orientations. The 2-cube construction has 4 vertices (±1; ±1). The dual 2-orthoplex construction vertices are listed at ([±1,0]), with the brackets to imply the bracket coordinates need to be permuted, here as (±1; 0), (0; ±1).
The binary construction is named xx because any values produce a square.
| # | Construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | f0 | f1 | ||
| 1 | xx=00 or 01 or 10 or 11 |
CΔ 2 = C2 |
square | {4} = { }+{ } = { }×{ } |
4 | 4 | ([±1,0]) = (±1; 0), (0; ±1) (±1; ±1) | |
Polyhedra[edit]
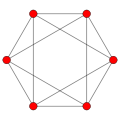 Octahedron {3,4} |
 Cube {4,3} |
There are two Hanner polyhedra, the regular cube and octahedron.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | f0 | f1 | f2 | ||
| 1 | 0xx | CΔ 3 |
octahedron | { }+{ }+{ } = 3{ } = {3,4} | 6 | 12 | 8 | ([±1,0,0]) = (±1; 0; 0), (0; ±1; 0), (0; 0; ±1) | |
| 2 | 1xx | C3 | cube | { }×{ }×{ } = { }3 = {4,3} | 8 | 12 | 6 | (±1,±1,±1) | |
4-polytopes[edit]
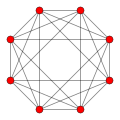 16-cell {3,3,4} ([±1,0,0,0]) |
 Tesseract {4,3,3} (±1,±1,±1,±1) |
| File:Cubic fusil-ortho.png Cubic difusil {4,3} + { } (±1,±1,±1; 0), (0,0,0; ±1) |
 Octahedral prism {3,4}×{ } ([±1,0,0]; ±1) |
There are 4 Hanner polytopes in 4-dimensions, all from 22 binary constructions.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | |||
| 1 | 00xx | CΔ 4 |
16-cell | { }+{ }+{ }+{ } = 4{ } = {3,3,4} | 8 | 8 | 24 | 32 | 16 | ([±1,0,0,0]) | ||
| 2 | 11xx | C4 | 4-cube | { }×{ }×{ }×{ } = { }4 = {4,3,3} | 16 | 16 | 32 | 24 | 8 | (±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
| 3 | 01xx | bip C3 | cubical fusil | {4,3}+{ } = dt{2,3,4} | 8 + 2 | 10 | 28 | 30 | 12 | (±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; ±1) | |
| 4 | 10xx | prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral prism | {3,4}×{ } = t{2,3,4} | 6×2 | 12 | 30 | 28 | 10 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1) | ||
5-polytopes[edit]
 5-orthoplex {3,3,3,4} |
 5-cube {4,3,3,3} |
There are 8 Hanner polytopes in 5-dimensions, all from 23 binary constructions.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | |||
| 1 | 000xx | CΔ 5 |
5-orthoplex | 5{ } = {3,3,3,4} | 10 | 10 | 40 | 80 | 80 | 32 | ([±1,0,0,0,0]) | ||
| 2 | 111xx | C5 | 5-cube | { }5 = {4,3,3,3} | 32 | 32 | 80 | 80 | 40 | 10 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
| 3 | 001xx | bip bip C3 | cube,square di-fusil | {4,3}+{4} | 8 + 4 | 12 | 48 | 86 | 72 | 24 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1) | |
| 4 | 110xx | prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron,square di-prism | {3,4}×{4} | 6×4 | 24 | 72 | 86 | 48 | 12 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1) | ||
| 5 | 010xx | bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral prism fusil | {3,4}×{ }+{ } | 6×2 + 2 | 14 | 54 | 88 | 66 | 20 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0; ±1) | |
| 6 | 101xx | prism bip C3 | cubic fusil prism | ({4,3}+{ })×{ } | (8 + 2)×2 | 20 | 66 | 88 | 54 | 14 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1) | |
| 7 | 100xx | prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell prism | {3,3,4}×{ } | 8×2 | 16 | 56 | 88 | 64 | 18 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1) | ||
| 8 | 011xx | bip C4 | tesseractic fusil | {4,3,3}+{ } | 16 + 2 | 18 | 64 | 88 | 56 | 16 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0; ±1) | |
6-polytopes[edit]
 6-orthoplex {3,3,3,3,4} |
 6-cube {4,3,3,3,3} |
There are 18 Hanner polytopes in 6-dimensions, 16 from 24 binary constructions, and 2 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Coxeter | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | ||||
| 1 | 0000xx | CΔ 6 |
6-orthoplex | {3,3,3,3,4} | 12 | 12 | 60 | 160 | 240 | 192 | 64 | (±1,0,0,0,0,0) | |||
| 2 | 1111xx | C6 | 6-cube | {4,3,3,3,3} | 64 | 64 | 192 | 240 | 160 | 60 | 12 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | |||
| 3 | 0001xx | bip bip bip C3 | octahedron,cube di-fusil | {4,3}+{3,4} | 8 + 6 | 14 | 72 | 182 | 244 | 168 | 48 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0) | (0,0,0; [±1,0,0]) | ||
| 4 | 1110xx | prism prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron,cube di-prism | {4,3}×{3,4} | 8×6 | 48 | 168 | 244 | 182 | 72 | 14 | (±1,±1,±1; [±1,0,0]) | |||
| 5 | 0010xx | bip bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral-prism,square di-fusil | {3,4}×{ }+{4} | 6×2 + 4 | 16 | 82 | 196 | 242 | 152 | 40 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0; 0; ±1,±1) | ||
| 6 | 1101xx | prism prism bip C3 | cubic-fusil,square di-prism | ({4,3}+{ })×{4} | 8 + 2×4 | 40 | 152 | 242 | 196 | 82 | 16 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1,±1) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1,±1) | ||
| 7 | 0100xx | bip prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell prism fusil | {3,3,4}×{ }+{ } | 8×2 + 2 | 18 | 88 | 200 | 240 | 146 | 36 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0; 0; ±1) | ||
| 8 | 1011xx | prism bip C4 | tesseract fusil prism | ({4,3,3}+{ })×{ } | 16 + 2×2 | 36 | 146 | 240 | 200 | 88 | 18 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0,0; ±1; ±1) | ||
| 9 | 0011xx | bip bip C4 | tesseract,square di-fusil | {4,3,3}+{4} | 16 + 4 | 20 | 100 | 216 | 232 | 128 | 32 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0,0; ±1,±1) | ||
| 10 | 1100xx | prism prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell,square di-prism | {3,3,4}×{4} | 8×4 | 32 | 128 | 232 | 216 | 100 | 20 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1; ±1) | |||
| 11 | 1000xx | prism CΔ 5 |
5-orthoplex prism | {3,3,3,4}×{ } | 10×2 | 20 | 90 | 200 | 240 | 144 | 34 | ([±1,0,0,0,0]; ±1) | |||
| 12 | 0111xx | bip C5 | 5-cube fusil | {4,3,3,3}+{ } | 32 + 2 | 34 | 144 | 240 | 200 | 90 | 20 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0,0; ±1) | ||
| 13 | 0101xx | bip prism bip C3 | cubic fusil prism fusil | ({4,3}+{ })×{ }+{ } | (8 + 2)×2 + 2 | 22 | 106 | 220 | 230 | 122 | 28 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0; 0; ±1) | |
| 14 | 1010xx | prism bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral prism fusil prism | ({3,4}×{ }+{ })×{ } | (6×2 + 2)×2 | 28 | 122 | 230 | 220 | 106 | 22 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0; 0; ±1; ±1) | ||
| 15 | 1001xx | prism bip bip C3 | cube,square di-fusil prism | ({4,3}+{4})×{ } | (8 + 4)×2 | 24 | 108 | 220 | 230 | 120 | 26 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0; ±1) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1; ±1) | ||
| 16 | 0110xx | bip prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron,square di-prism fusil | {3,4}×{4}+{ } | 6×4 + 2 | 26 | 120 | 230 | 220 | 108 | 24 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0,0; ±1) | ||
| 17 | -- | C3 ⊕ C3 | cube,cube di-fusil | {4,3}+{4,3} | 8 + 8 | 16 | 88 | 204 | 240 | 144 | 36 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1,±1) | ||
| 18 | -- | CΔ 3 × CΔ 3 |
octahedron,octahedron di-prism | {3,4}×{3,4} | 6×6 | 36 | 144 | 240 | 204 | 88 | 16 | ([±1,0,0]; [±1,0,0]) | |||
7-polytopes[edit]
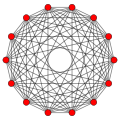 7-orthoplex {3,3,3,3,3,4} |
 7-cube {4,3,3,3,3,3} |
There are 40 Hanner polytopes in 7-dimensions, 32 from 25 binary constructions, and 8 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | ||||
| 1 | 00000xx | CΔ 7 |
7-orthoplex | {3,3,3,3,3,4} | 14 | 14 | 84 | 280 | 560 | 672 | 448 | 128 | (±1,0,0,0,0,0,0) | ||
| 2 | 11111xx | C7 | 7-cube | {4,3,3,3,3,3} | 128 | 128 | 448 | 672 | 560 | 280 | 84 | 14 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
| 3 | 00001xx | bip bip bip bip C3 | cube,16-cell di-fusil | {4,3}+{3,3,4} | 8 + 8 | 16 | 100 | 326 | 608 | 656 | 384 | 96 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0,0) | (0,0,0; [±1,0,0,0]} | |
| 4 | 11110xx | prism prism prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron,tesseract di-prism | {3,4}×{4,3,3} | 6×16 | 96 | 384 | 656 | 608 | 326 | 100 | 16 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
| 5 | 00010xx | bip bip bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral-prism,octahedron di-fusil | {3,4}×{ }+{3,4} | 6×2 + 6 | 18 | 114 | 360 | 634 | 636 | 344 | 80 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0,0,0) | (0,0,0; 0; [±1,0,0]) | |
| 6 | 11101xx | prism prism prism bip C3 | cubic-bipyramid,cube di-prism | ({4,3}+{ })×{4,3} | (8 + 2)×8 | 80 | 344 | 636 | 634 | 360 | 114 | 18 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1,±1,±1) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1,±1,±1) | |
| 7 | 00011xx | bip bip bip C4 | tesseract,octahedron di-fusil | {4,3,3}+{3,4} | 16 + 6 | 22 | 140 | 416 | 904 | 656 | 592 | 64 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0) | 0,0,0,0; [±1,0,0]) | |
| 8 | 11100xx | prism prism prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell,cube di-prism | {3,3,4}×{4,3} | 8×8 | 64 | 592 | 656 | 904 | 416 | 140 | 22 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1,±1,±1] | ||
| 9 | 00100xx | bip bip prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell-prism,square di-fusil | ({3,3,4}×{ })+{4} | (8×2) + 4 | 20 | 124 | 376 | 640 | 626 | 328 | 72 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0,0; 0; ±1,±1) | |
| 10 | 11011xx | prism prism bip C4 | tesseractic-bipyramid,square di-prism | ({4,3,3}+{ })×{4} | (16 + 2)×4 | 72 | 328 | 626 | 640 | 376 | 124 | 20 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1,±1) | (0,0,0,0; ±1; ±1,±1) | |
| 11 | 00101xx | bip bip prism bip C3 | square-bipyramid-prism,square di-fusil | ({4,3}+{ })×{ }+{4} | (8 + 2)×2 + 4 | 24 | 150 | 432 | 670 | 582 | 272 | 56 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0; 0; 0; ±1,±1) |
| 12 | 11010xx | prism prism bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral-prism-bipyramid,square di-prism | ({3,4}×{ }+{ })×{4} | (6×2 + 2)×4 | 56 | 272 | 582 | 670 | 432 | 150 | 24 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0, ±1,±1) | (0,0,0; 0; ±1; ±1,±1) | |
| 13 | 00110xx | bip bip prism prism CΔ 3 |
(octahedron,square di-prism),square di-fusil | {3,4}×{4}+{4} | 6×4 + 4 | 28 | 172 | 470 | 680 | 548 | 240 | 48 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0; 0,0; ±1,±1) | |
| 14 | 11001xx | prism prism bip bip C3 | (cube,square di-fusil),square di-prism | ({4,3}+{4})×{4} | (8 + 4)×4 | 48 | 240 | 548 | 680 | 470 | 172 | 28 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0; ±1,±1) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1; ±1,±1) | |
| 15 | 00111xx | bip bip C5 | 5-cube,square di-fusil | {4,3,3,3}+{4} | 32 + 4 | 36 | 212 | 528 | 680 | 490 | 200 | 40 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1; 0,0) | (0,0,0,0,0; ±1,±1) | |
| 16 | 11000xx | prism prism CΔ 5 |
5-orthoplex,square di-prism | {3,3,3,4}×{4} | 10×4 | 40 | 200 | 490 | 680 | 528 | 212 | 36 | ([±1,0,0,0,0]; ±1,±1) | ||
| 17 | 01000xx | bip prism CΔ 5 |
5-orthoplex-prism fusil | {3,3,3,4}×{ }+{ } | 10×2 + 2 | 22 | 130 | 380 | 640 | 624 | 322 | 68 | ([±1,0,0,0,0]; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0,0; 0; ±1) | |
| 18 | 10111xx | prism bip C5 | 5-cube-bipyramid prism | ({4,3,3,3}+{ })×{ } | (32 + 2)×2 | 68 | 322 | 624 | 640 | 380 | 130 | 22 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0,0,0; ±1; ±1) | |
| 19 | 01001xx | bip prism bip bip C3 | cube,square di-fusil prism fusil | ({4,3}+{4})×{ }+{ } | (8 + 4)×2 + 2 | 26 | 156 | 436 | 670 | 580 | 266 | 52 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0,0; 0; ±1) |
| 20 | 10110xx | prism bip prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron-square di-prism fusil prism | ({3,4}×{4}+{ })×{ } | (6×4 + 2)×2 | 52 | 266 | 580 | 670 | 436 | 156 | 26 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0; 0,0; ±1; ±1) | |
| 21 | 01010xx | bip prism bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron prism fusil prism fusil | ({3,4}×{ }+{ })×{ }+{ } | (6×2 + 2)×2 + 2 | 30 | 178 | 474 | 680 | 546 | 234 | 44 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0; ±1; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0; 0; ±1) |
| 22 | 10101xx | prism bip prism bip C3 | cube fusil prism fusil prism | (({4,3}+{ })×{ }+{ })×{ } | ((8 + 2)×2 + 2)×2 | 44 | 234 | 546 | 680 | 474 | 178 | 30 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0; 0; 0; ±1; ±1) |
| 23 | 01011xx | bip prism bip C4 | tesseract fusil prism fusil | ({4,3,3}+{ })×{ }+{ } | (16 + 2)×2 + 2 | 38 | 216 | 528 | 684 | 496 | 192 | 32 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0; ±1; ±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0; 0; 0; ±1) |
| 24 | 10100xx | prism bip prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell prism fusil prism | ({3,3,4}×{ }+{ })×{ } | (8×2 + 2)×2 | 36 | 192 | 496 | 684 | 528 | 216 | 38 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1; 0; ±1) | (0,0,0,0; 0; ±1; ±1) | |
| 25 | 01100xx | bip prism prism CΔ 4 |
16-cell-square di-prism fusil | {3,3,4}×{4}+{ } | 8×4 + 2 | 34 | 192 | 488 | 680 | 532 | 220 | 40 | ([±1,0,0,0]; ±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0; 0,0; ±1) | |
| 26 | 10011xx | prism bip bip C4 | tesseract,square di-fusil prism | ({4,3,3}+{4})×{ } | (16 + 4)×2 | 40 | 220 | 532 | 680 | 488 | 192 | 34 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0,0; ±1) | (0,0,0,0; ±1,±1; ±1) | |
| 27 | 01101xx | bip prism prism bip C3 | cubic-bipyramid,square di-prism fusil | ({4,3}+{ })×{4}+{ } | (8 + 2)×4 + 2 | 42 | 232 | 546 | 680 | 474 | 180 | 32 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; ±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; ±1; ±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0; 0,0; ±1) |
| 28 | 10010xx | prism bip bip prism CΔ 3 |
octahedral-prism,square di-fusil prism | ({3,4}×{ }+{4})×{ } | (6×2 + 4)×2 | 32 | 180 | 474 | 680 | 546 | 232 | 42 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0,0; ±1) | (,0,0; 0; ±1,±1; ±1) | |
| 29 | 01110xx | bip prism prism prism CΔ 3 |
octahedron,square di-prism fusil | {3,4}×{4,3}+{ } | 6×8 + 2 | 50 | 264 | 580 | 670 | 436 | 158 | 28 | ([±1,0,0]; ±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0,0,0; ±1) | |
| 30 | 10001xx | prism bip bip bip C3 | cube,octahedron di-fusil prism | ({4,3}+{3,4})×{ } | (8 + 6)×2 | 28 | 158 | 436 | 670 | 580 | 264 | 50 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0; ±1) | (0,0,0; [±1,0,0]; ±1) | |
| 31 | 01111xx | bip C6 | 6-cube fusil | {4,3,3,3,3}+{ } | 64 + 2 | 66 | 320 | 624 | 640 | 380 | 132 | 24 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0,0,0,0; ±1) | |
| 32 | 10000xx | prism CΔ 6 |
6-orthoplex prism | {3,3,3,3,4}×{ } | 12×2 | 24 | 132 | 380 | 640 | 624 | 320 | 66 | ([±1,0,0,0,0,0]; ±1) | ||
| 33 | -- | bip (C3⊕C3) | cube,cube di-fusil fusil | {4,3}+{4,3}+{ } | 8 + 8 + 2 | 18 | 120 | 380 | 648 | 624 | 324 | 72 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0; 0) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1,±1; 0) | (0,0,0; 0,0,0; ±1) |
| 34 | -- | prism (CΔ 3×CΔ 3) |
octahedron,octahedron di-prism prism | {3,4}×{3,4}×{ } | 6×6×2 | 72 | 324 | 624 | 648 | 380 | 120 | 18 | ([±1,0,0]; [±1,0,0]; ±1) | ||
| 35 | -- | prism (C3⊕C3) | cube,cube di-fusil prism | ({4,3}+{4,3})×{ } | (8 + 8)×2 | 32 | 192 | 496 | 684 | 528 | 216 | 38 | (±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0; ±1) | (0,0,0; ±1,±1,±1; ±1) | |
| 36 | -- | bip (CΔ 3×CΔ 3) |
octahedron,octahedron di-prism fusil | {3,4}×{3,4}+{ } | 6×6 + 2 | 38 | 216 | 528 | 684 | 496 | 192 | 32 | ([±1,0,0]; [±1,0,0]; 0) | (0,0,0; 0,0,0; ±1) | |
| 37 | -- | C4⊕C3 | tesseract,cube di-fusil | {4,3,3}+{4,3} | 16 + 8 | 24 | 172 | 478 | 680 | 544 | 240 | 48 | (±1,±1,±1,±1; 0,0,0) | (0,0,0,0; ±1,±1,±1) | |
| 38 | -- | CΔ 4×CΔ 3 |
16-cell,octahedron di-prism | {3,3,4}×{3,4} | 8×6 | 48 | 240 | 544 | 680 | 478 | 172 | 24 | ([±1,0,0,0]; [±1,0,0]) | ||
| 39 | -- | (prism CΔ 3)⊕C3 |
octahedral-prism,cube di-fusil | {3,4}×{ }+{4,3} | 6×2 + 8 | 20 | 138 | 418 | 666 | 596 | 288 | 60 | (0,0,0; 0; ±1,±1,±1) | ([±1,0,0]; ±1; 0,0,0) | |
| 40 | -- | (bip C3)×CΔ 3 |
cubical-fusil,octahedron di-prism | ({4,3}+{ })×{3,4} | (8 + 2)×6 | 60 | 288 | 596 | 666 | 418 | 138 | 20 | (±1,±1,±1; 0; [±1,0,0]) | (0,0,0; ±1; [±1,0,0]) | |
8-polytopes[edit]
 8-orthoplex {3,3,3,3,3,3,4} |
 8-cube {4,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
There are 94 Hanner polytopes in 8-dimensions, 64 from 26 binary constructions, and 30 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | ||||
| 1 | 000000xx | CΔ 8 |
8-orthoplex | {3,3,3,3,3,3,4} | 16 | 16 | 112 | 448 | 1120 | 1792 | 1792 | 1024 | 256 | (±1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) | ||
| 2 | 111111xx | C8 | 8-cube | {4,3,3,3,3,3,3} | 256 | 256 | 1024 | 1792 | 1792 | 1120 | 448 | 112 | 16 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
9-polytopes[edit]
 9-orthoplex {3,3,3,3,3,3,3,4} |
 9-cube {4,3,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
There are 224 Hanner polytopes in 9-dimensions, 128 from 27 binary constructions, and 96 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | f8 | ||||
| 1 | 0000000xx | CΔ 9 |
9-orthoplex | {3,3,3,3,3,3,3,4} | 18 | 18 | 144 | 672 | 2016 | 4032 | 5376 | 4608 | 2304 | 512 | (±1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) | ||
| 2 | 1111111xx | C9 | 9-cube | {4,3,3,3,3,3,3,3} | 512 | 512 | 2304 | 4608 | 5376 | 4032 | 2016 | 672 | 144 | 18 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
10-polytopes[edit]
 10-orthoplex {3,3,3,3,3,3,3,4} |
 10-cube {4,3,3,3,3,3,3,3} |
There are 548 Hanner polytopes in 10-dimensions, 256 from 28 binary constructions, and 292 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
| # | Binary construction | Polytope | f-vector | Coordinates | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary | Name | Name | Schläfli | Vertices | f0 | f1 | f2 | f3 | f4 | f5 | f6 | f7 | f8 | f9 | ||||
| 1 | 00000000xx | CΔ 10 |
10-orthoplex | {3,3,3,3,3,3,3,4} | 20 | 20 | 180 | 960 | 3360 | 8064 | 13440 | 15360 | 11520 | 5120 | 1024 | (±1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0) | ||
| 2 | 11111111xx | C10 | 10-cube | {4,3,3,3,3,3,3,3} | 1024 | 1024 | 5120 | 11520 | 15360 | 13440 | 8064 | 3360 | 960 | 180 | 20 | (±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1,±1) | ||
11-polytopes[edit]
There are 1356 Hanner polytopes in 11-dimensions, 512 from 29 binary constructions, and 884 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
12-polytopes[edit]
There are 3418 Hanner polytopes in 12-dimensions, 1024 from 210 binary constructions, and 2394 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
13-polytopes[edit]
There are 8692 Hanner polytopes in 13-dimensions, 2048 from 211 binary constructions, and 6644 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
14-polytopes[edit]
There are 22352 Hanner polytopes in 14-dimensions, 4096 from 212 binary constructions, and 18256 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
15-polytopes[edit]
There are 57932 Hanner polytopes in 15-dimensions, 8192 from 213 binary constructions, and 49740 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
16-polytopes[edit]
There are 151,312 Hanner polytopes in 16-dimensions, 16,384 from 214 binary constructions, and 134,928 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
17-polytopes[edit]
There are 397,628 Hanner polytopes in 17-dimensions, 32,768 from 215 binary constructions, and 364,860 requiring di-prisms or di-fusils.
Refernces[edit]
- ^ Hanner, Olof (1956), "Intersections of translates of convex bodies", Mathematica Scandinavica, 4: 65–87, MR 0082696.
- ^ a b Freij, Ragnar (2012), Topics in algorithmic, enumerative and geometric combinatorics (PDF), Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mathematical Sciences, Chalmers Institute of Technology.
- ^ Raman Sanyal, Axel Werner Gunter, M. Ziegler, On Kalai’s conjectures concerning centrally symmetric polytopes, Discrete Comput Geom (2009) 41: 183–198, DOI 10.1007/s00454-008-9104-8 [1] pp. 190, 196
