Xiaotingia
| Xiaotingia Temporal range: Late Jurassic,
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Type specimen | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Anchiornithidae |
| Genus: | †Xiaotingia Xu et al., 2011 |
| Species: | †X. zhengi
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Xiaotingia zhengi Xu et al., 2011
| |
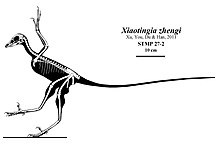
Xiaotingia is a genus of bird-like theropod dinosaur from early Late Jurassic deposits of western Liaoning, China, containing a single species, Xiaotingia zhengi.[1]
Discovery

Xiaotingia is known from the holotype STM 27-2, an articulated and almost complete skeleton including the skull. It was probably collected in the Linglongta area, Jianchang, from the Tiaojishan Formation.[1]
Etymology
Xiaotingia was first named by Xu Xing, You Hailu, Du Kai and Han Fenglu in 2011 and the type species is Xiaotingia zhengi. The generic name and specific name together honour Zheng Xiaoting.[1]
Classification
The initial analysis by Xu et al. showed that Xiaotingia formed a clade with Archaeopteryx, Dromaeosauridae and Troodontidae to the exclusion of other groups traditionally seen as birds. Xu et al therefore (re)defined the concepts of Deinonychosauria and Avialae to the extent that Archaeopteryx and Xiaotingia belonged to the Deinonychosauria in the clade Archaeopterygidae.[1] This led to popular reports that "Archaeopteryx is no longer a bird",[2] although Xu et al noted that there are several competing definitions of the clade Aves currently in use, pointing out that their definitions are compatible with a traditional Aves with Archaeopteryx as a specifier.[1] This was challenged by an analysis using different methods published several months later however, in which Archaeopteryx was again recovered as an avialan, while Xiaotingia remained closely allied to Anchiornis within the Troodontidae.[3] In 2012, an expanded and revised version of the initial analysis also found Archaeopteryx to be avialan and Anchiornis to be troodontid, but recovered Xiaotingia as the most primitive member of the clade Dromaeosauridae rather than a close relative of Anchiornis within Troodontidae.[4]

Relationships found by the revised analysis of Senter et al., 2012:[4]
Below is a cladogram published in 2013 by Godefroit et al.[5]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e "An Archaeopteryx-like theropod from China and the origin of Avialae" (PDF). Nature. 475 (7357): 465–470. 28 July 2011. doi:10.1038/nature10288. PMID 21796204.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Feathers fly in first bird debate". BBC News. 27 July 2011.
- ^ Lee, M.S.Y. and Worthy, T.H. (2011). "Likelihood reinstates Archaeopteryx as a primitive bird". Biology Letters. 8 (2): 299–303. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.0884. PMC 3297401. PMID 22031726.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Senter, P., Kirkland, J.I., DeBlieux, D.D., Madsen, S., and Toth, N. (2012). "New Dromaeosaurids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah, and the Evolution of the Dromaeosaurid Tail". PloS one. 7 (5): e36790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036790. PMC 3352940. PMID 22615813.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Godefroit, Pascal; Cau, Andrea; Hu, Dong-Yu; Escuillié, François; Wu, Wenhao; Dyke, Gareth (2013). "A Jurassic avialan dinosaur from China resolves the early phylogenetic history of birds". Nature. 498 (7454): 359–362. Bibcode:2013Natur.498..359G. doi:10.1038/nature12168. PMID 23719374.
