Epitympanic recess
| Epitympanic recess | |
|---|---|
 The right membrana tympani with the hammer and the chorda tympani, viewed from within, from behind, and from above. (Epitympanic recess labeled at upper right.) | |
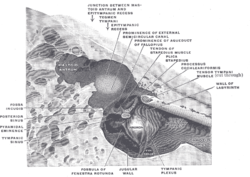 The medial wall and part of the posterior and anterior walls of the right tympanic cavity, lateral view. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | recessus epitympanicus |
| TA98 | A15.3.02.004 |
| TA2 | 6879 |
| FMA | 56717 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The epitympanic recess is the portion of the tympanic cavity (of the middle ear) situated superior to the tympanic membrane.[1]: 414 The recess lodges the head of malleus, and the body of incus.[1]: 416
The mastoid antrum is situated posterior to the recess and opens into the recess at the posterior wall of the recess via the aditus to mastoid antrum.[1]: 416 The ampulla of the lateral semicircular canal creates a prominence upon the medial wall of the recess.[1]: 420
Clinical significance
[edit]This recess is a possible route of spread of infection to the mastoid air cells located in the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Inflammation which has spread to the mastoid air cells is very difficult to drain and causes considerable pain. Before the advent of antibiotics, it could only be drained by drilling a hole in the mastoid bone, a process known as mastoidectomy.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Sinnatamby, Chummy S. (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ "Mastoidectomy, middle ear infection, otitis media, swimmers ear treatment, ear infection symptoms, chronic ear infection, acute ear infection, mastoiditis, mastoidectomy, tympanostomy tubes, adenoidectomy". Archived from the original on 2008-11-02. Retrieved 2008-11-04.
