Effect of spaceflight on the human body: Difference between revisions
→Psychological effects of spaceflight: added text/ref - re NASA-supported study suggests travel in outer space may harm the brain of astronauts & accelerate the onset of Alzheimer's Disease. |
|||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
During long missions, astronauts are [[Isolation (psychology)|isolated]] and confined into small spaces. [[depression (mood)|Depression]], [[cabin fever]] and other psychological problems may impact the crew's safety and mission success.{{Citation needed|date=March 2009}} Astronauts may not be able to quickly return to Earth or receive medical supplies, equipment or personnel if a medical emergency occurs. The astronauts may have to rely for long periods on their limited existing resources and medical advice from the ground. |
During long missions, astronauts are [[Isolation (psychology)|isolated]] and confined into small spaces. [[depression (mood)|Depression]], [[cabin fever]] and other psychological problems may impact the crew's safety and mission success.{{Citation needed|date=March 2009}} Astronauts may not be able to quickly return to Earth or receive medical supplies, equipment or personnel if a medical emergency occurs. The astronauts may have to rely for long periods on their limited existing resources and medical advice from the ground. |
||
On December 31, 2012, a [[NASA]]-supported study suggested that traveling in [[outer space]] may harm the [[brain]] of [[astronauts]] and accelerate the onset of [[Alzheimer's disease]].<ref name="PLOS-20121231">{{cite journal |last=Cherry |first=Jonathan D. |last2=Frost |first2=Jeffrey L. |last3=Lemere |first3=Cynthia A. |last4=Williams |first4=Jacqueline P. |last5=Olschowka |first5=John A. |last6=O'Banion |first6=M. Kerry |title=Galactic Cosmic Radiation Leads to Cognitive Impairment and Increased Aβ Plaque Accumulation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease |url=http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0053275 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0053275 |volume=7 |number=12 |page=e53275 |journal=[[PLOS ONE]] |accessdate=January 7, 2013 }}</ref><ref name="SpaceRef-20130101">{{cite web |authors=Staff |title=Study Shows that Space Travel is Harmful to the Brain and Could Accelerate Onset of Alzheimer's |url=http://spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=39650 |date=January 1, 2013 |publisher=SpaceRef |accessdate=January 7, 2013 }}</ref><ref name="NasaWatch-20130103">{{cite web |last=Cowing |first=Keith |authorlink=Keith Cowing |title=Important Research Results NASA Is Not Talking About (Update) |url=http://nasawatch.com/archives/2013/01/important-resea.html |date=January 3, 2013 |publisher=NASA Watch |accessdate=January 7, 2013 }}</ref> |
|||
==Future prospects== |
==Future prospects== |
||
Revision as of 00:06, 8 January 2013
Humans are physiologically well-adapted to life on Earth. Consequently, spaceflight has many negative effects on the body. The most significant adverse effects of long-term weightlessness are muscle atrophy and deterioration of the skeleton (spaceflight osteopenia).[1] Other significant effects include a slowing of cardiovascular system functions, decreased production of red blood cells, balance disorders, and a weakening of the immune system. Lesser symptoms include fluid redistribution (causing the "moon-face" appearance typical in pictures of astronauts experiencing weightlessness),[2][3] loss of body mass, nasal congestion, sleep disturbance, and excess flatulence. Most of these effects begin to reverse quickly upon return to Earth.
The engineering problems associated with leaving Earth and developing space propulsion systems have been examined for over a century, and millions of man-hours of research have been spent on them. In recent years there has been an increase in research on the issue of how humans can survive and work in space for extended and possibly indefinite periods of time. This question requires input from the physical and biological sciences and has now become the greatest challenge (other than funding) facing human space exploration. A fundamental step in overcoming this challenge is trying to understand the effects and impact of long-term space travel on the human body.
Studying the effects of space on human physiology
Space medicine is a developing medical practice that studies the health of astronauts living in outer space. The main purpose of this academic pursuit is to discover how well and for how long people can survive the extreme poba conditions in space, and how fast they can re-adapt to the Earth's environment after returning from space. Space medicine also seeks to develop preventative and palliative measures to ease the suffering caused by living in an environment to which humans are not well adapted.
List of effects of space on human physiology
Many of the environmental conditions experienced by humans during spaceflight are very different from those in which humans evolved; however, technology is able to shield people from the harshest conditions, such as that offered by a spaceship or spacesuit. The immediate needs for breathable air and drinkable water are addressed by a life support system, a group of devices that allow human beings to survive in outer space.[4] The life support system supplies air, water and food. It must also maintain temperature and pressure within acceptable limits and deal with the body's waste products. Shielding against harmful external influences such as radiation and micro-meteorites is also necessary.
Of course, it is not possible to remove all hazards; the most important factor affecting human physical well-being in space is weightlessness, more accurately defined as microgravity. Living in this type of environment impacts the body in three important ways: loss of proprioception, changes in fluid distribution, and deterioration of the musculoskeletal system.
Direct exposure to the extreme environment of space
The environment of space is lethal without appropriate protection: the greatest threat in the vacuum of space derives from the lack of oxygen and pressure, although temperature and radiation also pose risks.
The vacuum of space

Humans physiology is adapted to living within the atmosphere of Earth, and a certain amount of oxygen is required in the air we breathe. The minimum concentration, or partial pressure, of oxygen that can be tolerated is 16 kPa (0.16 bar). Below this, the astronaut is at risk of becoming unconscious and dying from hypoxia. In the vacuum of space, gas exchange in the lungs continues as normal but results in the removal of all gases, including oxygen, from the bloodstream. After 9 to 12 seconds, the deoxygenated blood reaches the brain, and loss of consciousness results.[5] Death would gradually follow after two minutes of exposure—though the absolute limits are uncertain.
Humans and other animals exposed to vacuum lose consciousness after a few seconds and die of hypoxia within minutes, but the symptoms are not nearly as graphic as the imagery in the public media suggests. Blood and other body fluids do boil when their pressure drops below 6.3 kPa (47 Torr), the vapour pressure of water at body temperature.[6] This condition is called ebullism.[7] The steam may bloat the body to twice its normal size and slow circulation, but tissues are elastic and porous enough to prevent rupture.[8] Ebullism is slowed by the pressure containment of blood vessels, so some blood remains liquid.[5] Swelling and ebullism can be reduced by containment in a flight suit. Space Shuttle astronauts wore a fitted elastic garment called a Crew Altitude Protection Suit (CAPS) which prevented ebullism at pressures as low as 2 kPa (15 Torr).[9] Spacesuits are necessary to prevent ebullism above 19 km.[6] Most spacesuits use 20 kPa (150 Torr) of pure oxygen, just enough to sustain full consciousness. This pressure is high enough to prevent ebullism, but simple evaporation of blood, or of gases dissolved in the blood, can still cause decompression sickness (the bends) and gas embolisms if not managed.
A short-term exposure to vacuum of up to 30 seconds is unlikely to cause permanent physical damage.[10] Animal experiments show that rapid and complete recovery is normal for exposures shorter than 90 seconds, while longer full-body exposures are fatal and resuscitation has never been successful.[11][12] There is only a limited amount of data available from human accidents, but it is consistent with animal data. Limbs may be exposed for much longer if breathing is not impaired.[6] Rapid decompression can be much more dangerous than vacuum exposure itself. Even if the victim does not hold his breath, venting through the windpipe may be too slow to prevent the fatal rupture of the delicate alveoli of the lungs.[6] Eardrums and sinuses may be ruptured by rapid decompression, soft tissues may bruise and seep blood, and the stress of shock accelerates oxygen consumption, leading to hypoxia.[7] Injuries caused by rapid decompression are called barotrauma, and are well known from scuba diving accidents. A pressure drop as small as 100 Torr (13 kPa), which produces no symptoms if it is gradual, may be fatal if it occurs suddenly.[6]
Most of the information known about the way the human body reacts are due to accidental decompression, especially during experimental spaceflight projects. One such case is discussed in a NASA technical report: Rapid (Explosive) Decompression Emergencies in Pressure-Suited Subjects:[13][page needed][14]
- "At NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center (now renamed Johnson Space Center) we had a test subject accidentally exposed to a near vacuum (less than 1 psi) [7 kPa] in an incident involving a leaking space suit in a vacuum chamber back in '65. He remained conscious for about 14 seconds, which is about the time it takes for O2 deprived blood to go from the lungs to the brain. The suit probably did not reach a hard vacuum, and we began repressurizing the chamber within 15 seconds. The subject regained consciousness at around 15,000 feet [4600 m] equivalent altitude. The subject later reported that he could feel and hear the air leaking out, and his last conscious memory was of the water on his tongue beginning to boil."
There has been one recorded incident of death from decompression in spaceflight, the Soyuz 11 decompression accident in 1971, which resulted in the death of the three cosmonauts on board.
Extreme variations in temperature
In a vacuum, there is no medium for removing heat from the body by conduction or convection. Loss of heat is by radiation from the 310 K temperature of a person to the 3 K of outer space. This is a slow process, especially in a clothed person, so there is no danger of immediately freezing.[15] Rapid evaporative cooling of skin moisture in a vacuum may create frost, particularly in the mouth, but this is not a significant hazard.
Exposure to the intense radiation of direct, unfiltered sunlight would lead to local heating, though that would likely be well distributed by the body's conductivity and blood circulation. Other solar radiation, particularly ultraviolet rays, however, may cause severe sunburn in a few seconds.
Increased radiation levels
Without the protection of Earth's atmosphere and magnetosphere astronauts are exposed to high levels of radiation. A year in low-earth orbit results in a dose of radiation 10 times that of the annual dose on earth.[citation needed] High levels of radiation damage lymphocytes, cells heavily involved in maintaining the immune system; this damage contributes to the lowered immunity experienced by astronauts. Radiation has also recently been linked to a higher incidence of cataracts in astronauts. Outside of the protection of low-earth orbit, galactic cosmic rays present further challenges to human spaceflight,[16] as the health threat from cosmic rays significantly increases the chances of cancer over a decade or more of exposure.[17] Solar flare events (though rare) can give a fatal radiation dose in minutes. It is thought that protective shielding and protective drugs may ultimately lower the risks to an acceptable level.[18]
Crew living on the International Space Station (ISS) are partially protected from the space environment by Earth's magnetic field, as the magnetosphere deflects solar wind around the earth and the ISS. Nevertheless, solar flares are powerful enough to warp and penetrate the magnetic defences, and so are still a hazard to the crew. The crew of Expedition 10 took shelter as a precaution in 2005 in a more heavily shielded part of the station designed for this purpose.[19][20] However, beyond the limited protection of Earth's magnetosphere, interplanetary manned missions are much more vulnerable. Lawrence Townsend of the University of Tennessee and others have studied the most powerful solar flare ever recorded. Radiation doses astronauts would receive from a flare of this magnitude could cause acute radiation sickness and possibly even death.[21]
There is scientific concern that extended spaceflight might slow down the body’s ability to protect itself against diseases.[22] Radiation can penetrate living tissue and cause both short and long-term damage to the bone marrow stem cells which create the blood and immune systems. In particular, it causes 'chromosomal aberrations' in lymphocytes. As these cells are central to the immune system, any damage weakens the immune system, which means that in addition to increased vulnerability to new exposures, viruses already present in the body—which would normally be suppressed—become active. In space, T-cells (a form of lymphocyte) are less able to reproduce properly, and the T-cells that do reproduce are less able to fight off infection. Over time immunodeficiency results in the rapid spread of infection among crew members, especially in the confined areas of space flight systems.
Radiation has also been linked to a higher incidence of cataracts in astronauts. Soviet cosmonaut Valentin Lebedev, who spent 221 days in orbit in 1982 (an absolute record for stay in Earth’s orbit), lost his eyesight to progressive cataracts. Lebedev stated: “I suffered from a lot of radiation in space. It was all concealed back then, during the Soviet years, but now I can say that I caused damage to my health because of that flight.”[23]
The effects of weightlessness

Following the advent of space stations that can be inhabited for long periods of time, exposure to weightlessness has been demonstrated to have some deleterious effects on human health. Humans are well-adapted to the physical conditions at the surface of the earth, and so in response to weightlessness, various physiological systems begin to change, and in some cases, atrophy. Though these changes are usually temporary, some do have a long-term impact on human health.
Short-term exposure to microgravity causes space adaptation syndrome, a self-limiting nausea caused by derangement of the vestibular system. Long-term exposure causes multiple health problems, one of the most significant being loss of bone and muscle mass. Over time these deconditioning effects can impair astronauts’ performance, increase their risk of injury, reduce their aerobic capacity, and slow down their cardiovascular system.[24] As the human body consists mostly of fluids, gravity tends to force them into the lower half of the body, and our bodies have many systems to balance this situation. When released from the pull of gravity, these systems continue to work, causing a general redistribution of fluids into the upper half of the body. This is the cause of the round-faced 'puffiness' seen in astronauts.[18] Redistributing fluids around the body itself causes balance disorders, distorted vision, and a loss of taste and smell.
Motion sickness

The most common problem experienced by humans in the initial hours of weightlessness is known as space adaptation syndrome or SAS, commonly referred to as space sickness. It is related to motion sickness, and arises as the vestibular system adapts to weightlessness.[25] Symptoms of SAS include nausea and vomiting, vertigo, headaches, lethargy, and overall malaise.[1] The first case of SAS was reported by cosmonaut Gherman Titov in 1961. Since then, roughly 45% of all people who have flown in space have suffered from this condition. The duration of space sickness varies, but rarely has it lasted for more than 72 hours, after which the body adjusts to the new environment.
On Earth, our bodies react automatically to gravity, maintaining both posture and locomotion in a downward pulling world. In microgravity environments, these constant signals are absent: the otolith organs in the middle ear are sensitive to linear acceleration and no longer perceive a downwards bias; muscles are no longer required to contract to maintain posture, and pressure receptors in the feet and ankles no longer signal the direction of "down". These changes can immediately result in visual-orientation illusions where the astronaut feels he has flipped 180 degrees. Over half of astronauts also experience symptoms of motion sickness for the first three days of travel due to the conflict between what the body expects and what the body actually perceives.[26] Over time however the brain adapts and although these illusions can still occur, most astronauts begin to see "down" as where the feet are. People returning to Earth after extended weightless periods have to readjust to the force of gravity and may have problems standing up, focusing their gaze, walking and turning. This is just an initial problem, as they recover these abilities quickly.[vague]
NASA jokingly measures SAS using the "Garn scale", named for United States Senator Jake Garn, whose sickness during STS-51-D was the worst on record. Accordingly, one "Garn" is equivalent to the most severe possible case of space sickness.[27] By studying how changes can affect balance in the human body—involving the senses, the brain, the inner ear, and blood pressure—NASA hopes to develop treatments that can be used on Earth and in space to correct balance disorders. Until then, astronauts rely on medication, such as midodrine and dimenhydrinate anti-nausea patches, as required (such as when space suits are worn, because vomiting into a space suit could be fatal).
Loss of bone and muscle mass

A major effect of long-term weightlessness involves the loss of bone and muscle mass. Without the effects of gravity, skeletal muscle is no longer required to maintain posture and the muscle groups used in moving around in a weightless environment differ from those required in terrestrial locomotion.[citation needed] In a weightless environment, astronauts put almost no weight on the back muscles or leg muscles used for standing up. Those muscles then start to weaken and eventually get smaller. Consequently some muscles atrophy rapidly, and astronauts can lose up to 25% of their muscle mass on long flights.[citation needed] The types of muscle fibre prominent in muscles also change. Slow twitch endurance fibres used to maintain posture are replaced by fast twitch rapidly contracting fibres that are insufficient for any heavy labour. Advances in research on exercise, hormone supplements and medication may help maintain muscle and body mass.
Bone metabolism also changes. Normally, bone is laid down in the direction of mechanical stress, however in a microgravity environment there is very little mechanical stress. This results in a loss of bone tissue approximately 1.5% per month especially from the lower vertebrae, hip and femur.[28] Elevated blood calcium levels from the lost bone result in dangerous calcification of soft tissues and potential kidney stone formation.[28] It is still unknown whether bone recovers completely. Unlike people with osteoporosis, astronauts eventually regain their bone density.[citation needed] After a 3-4 month trip into space, it takes about 2–3 years to regain lost bone density.[citation needed] New techniques are being developed to help astronauts recover faster. Research on diet, exercise and medication may hold the potential to aid the process of growing new bone.
To prevent some of these adverse physiological effects, the ISS is equipped with two treadmills (including the COLBERT), and the aRED (advanced Resistive Exercise Device), which enable various weight-lifting exercises which add muscle but do nothing for bone density,[29] and a stationary bicycle; each astronaut spends at least two hours per day exercising on the equipment.[30][31] Astronauts use bungee cords to strap themselves to the treadmill.[32][33] Astronauts subject to long periods of weightlessness wear pants with elastic bands attached between waistband and cuffs to compress the leg bones and reduce osteopenia.[2]

Fluid redistribution
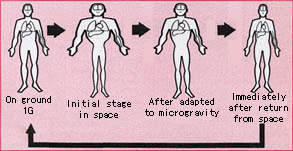
The second effect of weightlessness takes place in human fluids. The body is made up of 60% water, much of it intra-vascular and inter-cellular. Within a few moments of entering a microgravity environment, fluid is immediately re-distributed to the upper body resulting in bulging neck veins, puffy face and sinus and nasal congestion which can last throughout the duration of the trip and is very much like the symptoms of the common cold. In space the autonomic reactions of the body to maintain blood pressure are not required and fluid is distributed more widely around the whole body. This results in a decrease in plasma (water in the blood stream) volume of around 20%. These fluid shifts initiate a cascade of adaptive systemic effects that can be dangerous upon return to earth. Orthostatic intolerance results in astronauts returning to Earth after extended space missions being unable to stand unassisted for more than 10 minutes at a time without fainting. This is due in part to changes in the autonomic regulation of blood pressure and the loss of plasma volume. Although this effect becomes worse the longer the time spent in space, as yet all individuals have returned to normal within at most a few weeks of landing.[citation needed]
In space, astronauts lose fluid volume—including up to 22% of their blood volume. Because it has less blood to pump, the heart will atrophy. A weakened heart results in low blood pressure and can produce a problem with “orthostatic tolerance,” or the body’s ability to send enough oxygen to the brain without the astronaut's fainting or becoming dizzy. "Under the effects of the earth's gravity, blood and other body fluids are pulled towards the lower body. When gravity is taken away or reduced during space exploration, the blood tends to collect in the upper body instead, resulting in facial edema and other unwelcome side effects. Upon return to earth, the blood begins to pool in the lower extremities again, resulting in orthostatic hypotension."[34]
Disruption of vision
Because weightlessness increases the amount of fluid in the upper part of the body, astronauts experience increased intracranial pressure. This appears to increase pressure on the backs of the eyeballs, affecting their shape and slightly crushing the optic nerve.[35][36][37][38][39] This effect was noticed in 2012 in a study using MRI scans of astronauts who had returned to Earth following at least one month in space.[40] Such eyesight problems may be a major concern for future deep space flight missions, including a manned mission to the planet Mars.[35][36][37][38]
Disruption of taste
One effect of weightlessness on humans is that some astronauts report a change in their sense of taste when in space.[41][dead link] Some astronauts find that their food is bland, others find that their favorite foods no longer taste as good; some astronauts enjoy eating certain foods that they would not normally eat, and some experience no change whatsoever. The reason is uncertain, and several theories have been suggested, including congestion, food degradation, and psychological changes such as tedium. Astronauts often choose strong-tasting food to combat the loss of taste.
Other physical effects
After two months, calluses on the bottoms of feet molt and fall off from lack of use, leaving soft new skin. Tops of feet become, by contrast, raw and painfully sensitive.[42] Various other physical discomforts such as back and abdominal pain are commonly experienced with no clear cause. These may be part of the asthenization syndrome reported by cosmonauts living in space over an extended period of time, but regarded as anecdotal by astronauts.[43] Fatigue, listlessness, and psychosomatic worries are also part of the syndrome. The data is inconclusive; however the syndrome does appear to exist as a manifestation of all the internal and external stress crews in space must face.[citation needed]
Psychological effects of spaceflight

The psychological effects of living in space have not been clearly analyzed but analogies on Earth do exist, such as Arctic research stations and submarines. The enormous stress on the crew, coupled with the body adapting to other environmental changes, can result in anxiety, insomnia and depression. According to current data[citation needed], however, astronauts and cosmonauts seem extremely resilient to psychological stresses. Interpersonal issues can have an enormous influence on a human's well-being and yet little research has been undertaken to examine the relevant crew-selection procedures. The Mars Arctic Research Station and Mars Desert Research Station have examined the influence of different crew selection procedures for living in a completely isolated environment and may provide important data for planning future spaceflights.[citation needed]
There has been considerable evidence that psychosocial stressors are among the most important impediments to optimal crew morale and performance.[44] Cosmonaut Valery Ryumin, twice Hero of the Soviet Union, wrote in his journal during a particularly difficult period on board the Salyut 6 space station: “All the conditions necessary for murder are met if you shut two men in a cabin measuring 18 feet by 20 and leave them together for two months.”
NASA's interest in psychological stress caused by space travel, initially studied when their manned missions began, was rekindled when astronauts joined cosmonauts on the Russian space station Mir. Common sources of stress in early American missions included maintaining high performance while under public scrutiny, as well as isolation from peers and family. On the ISS, the latter is still often a cause of stress, such as when NASA Astronaut Daniel Tani's mother died in a car accident, and when Michael Fincke was forced to miss the birth of his second child.
The amount and quality of sleep experienced in space is poor due to highly variable light and dark cycles on flight decks and poor illumination during daytime hours in the space craft. Even the habit of looking out of the window before retiring can send the wrong messages to the brain, resulting in poor sleep patterns. These disturbances in circadian rhythm have profound effects on the neurobehavioural responses of crew and aggravate the psychological stresses they already experience (see Fatigue and sleep loss during spaceflight for more information). Sleep is disturbed on the ISS regularly due to mission demands, such as the scheduling of incoming or departing space vehicles. Sound levels in the station are unavoidably high because the atmosphere is unable to thermosyphon; fans are required at all times to allow processing of the atmosphere, which would stagnate in the freefall (zero-g) environment. Fifty percent of space shuttle astronauts take sleeping pills and still get two hours or less of sleep. NASA is researching two areas which may provide the keys to a better night’s sleep, as improved sleep decreases fatigue and increases daytime productivity. A variety of methods for combating this phenomenon are constantly under discussion.
A study of the longest spaceflight concluded that the first three weeks represent a critical period where attention is adversely affected because of the demand to adjust to the extreme change of environment.[45] While Skylab's three crews remained in space 1, 2, and 3 months respectively, long-term crews on Salyut 6, Salyut 7, and the ISS remain about 5–6 months, while MIR expeditions often lasted longer. The ISS working environment includes further stress caused by living and working in cramped conditions with people from very different cultures who speak different languages. First generation space stations had crews who spoke a single language, while 2nd and 3rd generation stations have a crew from many cultures who speak many languages. The ISS is unique because visitors are not classed automatically into 'host' or 'guest' categories as with previous stations and spacecraft, and may not suffer from feelings of isolation in the same way. Crew members with a military pilot background and those with an academic science background or teachers and politicians may have problems understanding each other’s jargon and worldview.
During long missions, astronauts are isolated and confined into small spaces. Depression, cabin fever and other psychological problems may impact the crew's safety and mission success.[citation needed] Astronauts may not be able to quickly return to Earth or receive medical supplies, equipment or personnel if a medical emergency occurs. The astronauts may have to rely for long periods on their limited existing resources and medical advice from the ground.
On December 31, 2012, a NASA-supported study suggested that traveling in outer space may harm the brain of astronauts and accelerate the onset of Alzheimer's disease.[46][47][48]
Future prospects
The sum of human experience has resulted in the accumulation of 58 solar years in space and a much better understanding of how the human body adapts. In the future, industrialisation of space and exploration of inner and outer planets will require humans to endure longer and longer periods in space. The majority of current data comes from missions of short duration and so some of the long-term physiological effects of living in space are still unknown. A round trip to Mars with current technology is estimated to involve at least 18 months in transit alone. Knowing how the human body reacts to such time periods in space is a vital part of the preparation for such journeys. On-board medical facilities need to be adequate for coping with any type of trauma or emergency as well as contain a huge variety of diagnostic and medical instruments in order to keep a crew healthy over a long period of time, as these will be the only facilities available on board a spacecraft for coping not only with trauma, but also with the adaptive responses of the human body in space.
At the moment only rigorously tested humans have experienced the conditions of space. If off-world colonization someday begins, many types of people will be exposed to these dangers, and the effects on the elderly and on the very young are completely unknown. Factors such as nutritional requirements and physical environments which have so far not been examined will become important. Overall, there is little data on the manifold effects of living in space, and this makes attempts toward mitigating the risks during a lengthy space habitation difficult. Test beds such as the ISS are presently being utilized to research some of these risks.
The environment of space is still largely unknown, and there will likely be as-yet-unknown hazards. Meanwhile, future technologies such as artificial gravity and more complex bioregenerative life support systems may someday be capable of mitigating some risks.
See also
References
- ^ a b Kanas, Nick; Manzey, Dietrich (2008), "Basic Issues of Human Adaptation to Space Flight", Space Psychology and Psychiatry, Space Technology Library, 22: 15–48, doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6770-9_2
- ^ a b "Health and Fitness". Space Future. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
- ^ Toyohiro Akiyama (April 14, 1993). "The Pleasure of Spaceflight". Journal of Space Technology and Science. 9 (1): 21–23. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
- ^ "Breathing Easy on the Space Station". NASA. Retrieved 2012-04-26.
- ^ a b Landis, Geoffrey A. (7 August 2007). "Human Exposure to Vacuum". www.geoffreylandis.com. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ^ a b c d e Harding, Richard M. (1989). Survival in Space: Medical Problems of Manned Spaceflight. London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-00253-2.
- ^ a b Czarnik, Tamarack R. (1999). "Ebullism at 1 Million Feet: Surviving Rapid/Explosive Decompressionn". Retrieved 2009-20-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Billings, Charles E. (1973). "Chapter 1) Barometric Pressure". In Parker, James F.; West, Vita R. (ed.). Bioastronautics Data Book (Second ed.). NASA. p. 5. NASA SP-3006. Retrieved 2012-09-23.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) 942 pages. Template:Pdf - ^ Webb, P. (1968). "The Space Activity Suit: An Elastic Leotard for Extravehicular Activity". Aerospace Medicine. 39 (4): 376–383. PMID 4872696.
- ^ Author/s not stated (3 June 1997). "Ask an Astrophysicist: Human Body in a Vacuum". NASA(Goddard Space Flight Centre). Retrieved 2012-04-25.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "Some Cardiovascular Responses in Anesthetized Dogs During Repeated Decompressions to a Near-Vacuum". Aerospace Medicine. 37: 1148–1152. 1966. PMID 5297100.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Greene, Nick (undated). "What Happens To The Human Body In A Vacuum?". About.com. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Roth (M.D.), Emanuel M. (November 1, 1968). "Rapid (Explosive) Decompression Emergencies in Pressure-suited Subjects". The Lovelace Foundation (for NASA). NASA-CR-1223. Retrieved 2012-09-23. 131 pages. Template:Pdf
- ^ "Two MSC Employees Commended For Rescue in Chamber Emergency" (PDF). Roundup. Vol. Vol.6 No.6. Hoston, Texas: NASA Manned Spacecraft Center. 6 January 1967. p. 3. Retrieved 2012-09-23.
{{cite news}}:|volume=has extra text (help) Template:Pdf - ^ "Ask a scientist. Why is space cold?". Argonne National Laboratory, Division of Educational Programs. Retrieved 2008-11-27.
- ^ Space Radiation Hazards and the Vision for Space Exploration. NAP. 2006. ISBN 0-309-10264-2.
- ^ "The Right Stuff for Super Spaceships". NASA. 16 September 2002. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
- ^ a b Jay Buckey (23 February 2006). Space Physiology. Oxford University Press USA. ISBN 978-0-19-513725-5.
- ^ Ker Than (23 February 2006). "Solar Flare Hits Earth and Mars". Space.com.
- ^ "A new kind of solar storm". NASA. 10 June 2005.
- ^ Stephen Battersby (21 March 2005). "Superflares could kill unprotected astronauts". New Scientist.
- ^ Gueguinou, N.; Huin-Schohn, C.; Bascove, M.; Bueb, J.-L.; Tschirhart, E.; Legrand-Frossi, C.; Frippiat, J.-P. (2009). "Could spaceflight-associated immune system weakening preclude the expansion of human presence beyond Earth's orbit". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 86 (5): 1027–1038. doi:10.1189/jlb.0309167. PMID 19690292.
- ^ "Soviet cosmonauts burnt their eyes in space for USSR's glory". Pravda.Ru. 17 December 2008. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ^ "Exercise Physiology and Countermeasures Project (ExPC): Keeping Astronauts Healthy in Reduced Gravity". NASA. Retrieved 2012-05-11.
- ^ "Why Do Astronauts Suffer From Space Sickness?". ScienceDaily. 2008-05-23.
- ^ Bloomberg, Jacob J. and Kozlovskaya, Inessa B. (1996–97). "The Effects of Long-Duration Space Flight on Eye, Head, and Trunk Coordination During Locomotion (9307191)". NASA. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Robert E. Stevenson, interviewed by Carol Butler (13 May 1999). "Oral History 2 Transcript" (PDF). Johnson Space Center Oral History Project. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
Jake Garn was sick, was pretty sick. I don't know whether we should tell stories like that. But anyway, Jake Garn, he has made a mark in the Astronaut Corps because he represents the maximum level of space sickness that anyone can ever attain, and so the mark of being totally sick and totally incompetent is one Garn. Most guys will get maybe to a tenth Garn, if that high. And within the Astronaut Corps, he forever will be remembered by that.
- ^ a b "Space Bones". NASA. October 1, 2001. Retrieved 2012-05-12.
- ^ Schneider SM, Amonette WE, Blazine K, Bentley J, Lee SM, Loehr JA, Moore AD Jr, Rapley M, Mulder ER, Smith SM. (November 2003). "Training with the International Space Station interim resistive exercise device". Medical Science Sports Exercise. 35 (11): 1935–45. doi:10.1249/01.MSS.0000093611.88198.08. PMID 14600562.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Daily life". ESA. 19 July 2004. Retrieved 28 October 2009.
- ^ Cheryl L. Mansfield (7 November 2008). "Station Prepares for Expanding Crew". NASA. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ "Bungee Cords Keep Astronauts Grounded While Running". NASA. 16 June 2009. Retrieved 23 August 2009.
- ^ Amiko Kauderer (19 August 2009). "Do Tread on Me". NASA. Retrieved Augist 23, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "When Space Makes You Dizzy". NASA. 2002. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ^ a b Mader, T. H.; et al. (2011). Oph "Optic Disc Edema, Globe Flattening, Choroidal Folds, and Hyperopic Shifts Observed in Astronauts after Long-duration Space Flight". Ophthalmology (journal). 118 (10): 2058–2069. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.06.021.
{{cite journal}}: Check|url=value (help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ a b Puiu, Tibi (November 9, 2011). "Astronauts' vision severely affected during long space missions". zmescience.com. Retrieved February 9, 2012.
- ^ a b "Male Astronauts Return With Eye Problems (video)". CNN News. 9 February 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ^ a b Space Staff (13 March 2012). "Spaceflight Bad for Astronauts' Vision, Study Suggests". Space.com. Retrieved 14 March 2012.
- ^ Kramer, Larry A.; et al. (13 March 2012). "Orbital and Intracranial Effects of Microgravity: Findings at 3-T MR Imaging". Radiology (journal). doi:10.1148/radiol.12111986. Retrieved 14 March 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help) - ^ "Eye Problems Common in Astronauts". Discovery News. 13 March 2012. Retrieved 2012-04-25.
- ^ "NASAeplores 5-8: A matter of taste", NASA, http://www.nasaexplores.com/show2_5_8a.php?id=03-038&gl=58
- ^ Pettit, Don (2012-05-04). "Toe Koozies". Air & Space/Smithsonian. Retrieved May 8, 2012.
- ^ Nick Kanas, MD, Vyacheslav Salnitskiy, PhD, Vadim Gushin, MD, Daniel S. Weiss, PhD, Ellen M. Grund, MS, Christopher Flynn, MD, Olga Kozerenko, MD, Alexander Sled, MS and Charles R. Marmar, MD (November 1, 2001). "Asthenia—Does It Exist in Space?". Psychosomatic Medicine. 63 (6): 874–80. PMID 11719624.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Peter Suedfeld1; Kasia E. Wilk; Lindi Cassel. Flying with Strangers: Postmission Reflections of Multinational Space Crews.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Dietrich Manzey, Bernd Lorenz & Valeri Poljakov (1998). "Mental performance in extreme environments: results from a performance monitoring study during a 438-day spaceflight". Ergonomics. 41 (4): 537–559. doi:10.1080/001401398186991. Retrieved 2012-05-10.
- ^ Cherry, Jonathan D.; Frost, Jeffrey L.; Lemere, Cynthia A.; Williams, Jacqueline P.; Olschowka, John A.; O'Banion, M. Kerry. "Galactic Cosmic Radiation Leads to Cognitive Impairment and Increased Aβ Plaque Accumulation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease". PLOS ONE. 7 (12): e53275. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053275. Retrieved January 7, 2013.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Study Shows that Space Travel is Harmful to the Brain and Could Accelerate Onset of Alzheimer's". SpaceRef. January 1, 2013. Retrieved January 7, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ Cowing, Keith (January 3, 2013). "Important Research Results NASA Is Not Talking About (Update)". NASA Watch. Retrieved January 7, 2013.
Further reading
- Nasa Report: Space Travel 'Inherently Hazardous' to Human Health. Leonard David. 2001
- Space Physiology and Medicine. Third edition. A. E. Nicogossian, C. L. Huntoon and S. L. Pool. Lea & Febiger, 1993.
- L.-F. Zhang. Vascular adaptation to microgravity: What have we learned?. Journal of Applied Physiology. 91(6) (pp 2415–2430), 2001.
- G. Carmeliet, Vico. L, Bouillon R. Critical Reviews in Eukaryotic Gene Expression. Vol 11(1-3) (pp 131–144), 2001.
- F.A. Cucinotta et al. Space radiation cancer risks and uncertainties for Mars missions. Radiation Research. Vol 156:5 II;pp 682–688, 2001.
- F.A. Cucinotta et al. Space radiation and cataracts in astronauts. Radiation Research. Vol 156(5 I) (pp 460–466), 2001.
- Styf, Jorma R. MD; Hutchinson, Karen BS; Carlsson, Sven G. PhD, and; Hargens, Alan R. Ph.D. Depression, Mood State, and Back Pain During
- Altitude Decompression Sickness Susceptibility, MacPherson, G; Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, Volume 78, Number 6, June 2007, pp. 630–631(2)
- Decision Analysis in Aerospace Medicine: Costs and Benefits of a Hyperbaric Facility in Space, John-Baptiste, A; Cook, T; Straus, S; Naglie, G; et al. Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, Volume 77, Number 4, April 2006, pp. 434–443(10)
- Incidence of Adverse Reactions from 23,000 Exposures to Simulated Terrestrial Altitudes up to 8900 m, DeGroot, D; Devine JA; Fulco CS; Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, Volume 74, Number 9, September 2003, pp. 994–997(4)
