Chromosome 6
| Chromosome 6 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 6 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 6 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 170,805,979 bp[1] |
| No. of genes | 3,000[2] 2,516[3] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | ? |
| HGNC | ? |
| UniProt | ? |
| NCBI | ? |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 6 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 6 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 6 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 6 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000006 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000668 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the Major Histocompatibility Complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of genetic research. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies. In January 2017, two estimates differed by 16%, with one estimate giving 3,000[2] genes, and the other estimate giving 2,516[3] genes.
History
In 2003, the entirety of chromosome 6 was manually annotated for proteins, resulting in the identification of 1,557 genes, and 633 pseudogenes.[4]
Genes
The human leukocyte antigen lies on chromosome 6 (exception: the gene for β2-microglobulin which is located on chromosome 15), and encodes cell-surface antigen-presenting proteins among other functions. The following are some of the genes and their corresponding Cytogenetic location on chromosome 6:
- C6orf10: encoding protein Uncharacterized protein C6orf10
- C6orf165: encoding protein DUF3508
- RPL10A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L10a
q-arm
- AIM1: encoding protein Absent in melanoma 1 protein (6q21)
- AIG1: encoding protein Androgen-induced protein 1 (6q24.2)
- BCKDHB: branched-chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide (maple syrup urine disease) (6q14.1)
- MYO6: myosin VI (6q14.1)
- CNR1: cannabinoid 1 receptor (6q14-q15)[5]
- HACE1: HECT domain and Ankyrin repeat containing, E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (6q21)
- TAAR1: trace amine associated receptor 1 (6q23.1)
- TAAR2: trace amine associated receptor 2 (6q24)
- EYA4: eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila)(6q23.2)
- IFNGR: interferon-γ receptor gene (6q23-q24)
- OPRM1: μ-opioid receptors (6q24-q25)
- IGF2R: insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor (6q25.3)
- PLG: plasminogen (6q26)
- PARK2: Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, juvenile) 2, parkin (6q26)
- T: T brachyury transcription factor (more commonly known as the T gene) linked to Hepatocellular carcinoma and Chordoma (6q27)[6]
- ESR1: Estrogen receptor 1 (6q25)
p-arm
- APOM: encoding protein Apolipoprotein M (6p21.33)
- MUT: methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase (6p12.3)
- VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor A (angiogenic growth factor) (6p21.1)
- PKHD1: polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (6p21.2-p12)
- COL11A2: collagen, type XI, alpha 2(6p21.3)
- CYP21A2: cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 (6p21.33)
- HFE: hemochromatosis (6p21.3)
- HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C: major histocompatibility complex (MHC), class I, A, B, and C loci. (6p21.3)
- HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1 form HLA-DQ heterodimer MHC class II, DQ: Celiac1, IDDM (6p21.3)
- HLA-DRA, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB3, HLA-DRB4, HLA-DRB5 forms HLA-DR, heterodimer MHC class II, DR (6p21.3)
- HLA-DPA1 and HLA-DPB1 forms HLA-DR, MHC class II, DP (6p21.3)
- HLA-Cw*06:02: gene variation related to psoriasis (6p21.3)
- TNXB: tenascin XB (6p21.3)
- DSP: Desmoplakin gene linked to cardiomyopathy (6p24.3)
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (June 2008) |
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are some of those related to genes on chromosome 6:
- ankylosing spondylitis, HLA-B
- collagenopathy, types II and XI
- Coeliac disease HLA-DQA1 & DQB1
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classical, hypermobility, and Tenascin-X types
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- hemochromatosis
- Hemochromatosis type 1
- 21-hydroxylase deficiency
- maple syrup urine disease
- methylmalonic acidemia
- Autosomal nonsyndromic deafness
- otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia
- Parkinson disease
- polycystic kidney disease
- porphyria
- porphyria cutanea tarda
- Rheumatoid arthritis, HLA-DR
- Stickler syndrome, COL11A2
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Diabetes mellitus type 1, HLA-DR, DQA1 & DQB1
- X-linked sideroblastic anemia
- Epilepsy
- Guillain Barre Syndrome
- Chordoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
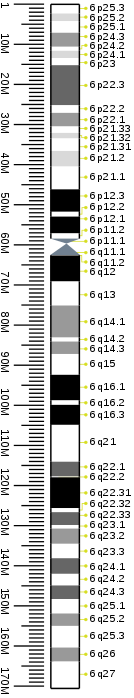
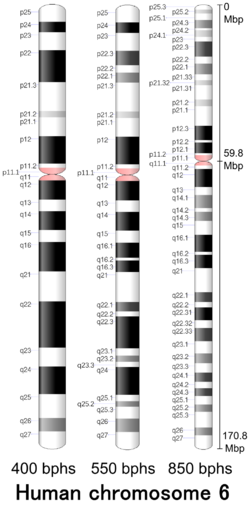
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[13] | Band[14] | ISCN start[15] |
ISCN stop[15] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[16] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | p | 25.3 | 0 | 118 | 1 | 2,300,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 25.2 | 118 | 207 | 2,300,001 | 4,200,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 25.1 | 207 | 355 | 4,200,001 | 7,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 24.3 | 355 | 548 | 7,100,001 | 10,600,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | p | 24.2 | 548 | 592 | 10,600,001 | 11,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 24.1 | 592 | 740 | 11,600,001 | 13,400,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 23 | 740 | 844 | 13,400,001 | 15,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 22.3 | 844 | 1185 | 15,200,001 | 25,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | p | 22.2 | 1185 | 1348 | 25,200,001 | 27,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 22.1 | 1348 | 1585 | 27,100,001 | 30,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | p | 21.33 | 1585 | 1718 | 30,500,001 | 32,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 21.32 | 1718 | 1836 | 32,100,001 | 33,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 21.31 | 1836 | 2162 | 33,500,001 | 36,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 21.2 | 2162 | 2310 | 36,600,001 | 40,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 6 | p | 21.1 | 2310 | 2755 | 40,500,001 | 46,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 12.3 | 2755 | 3080 | 46,200,001 | 51,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | p | 12.2 | 3080 | 3140 | 51,800,001 | 53,000,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 12.1 | 3140 | 3377 | 5,300,0001 | 57,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | p | 11.2 | 3377 | 3421 | 57,200,001 | 58,500,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | p | 11.1 | 3421 | 3554 | 58,500,001 | 59,800,000 | acen | |
| 6 | q | 11.1 | 3554 | 3658 | 59,800,001 | 62,600,000 | acen | |
| 6 | q | 11.2 | 3658 | 3732 | 62,600,001 | 62,700,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 12 | 3732 | 4147 | 62,700,001 | 69,200,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 13 | 4147 | 4324 | 69,200,001 | 75,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 14.1 | 4324 | 4621 | 75,200,001 | 83,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 14.2 | 4621 | 4709 | 83,200,001 | 84,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 14.3 | 4709 | 4917 | 84,200,001 | 87,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 15 | 4917 | 5228 | 87,300,001 | 92,500,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 16.1 | 5228 | 5613 | 92,500,001 | 98,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 16.2 | 5613 | 5687 | 98,900,001 | 100,000,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 16.3 | 5687 | 5983 | 10,000,0001 | 105,000,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 21 | 5983 | 6531 | 10,500,0001 | 114,200,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.1 | 6531 | 6753 | 114,200,001 | 117,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 22.2 | 6753 | 6872 | 117,900,001 | 118,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.31 | 6872 | 7168 | 118,100,001 | 125,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 6 | q | 22.32 | 7168 | 7345 | 125,800,001 | 126,800,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 22.33 | 7345 | 7642 | 126,800,001 | 130,000,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 23.1 | 7642 | 7923 | 13,000,0001 | 130,900,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 23.2 | 7923 | 8145 | 130,900,001 | 134,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 23.3 | 8145 | 8352 | 134,700,001 | 138,300,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 24.1 | 8352 | 8560 | 138,300,001 | 142,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 24.2 | 8560 | 8708 | 142,200,001 | 145,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 24.3 | 8708 | 8886 | 145,100,001 | 148,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 6 | q | 25.1 | 8886 | 9078 | 148,500,001 | 152,100,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 25.2 | 9078 | 9241 | 152,100,001 | 155,200,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 25.3 | 9241 | 9596 | 155,200,001 | 160,600,000 | gneg | |
| 6 | q | 26 | 9596 | 9774 | 160,600,001 | 164,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 6 | q | 27 | 9774 | 10100 | 164,100,001 | 170,805,979 | gneg |
References
- ^ "Human Genome Assembly GRCh38.p10 - Genome Reference Consortium". National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2017-01-06. Retrieved 2017-03-04.
- ^ a b "Homo sapiens (human) Chromosome 6". NCBI Map Viewer. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved January 20, 2017.
- ^ a b "Homo sapiens: Chromosome summary: Chromosome 6:1-170805979". Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Vega Genome Browser 58. Retrieved January 20, 2017.
- ^ Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, Edwards CA, Ashurst JL, Wilming L, Jones MC, Horton R, Hunt SE, Scott CE, Gilbert JG, Clamp ME, Bethel G, Milne S, Ainscough R, Almeida JP, Ambrose KD, Andrews TD, Ashwell RI, Babbage AK, Bagguley CL, Bailey J, Banerjee R, Barker DJ, Barlow KF, Bates K, Beare DM, Beasley H, Beasley O, Bird CP, Blakey S, Bray-Allen S, Brook J, Brown AJ, Brown JY, Burford DC, Burrill W, Burton J, Carder C, Carter NP, Chapman JC, Clark SY, Clark G, Clee CM, Clegg S, Cobley V, Collier RE, Collins JE, Colman LK, Corby NR, Coville GJ, Culley KM, Dhami P, Davies J, Dunn M, Earthrowl ME, Ellington AE, Evans KA, Faulkner L, Francis MD, Frankish A, Frankland J, French L, Garner P, Garnett J, Ghori MJ, Gilby LM, Gillson CJ, Glithero RJ, Grafham DV, Grant M, Gribble S, Griffiths C, Griffiths M, Hall R, Halls KS, Hammond S, Harley JL, Hart EA, Heath PD, Heathcott R, Holmes SJ, Howden PJ, Howe KL, Howell GR, Huckle E, Humphray SJ, Humphries MD, Hunt AR, Johnson CM, Joy AA, Kay M, Keenan SJ, Kimberley AM, King A, Laird GK, Langford C, Lawlor S, Leongamornlert DA, Leversha M, Lloyd CR, Lloyd DM, Loveland JE, Lovell J, Martin S, Mashreghi-Mohammadi M, Maslen GL, Matthews L, McCann OT, McLaren SJ, McLay K, McMurray A, Moore MJ, Mullikin JC, Niblett D, Nickerson T, Novik KL, Oliver K, Overton-Larty EK, Parker A, Patel R, Pearce AV, Peck AI, Phillimore B, Phillips S, Plumb RW, Porter KM, Ramsey Y, Ranby SA, Rice CM, Ross MT, Searle SM, Sehra HK, Sheridan E, Skuce CD, Smith S, Smith M, Spraggon L, Squares SL, Steward CA, Sycamore N, Tamlyn-Hall G, Tester J, Theaker AJ, Thomas DW, Thorpe A, Tracey A, Tromans A, Tubby B, Wall M, Wallis JM, West AP, White SS, Whitehead SL, Whittaker H, Wild A, Willey DJ, Wilmer TE, Wood JM, Wray PW, Wyatt JC, Young L, Younger RM, Bentley DR, Coulson A, Durbin R, Hubbard T, Sulston JE, Dunham I, Rogers J, Beck S; Palmer; Sims; Edwards; Ashurst; Wilming; Jones; Horton; Hunt; Scott; Gilbert; Clamp; Bethel; Milne; Ainscough; Almeida; Ambrose; Andrews; Ashwell; Babbage; Bagguley; Bailey; Banerjee; Barker; Barlow; Bates; Beare; Beasley; Beasley; et al. (October 2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Matsuda LA, Lolait SJ, Brownstein MJ, Young AC, Bonner TI; Lolait; Brownstein; Young; Bonner (August 1990). "Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA". Nature. 346 (6284): 561–4. Bibcode:1990Natur.346..561M. doi:10.1038/346561a0. PMID 2165569.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "T brachyury transcription factor". T - T brachyury transcription factor - Genetics Home Reference.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- ^ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images" (PDF). In Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE), 2012 International Joint Conference on: 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ^ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ^ a b These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ^ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
- Some text in this article was taken from http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=6 (public domain)
- Gilbert F (2002). "Chromosome 6". Genet Test. 6 (4): 341–58. doi:10.1089/10906570260471912. PMID 12537662.