Masubi (volcano): Difference between revisions
Volcanopele (talk | contribs) adjusted naming references; added one for Masubi Fluctus, italicized spacecraft names in section titles |
Volcanopele (talk | contribs) →Gallery: added image showing changes at Masubi in the late 1990s |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Image:Galileo July1999 MasubiPlume.jpg|<small>False color image of the Masubi plume taken by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft on July 2, 1999.</small> |
Image:Galileo July1999 MasubiPlume.jpg|<small>False color image of the Masubi plume taken by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft on July 2, 1999.</small> |
||
Image:Galileo_August1999_MasubiPlume.jpg|<small>Low-resolution images of the Masubi volcanic plume taken by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft on August 14, 1999.</small> |
Image:Galileo_August1999_MasubiPlume.jpg|<small>Low-resolution images of the Masubi volcanic plume taken by the ''Galileo'' spacecraft on August 14, 1999.</small> |
||
Image:Masubi Changes Galileo.jpg|<small>Surface changes observed at Masubi during the ''Galileo'' mission of the late 1990s. Plume deposits seen in September 1997 (image 2) and August 1999 (image 4). Plume fallout absent in June 1997 (image 1) and May 1998 (image 3)</small> |
|||
Image:NH Masubi changes.jpg|<small>Surface changes at Masubi between Galileo in 1997 (B) and New Horizons in 2007 (C and D). New Horizons images reveal a two-lobed plume deposit surrounding a new, 240-kilometer long lava flow.</small> |
Image:NH Masubi changes.jpg|<small>Surface changes at Masubi between Galileo in 1997 (B) and New Horizons in 2007 (C and D). New Horizons images reveal a two-lobed plume deposit surrounding a new, 240-kilometer long lava flow.</small> |
||
</gallery></center> |
</gallery></center> |
||
Revision as of 21:52, 2 February 2010
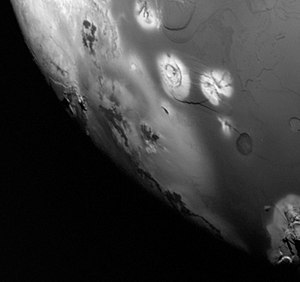
Masubi is an active volcano on Jupiter's moon Io. It is located on Io's leading hemisphere at 49°36′S 56°11′W / 49.6°S 56.18°W[1] within a bright terrain region named Tarsus Regio. A volcanic plume has been observed at Masubi by various spacecraft starting with Voyager 1 in 1979, though it has not been persistent like similar Ionian volcanoes Amirani and Prometheus.[2] Masubi is also notable for having one of the largest active lava flows on Io, with a new 240-kilometer flow forming between 1999 and 2007.[3]
Observations by Voyager 1
The volcano was first observed during the Voyager 1 encounter with the Jupiter system on March 5, 1979. Voyager discovered a 64-kilometer tall, 177-kilometer wide volcanic dust plume, composed primarily of sulfur dioxide, at the northern end of a 501-kilometer long dark lava flow.[4][5] To date, images taken by Voyager 1's Imaging Science Sub-system Wide-Angle Camera shortly before the spacecraft's closest approach to Io have the highest spatial resolution coverage of this volcano at two kilometers per pixel.[6] These images reveal a lava flow with a V-shaped northern end, associated with the plume source as noted by the dark plume deposit ring surrounding it, and bifurcated southern section.[6] The two-lobed shape of the plume deposit may result from the Masubi volcanic plume during Voyager 1 encounter having two sources on the flow field and two eruption columns.[7] This was the faintest of the plumes on Io observed by the two Voyager spacecraft. It was initially designated as Plume 8, but in 1979 the International Astronomical Union formally named it Masubi, after a Japanese fire god called Ho-Masubi.[1] The lava flow associated with the plume was named Masubi Fluctus shortly after the start of the Galileo mission.[8]
Observations by Galileo
The Galileo spacecraft and ground-based astronomers observed volcanic activity at Masubi on several occasions in the late 1990s, but it was not a persistent thermal hotspot.[9] The camera on Galileo observed a volcanic plume along Masubi Fluctus during the Galileo extended missions, in July/August 1999 and August 2001.[2] Galileo's cameras also observed a plume deposit form in September 1997. In each of these cases, the volcanic plumes emanated from different parts of Masubi Fluctus, providing further evidence that dust plumes like the one at Masubi result from the rapid sublimation of surficial sulfur dioxide frost by warm, advancing lava flow fronts, rather than erupting from the primary volcanic vent.[10] Ground-based astronomers in August 1998 briefly observed a high-temperature eruption at Masubi, confirming Masubi Fluctus' silicate mafic to ultramafic composition.[11]
Observations by New Horizons
Masubi was last observed by a spacecraft during New Horizons' February 28, 2007 encounter with the Jupiter system. During this encounter, two plumes were observed along Masubi Fluctus. One was seen at the northern end of the flow, interpreted as the main source vent for the flow. The second was observed near the middle of the elongated flow field.[3] These two plumes were 70 and 80 kilometers tall respectively. New Horizons also observed a fresh, 240-kilometer lava flow at Masubi. This was the largest new lava flow observed anywhere in the solar system since extra-terrestrial volcanism was discovered on Io in 1979.[12] The two plumes observed emanate from the northern and southern ends of this new flow. Fallout from the two volcanic plumes produced a two-lobed dark deposit around the new lava flow, similar to the deposit seen during the Voyager encounters.
Gallery
-
False color image of the Masubi plume taken by the Galileo spacecraft on July 2, 1999.
-
Low-resolution images of the Masubi volcanic plume taken by the Galileo spacecraft on August 14, 1999.
-
Surface changes observed at Masubi during the Galileo mission of the late 1990s. Plume deposits seen in September 1997 (image 2) and August 1999 (image 4). Plume fallout absent in June 1997 (image 1) and May 1998 (image 3)
-
Surface changes at Masubi between Galileo in 1997 (B) and New Horizons in 2007 (C and D). New Horizons images reveal a two-lobed plume deposit surrounding a new, 240-kilometer long lava flow.
References
- ^ a b "Masubi". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- ^ a b Geissler, P. E. (2008). "Galileo observations of volcanic plumes on Io". Icarus. 197: 505–18. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2008.05.005.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Spencer, J. R. (2007). "Io Volcanism Seen by New Horizons: A Major Eruption of the Tvashtar Volcano". Science. 318: 240–43. doi:10.1126/science.1147621.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Davies, Ashley (2007). "Io, 1610-1979". Volcanism on Io: A Comparison with Earth. Cambridge University Press. pp. 7–26. ISBN 0-521-85003-7.
- ^ Strom, R. G. (1979). "Volcanic eruption plumes on Io". Nature. 280: 733–736. doi:10.1038/280733a0.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Perry, Jason (March 9, 2009). "Taking another look at Voyager 1 images of Io". The Gish Bar Times. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ^ Perry, Jason (March 8, 2009). "30th Anniversary of the Discovery of Volcanism on Io". The Gish Bar Times. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ^ "Masubi Fluctus". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- ^ Lopes, R. M. C. (2001). "Io in the near infrared: Near-Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (NIMS) results from the Galileo flybys in 1999 and 2000". Journal of Geophysical Research. 106 (E12): 33, 053–33, 078. doi:10.1029/2000JE001463.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Phillips, Cynthia (October 7, 1999). "Migrating Volcanic Plumes on Io". Planetary Image Research Laboratory. Retrieved 2010-01-30.
- ^ Geissler, Paul (2003). "Volcanic Activity on Io During the Galileo Era". Annu. Rev. Earth Sci. 31: 175–211. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.31.100901.145428.
- ^ "Changes on Io". New Horizons: NASA's Pluto-Kuiper Belt Mission. October 9, 2007. Retrieved 2010-01-30.



