Neofetch: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
→Other implementations: rexxfetch |
→Example screenshots: Arya Linux |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
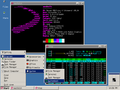
File:VirtualBox Test 15 05 2022 22 36 56.png|Neofetch and [[htop]] showing [[Devuan]] |
File:VirtualBox Test 15 05 2022 22 36 56.png|Neofetch and [[htop]] showing [[Devuan]] |
||
File:Debian10x Gnome.png|Neofetch showing [[Debian Buster]] |
File:Debian10x Gnome.png|Neofetch showing [[Debian Buster]] |
||
File:Aryalinux screenfetch.png|Arya Linux |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== Other implementations == |
== Other implementations == |
||
* afetch, written in [[ANSI C]] |
* afetch, written in [[ANSI C]] |
||
Revision as of 18:23, 15 May 2024
This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subject, potentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. (July 2022) |
 Neofetch running on macOS Mojave | |
| Developer(s) | Dylan Araps |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 31 December 2015 |
| Final release | 7.1.0[1] |
| Repository | github |
| Written in | Bash 3.2 |
| Operating system | Linux, macOS, BSD, Windows, iOS, Android, GNU Hurd, Haiku, IRIX, MINIX, Solaris |
| Size | 277 KB |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Benchmark |
| License | MIT License |
Neofetch is a system information tool written in the Bash shell scripting language.[2] By default, on the left side is a logo of the distribution, rendered in ASCII art.[3][4] Unlike a system monitor, the tool only features a static display of the computer's basic hardware and software configurations and their versions, typically operating system, the host (namely the technical name of the machine), uptime, package managers, the shell, display resolution, desktop environment, window manager, themes and icons, the computer terminal, CPU, GPU, and RAM. Neofetch can also display images on the terminal with w3m-img in place of the ASCII logo art. Neofetch development has been discontinued as of April 26, 2024.[5]
Example screenshots
-
Neofetch showing Arch Linux
-
Neofetch showing SteamOS on a Steam Deck
-
Neofetch showing Debian Buster
-
Arya Linux
Other implementations
- afetch, written in ANSI C
- CoalFetch, a one-liner program in Java
- dosfetch, written in Pascal for DOS[6]
- efetch, written in C++
- fastfetch, a maintained, feature-rich and performance oriented drop-in replacement of neofetch. Written in C.[7]
- fetch4FD and MySysInf for FreeDOS[8]
- gfetch, written in rc scripting language
- hfetch, written in Bash
- hyfetch, a updated fork of neofetch with pride flags' colors[9]
- nerdfetch, fetch script using icons and glyphs from "Nerd Fonts" (sourced mainly from Material Design and Font Awesome)[10]
- nextfetch, written in Go
- Pasfetch, written in Pascal
- perlfetch, written in Perl
- pfetch, written in Bourne scripting language
- rfetch, written in Rust
- rexxfetch, written in REXX[11]
- screenfetch, a screenshot fetch script written in Bash[12]
- swef, written in Lua
- swmfetch, written in Python
- ufetch, single shell script for each Unix-like platform[13]
- winfetch, written in Microsoft PowerShell scripting language[14]
References
- ^ "Release 7.1.0". 2 August 2020. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
- ^ Brian Schell (2019). Computing with the Raspberry Pi: Command Line and GUI Linux. p. 56
- ^ "Neofetch Creates Colorful System Information Screens using Ascii Art". BleepingComputer. Retrieved 2022-07-10.
- ^ Sneddon, Joey (2020-05-15). "NeoFetch: See System Information from the Command Line on Linux". OMG! Ubuntu!. Retrieved 2022-08-08.
- ^ dylan (2024-04-26), dylanaraps/neofetch, retrieved 2024-04-27
- ^ "Leahneukirchen/Dosfetch". GitHub.
- ^ "fastfetch-cli/fastfetch". GitHub.
- ^ "MySysInf announcement". SourceForge.
- ^ "Hykilpikonna/Hyfetch". GitHub.
- ^ "Nerd Fonts - Iconic font aggregator, glyphs/Icons collection, & fonts patcher".
- ^ http://aminet.net/package/util/moni/rexxfetch
- ^ Katie (2024-01-02), screenFetch - The Bash Screenshot Information Tool, retrieved 2024-01-03
- ^ "JSCHX / Ufetch · GitLab".
- ^ "LPTSTR/Winfetch". GitHub.