Germicidal lamp: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 299077539 by 94.196.139.86 (talk) removed incoherent blather |
|||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
As with all gas discharge lamps, all of the styles of germicidal lamps exhibit [[negative resistance]] and require the use of an external [[Ballast (electrical)|ballast]] to regulate the current flow through them. The older lamps that resembled an incandescent lamp were often operated in series with an ordinary 40 W incandescent "appliance" lamp; the incandescent lamp acted as the ballast for the germicidal lamp. |
As with all gas discharge lamps, all of the styles of germicidal lamps exhibit [[negative resistance]] and require the use of an external [[Ballast (electrical)|ballast]] to regulate the current flow through them. The older lamps that resembled an incandescent lamp were often operated in series with an ordinary 40 W incandescent "appliance" lamp; the incandescent lamp acted as the ballast for the germicidal lamp. |
||
U V lamps that produce ozone, usually the high discharge type can be used to produce normal oxygen' i.e. note; when ozone is warmed it is Uknown to revert back to normal oxygen; and so intern can be used to enrich combustion; example; cars lorry engines and for gas powered electricity production; a method called ozone seperation is encorperated using a long pipe with extra holes in the upper surface area,this physically diplaces nitrogen and facilitates ozone diplacement as ozone is heavier than air, and thus then can be used for oxygen enrichment processes etc; |
|||
== Uses == |
== Uses == |
||
Revision as of 02:58, 29 June 2009



A germicidal lamp is a special type of lamp which produces ultraviolet light (UVC). This short-wave ultraviolet light disrupts DNA base pairing causing thymine-thymine dimers leading to death of bacteria on exposed surfaces. It can also be used to produce ozone for water disinfection.
There are two common types available:
- Low pressure lamps
- Medium pressure lamps
Low pressure lamps
Low-pressure lamps are very similar to a fluorescent lamp, with a wavelength of 253.7 nm.
The most common form of germicidal lamp looks similar to an ordinary fluorescent lamp but the tube contains no fluorescent phosphor. In addition, rather than being made of ordinary borosilicate glass, the tube is made of fused quartz. These two changes combine to allow the 253.7 nm ultraviolet light produced by the mercury arc to pass out of the lamp unmodified (whereas, in common fluorescent lamps, it causes the phosphor to fluoresce, producing visible light). Germicidal lamps still produce a small amount of visible light due to other mercury radiation bands.
An older design looks like an incandescent lamp but with the envelope containing a few droplets of mercury. In this design, the incandescent filament heats the mercury, producing a vapor which eventually allows an arc to be struck, short circuiting the incandescent filament.
Medium pressure lamps
Medium-pressure lamps are much more similar to HID lamps than fluorescent lamps.
These lamps radiate a broad-band UV-C radiation, rather than a single line. They are widely used in industrial water treatment, because they are very intense radiation sources. They are as efficient as low-pressure lamps. Medium-pressure lamps produces very bright bluish white light.
Auxiliary equipment
As with all gas discharge lamps, all of the styles of germicidal lamps exhibit negative resistance and require the use of an external ballast to regulate the current flow through them. The older lamps that resembled an incandescent lamp were often operated in series with an ordinary 40 W incandescent "appliance" lamp; the incandescent lamp acted as the ballast for the germicidal lamp.
Uses
Germicidal lamps are used to sterilize workspaces and tools used in biology laboratories and medical facilities. They are also used wherever ozone is desired, for example, in the sanitizing systems of hot tubs and aquariums. They are also used by geologists to provoke fluorescence in mineral samples, aiding in their identification. In this application, the light produced by the lamp is usually filtered to remove as much visible light as possible, leaving just the UV light.
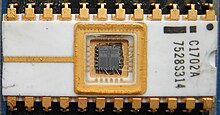
The light produced by germicidal lamps is also used to erase EPROMs; the ultraviolet photons are sufficiently energetic to allow the electrons trapped on the transistors' floating gates to tunnel through the gate insulation, eventually removing the stored charge that represents binary ones and zeroes.
Germicidal lamps are also used in waste water treatment in order to kill microorganisms.
Safety concerns
Short-wave UV light is harmful to humans. In addition to causing sunburn and (over time) skin cancer, this light can produce extremely painful inflammation of the cornea of the eye, which may lead to temporary or permanent vision impairment. It can also damage the retina of the eye. For this reason, the light produced by a germicidal lamp must be carefully shielded against both direct viewing and reflections and dispersed light that might be viewed.
