Western European Time: Difference between revisions
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
*{{flag|Sierra Leone}} |
*{{flag|Sierra Leone}} |
||
*{{flag|Togo}} |
*{{flag|Togo}} |
||
*{{flag| |
*{{flag|Morocco (Sahara)}} |
||
{{Col-end}} |
{{Col-end}} |
||
Revision as of 12:02, 5 May 2011

| Light Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Blue | Western European Time / Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Western European Summer Time / British Summer Time / Irish Standard Time (UTC+1) | |
| Red | Central European Time (UTC+1) |
| Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | |
| Yellow | Eastern European Time / Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2) |
| Ochre | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) |
| Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) | |
| Green | Moscow Time / Turkey Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | Armenia Time / Azerbaijan Time / Georgia Time / Samara Time (UTC+4) |
▉▉▉ Dark colours: Summer time observed
Western European Time (WET, UTC+0), defined legally as Greenwich Mean Time in the United Kingdom, is the time zone covering parts of western and northwestern Europe, and includes the following countries and regions:
- Canary Islands, since 1946 (rest of Spain is CET, i.e. UTC+1)
- Faroe Islands, since 1908
- northeastern Greenland (Danmarkshavn and surrounding area)
- Iceland, since 1968
- Portugal, since 1911 with pauses (except Azores, UTC-1)
- Ireland, since 1922 with pauses[citation needed]
- The United Kingdom (including England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales plus the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands, where the term GMT is legally used), since 1847 in England, Scotland and Wales, since 1922 in Northern Ireland with pauses[citation needed]
The nominal span of the time zone is 7.5°E to 7.5°W (0° ± 7.5°), but notably it does not include the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France, Gibraltar or Spain which use Central European Time (CET), even though these are mostly (France) or completely (the rest) west of 7.5E°. Note also the inclusion of Iceland and eastern Greenland, even though both are west of 15W°
During winter months, the countries above use WET (UK, GMT); however in the summer, most (but not all) of the above places move one hour ahead to Western European Summer Time (UTC+1), which additionally is known in the UK as British Summer Time (BST) and in Ireland as Irish Standard Time.
Irish Winter Time
In Ireland, the Standard Time (Amendment) Act, 1971 legally establishes Greenwich Mean Time (Western European Time) as a winter time period.[1] Ireland reverts to Irish Standard Time during the summer months. This is the reverse of the practice of most countries in the EU, but provides the same end results.
Time zones of Africa
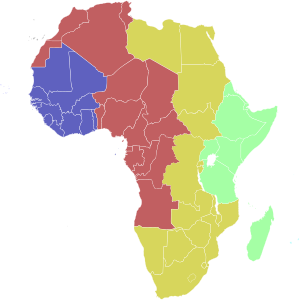
| Light Blue | Cape Verde Time[a] (UTC−1) |
| Blue | Greenwich Mean Time (UTC) |
| Red | (UTC+1) |
| Ochre | (UTC+2) |
| Green | East Africa Time (UTC+3) |
| Turquoise | (UTC+4) |
b Mauritius and the Seychelles are to the east and north-east of Madagascar respectively.
UTC+0 is used in the far west of Africa, where it is known in the former British colonies as GMT. The states here do not use daylight saving. (Note that West Africa Time, used in west central Africa, corresponds to Central European Time, and that West Africa uses both time zones).
The countries included are these:
|
Historical uses
A slight variation of this time zone, based until 1911 on the Paris Meridian, was used in:
- Andorra in years 1901-46
- Belgium in years 1892-1914 and 1919-1940
- France in years 1911-40 and 1944-45
- Gibraltar in years 1880-1957
- Luxembourg in years 1918-40
- Monaco in years 1911-45
In the United Kingdom in years 1940-45 British Summer Time (BST=CET) was used in winters and in years 1941-45 & 1947 British Double Summer Time (BDST=CEST) was used in summers. Between 18 February 1968 and 31 October 1971 BST was used all year round.
In Ireland in years 1940-46 Irish Summer Time (IST=CET) was used all year (Ireland did not adopt similar time changes to British Double Summer Time (BDST=CEST) in 1941-45, 1947). Between 18 February 1968 and 31 October 1971 Irish Standard Time was used all year round.
In Portugal, CET was used in the periods 1966-1976 and 1992-1996.
References
- ^ Standard Time (Amendment) Act, 1971– Schedule 1 Irish Statute Book
