Adverse Childhood Experiences Study: Difference between revisions
KolbertBot (talk | contribs) m Bot: HTTP→HTTPS (v485) |
m linked article to childhood trauma page |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Adverse Childhood Experiences Study''' ('''ACE Study''') is a research study conducted by the American [[health maintenance organization]] [[Kaiser Permanente]] and the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]].<ref name="ACE Study"/> Participants were recruited to the study between 1995 and 1997 and have been in long-term follow up for health outcomes. The study has demonstrated an association of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) with health and social problems |
The '''Adverse Childhood Experiences Study''' ('''ACE Study''') is a research study conducted by the American [[health maintenance organization]] [[Kaiser Permanente]] and the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]].<ref name="ACE Study"/> Participants were recruited to the study between 1995 and 1997 and have been in long-term follow up for health outcomes. The study has demonstrated an association of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) (aka [[childhood trauma]]) with health and social problems across the lifespan. The study is frequently cited as a notable landmark in [[epidemiology|epidemiological]] research,<ref name=Brooks2012/> and has produced many scientific articles and conference and workshop presentations that examine ACEs.<ref name="ACE Study"/> |
||
== Background == |
== Background == |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
In the 1980s, the dropout rate of participants at [[Kaiser Permanente]]'s [[obesity]] clinic in [[San Diego]], [[California]], was about 50%; despite all of the dropouts successfully [[weight loss|losing weight]] under the program.<ref name="Stevens October 2012"/> Vincent Felitti, head of Kaiser Permanente’s Department of Preventive Medicine in San Diego, conducted interviews with people who had left the program, and discovered that a majority of 286 people he interviewed had experienced [[child sexual abuse|childhood sexual abuse]]. The interview findings suggested to Felitti that weight gain might be a coping mechanism for [[Depression (mood)|depression]], [[anxiety]], and [[fear]].<ref name="Stevens October 2012"/> |
In the 1980s, the dropout rate of participants at [[Kaiser Permanente]]'s [[obesity]] clinic in [[San Diego]], [[California]], was about 50%; despite all of the dropouts successfully [[weight loss|losing weight]] under the program.<ref name="Stevens October 2012"/> Vincent Felitti, head of Kaiser Permanente’s Department of Preventive Medicine in San Diego, conducted interviews with people who had left the program, and discovered that a majority of 286 people he interviewed had experienced [[child sexual abuse|childhood sexual abuse]]. The interview findings suggested to Felitti that weight gain might be a coping mechanism for [[Depression (mood)|depression]], [[anxiety]], and [[fear]].<ref name="Stevens October 2012"/> |
||
Felitti and Robert Anda from the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] (CDC) went on to survey |
Felitti and Robert Anda from the [[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] (CDC) went on to survey [[childhood trauma]] experiences of over 17,000 Kaiser Permanente patient volunteers.<ref name="Stevens October 2012"/> The 17,337 participants were volunteers from approximately 26,000 consecutive Kaiser Permanente members. About half were female; 74.8% were white; the average age was 57; 75.2% had attended college; all had jobs and good health care, because they were members of the Kaiser [[health maintenance organization]].<ref name=Prevalence/> Participants were asked about 10 types of [[childhood trauma]] that had been identified in earlier research literature:<ref name=Anda200304/> |
||
* [[Physical abuse]] |
* [[Physical abuse]] |
||
* Sexual abuse |
* [[Pedophilia|Sexual abuse]] |
||
* [[Emotional abuse]] |
* [[Emotional abuse]] |
||
* Physical [[neglect]] |
* Physical/emotional [[neglect]] |
||
* [[Childhood trauma|Violence in the home]] |
|||
* Emotional neglect |
|||
* Mother treated violently |
|||
* Household [[substance abuse]] |
* Household [[substance abuse]] |
||
* Household [[mental illness]] |
* Household [[mental illness]] |
||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
According to the United States' [[Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration]], the ACE study found that: |
According to the United States' [[Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration]], the ACE study found that: |
||
* [[ |
* [[Childhood trauma|Adverse childhood experiences]] are common. For example, 28% of study participants reported physical abuse and 21% reported sexual abuse. Many also reported experiencing a divorce or parental separation, or having a parent with a mental and/or [[substance use disorder]].<ref name=SAMHSA/> |
||
* Adverse childhood experiences often occur together. Almost 40% of the original sample reported two or more ACEs and 12.5% experienced four or more. Because ACEs occur in clusters, many subsequent studies have examined the cumulative effects of ACEs rather than the individual effects of each.<ref name=SAMHSA/> |
* Adverse childhood experiences often occur together. Almost 40% of the original sample reported two or more ACEs and 12.5% experienced four or more. Because ACEs occur in clusters, many subsequent studies have examined the cumulative effects of ACEs rather than the individual effects of each.<ref name=SAMHSA/> |
||
* Adverse childhood experiences have a [[dose{{ndash}}response relationship]] with many health problems. As researchers followed participants over time, they discovered that a person's cumulative ACEs score has a strong, graded relationship to numerous health, [[social problem|social]], and behavioral problems throughout their lifespan, including substance use disorders. Furthermore, many problems related to ACEs tend to be [[comorbid]], or co-occurring.<ref name=SAMHSA/> |
* Adverse childhood experiences have a [[dose{{ndash}}response relationship]] with many health problems. As researchers followed participants over time, they discovered that a person's cumulative ACEs score has a strong, graded relationship to numerous health, [[social problem|social]], and behavioral problems throughout their lifespan, including substance use disorders. Furthermore, many problems related to ACEs tend to be [[comorbid]], or co-occurring.<ref name=SAMHSA/> |
||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
About two-thirds of individuals reported at least one adverse childhood experience; 87% of individuals who reported one ACE reported at least one additional ACE.<ref name=Anda200304/> The number of ACEs was strongly associated with adulthood high-risk health behaviors such as smoking, alcohol and drug abuse, promiscuity, and severe obesity, and correlated with ill-health including depression, [[heart disease]], [[cancer]], [[chronic obstructive pulmonary disease|chronic lung disease]] and shortened lifespan.<ref name=Anda200304/><ref name=Felitti1998/><ref name=Middlebrooks2008/> Compared to an ACE score of zero, having four adverse childhood experiences was associated with a seven-fold (700%) increase in [[alcoholism]], a doubling of risk of being diagnosed with cancer, and a four-fold increase in [[emphysema]]; an ACE score above six was associated with a 30-fold (3000%) increase in attempted suicide.<ref name=Brooks2012/> |
About two-thirds of individuals reported at least one adverse childhood experience; 87% of individuals who reported one ACE reported at least one additional ACE.<ref name=Anda200304/> The number of ACEs was strongly associated with adulthood high-risk health behaviors such as smoking, alcohol and drug abuse, promiscuity, and severe obesity, and correlated with ill-health including depression, [[heart disease]], [[cancer]], [[chronic obstructive pulmonary disease|chronic lung disease]] and shortened lifespan.<ref name=Anda200304/><ref name=Felitti1998/><ref name=Middlebrooks2008/> Compared to an ACE score of zero, having four adverse childhood experiences was associated with a seven-fold (700%) increase in [[alcoholism]], a doubling of risk of being diagnosed with cancer, and a four-fold increase in [[emphysema]]; an ACE score above six was associated with a 30-fold (3000%) increase in attempted suicide.<ref name=Brooks2012/> |
||
The ACE study's results suggest that maltreatment and [[dysfunctional family|household dysfunction]] in childhood contribute to health problems decades later. These include [[chronic condition|chronic]] diseases—such as heart disease, cancer, [[stroke]], and [[diabetes]]—that are the most common causes of death and [[disability]] in the [[United States]].<ref name=WorldHealth/> The study's findings, while relating to a specific population within the United States, might reasonably be assumed to reflect similar trends in other parts of the world, according to the [[World Health Organization]].<ref name=WorldHealth/> |
The ACE study's results suggest that [[Childhood trauma|maltreatment]] and [[dysfunctional family|household dysfunction]] in childhood contribute to health problems decades later. These include [[chronic condition|chronic]] diseases—such as heart disease, cancer, [[stroke]], and [[diabetes]]—that are the most common causes of death and [[disability]] in the [[United States]].<ref name=WorldHealth/> The study's findings, while relating to a specific population within the United States, might reasonably be assumed to reflect similar trends in other parts of the world, according to the [[World Health Organization]].<ref name=WorldHealth/> |
||
== Subsequent surveys == |
== Subsequent surveys == |
||
Revision as of 15:28, 13 April 2018
The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study (ACE Study) is a research study conducted by the American health maintenance organization Kaiser Permanente and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.[1] Participants were recruited to the study between 1995 and 1997 and have been in long-term follow up for health outcomes. The study has demonstrated an association of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) (aka childhood trauma) with health and social problems across the lifespan. The study is frequently cited as a notable landmark in epidemiological research,[2] and has produced many scientific articles and conference and workshop presentations that examine ACEs.[1]
Background
In the 1980s, the dropout rate of participants at Kaiser Permanente's obesity clinic in San Diego, California, was about 50%; despite all of the dropouts successfully losing weight under the program.[3] Vincent Felitti, head of Kaiser Permanente’s Department of Preventive Medicine in San Diego, conducted interviews with people who had left the program, and discovered that a majority of 286 people he interviewed had experienced childhood sexual abuse. The interview findings suggested to Felitti that weight gain might be a coping mechanism for depression, anxiety, and fear.[3]
Felitti and Robert Anda from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) went on to survey childhood trauma experiences of over 17,000 Kaiser Permanente patient volunteers.[3] The 17,337 participants were volunteers from approximately 26,000 consecutive Kaiser Permanente members. About half were female; 74.8% were white; the average age was 57; 75.2% had attended college; all had jobs and good health care, because they were members of the Kaiser health maintenance organization.[4] Participants were asked about 10 types of childhood trauma that had been identified in earlier research literature:[5]
- Physical abuse
- Sexual abuse
- Emotional abuse
- Physical/emotional neglect
- Violence in the home
- Household substance abuse
- Household mental illness
- Parental separation or divorce
- Incarcerated household member
Findings

According to the United States' Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, the ACE study found that:
- Adverse childhood experiences are common. For example, 28% of study participants reported physical abuse and 21% reported sexual abuse. Many also reported experiencing a divorce or parental separation, or having a parent with a mental and/or substance use disorder.[8]
- Adverse childhood experiences often occur together. Almost 40% of the original sample reported two or more ACEs and 12.5% experienced four or more. Because ACEs occur in clusters, many subsequent studies have examined the cumulative effects of ACEs rather than the individual effects of each.[8]
- Adverse childhood experiences have a dose–response relationship with many health problems. As researchers followed participants over time, they discovered that a person's cumulative ACEs score has a strong, graded relationship to numerous health, social, and behavioral problems throughout their lifespan, including substance use disorders. Furthermore, many problems related to ACEs tend to be comorbid, or co-occurring.[8]
About two-thirds of individuals reported at least one adverse childhood experience; 87% of individuals who reported one ACE reported at least one additional ACE.[5] The number of ACEs was strongly associated with adulthood high-risk health behaviors such as smoking, alcohol and drug abuse, promiscuity, and severe obesity, and correlated with ill-health including depression, heart disease, cancer, chronic lung disease and shortened lifespan.[5][9][10] Compared to an ACE score of zero, having four adverse childhood experiences was associated with a seven-fold (700%) increase in alcoholism, a doubling of risk of being diagnosed with cancer, and a four-fold increase in emphysema; an ACE score above six was associated with a 30-fold (3000%) increase in attempted suicide.[2]
The ACE study's results suggest that maltreatment and household dysfunction in childhood contribute to health problems decades later. These include chronic diseases—such as heart disease, cancer, stroke, and diabetes—that are the most common causes of death and disability in the United States.[11] The study's findings, while relating to a specific population within the United States, might reasonably be assumed to reflect similar trends in other parts of the world, according to the World Health Organization.[11]
Subsequent surveys
The ACE Study has produced more than 50 articles that look at the prevalence and consequences of ACEs.[12][non-primary source needed] It has been influential in several areas. Subsequent studies have confirmed the high frequency of adverse childhood experiences, or found even higher incidences in urban or youth populations.
The original study questions have been used to develop a 10-item screening questionnaire.[13][14] Numerous subsequent surveys have confirmed that adverse childhood experiences are frequent.
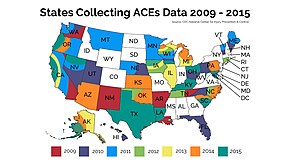
The CDC runs the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS),[15] an annual survey conducted by individual state health departments in all 50 states. An expanded survey instrument in several states found each state to be similar.[16] Some states have collected additional local data.[17][18] Adverse childhood experiences were even more frequent in studies in urban Philadelphia[19] and in a survey of young mothers (mostly younger than 19).[20] Internationally, an Adverse Childhood Experiences International Questionnaire (ACE-IQ) is undergoing validation testing.[21] Surveys of adverse childhood experiences have been conducted in Romania,[22] the Czech Republic,[23] the Republic of Macedonia,[24] Norway, the Philippines, the United Kingdom, Canada, China and Jordan.[7][not specific enough to verify] Child Trends used data from the 2011/12 National Survey of Children's Health (NSCH) to analyze ACEs prevalence in children nationally, and by state. The NSCH's list of "adverse family experiences" includes a measure of economic hardship and shows that this is the most common ACE reported nationally.[25]
Neurobiology of stress
Cognitive and neuroscience researchers have examined possible mechanisms that might explain the negative consequences of adverse childhood experiences on adult health.[26] Adverse childhood experiences can alter the structural development of neural networks and the biochemistry of neuroendocrine systems[27][28][29][30] and may have long-term effects on the body, including speeding up the processes of disease and aging and compromising immune systems.[31][32][33]
Additionally, epigenetic transmission may occur due to stress during pregnancy or during interactions between mother and newborns. Maternal stress, depression, and exposure to partner violence have all been shown to have epigenetic effects on infants.[30]
Implementing practices
As knowledge about the prevalence and consequences of adverse childhood experiences increases, trauma-informed and resilience-building practices based on the research is being implemented in communities, education, public health departments, social services, faith-based organizations and criminal justice. A few states are considering legislation.
Communities
As knowledge about the prevalence and consequences of ACEs increases, more communities seek to integrate trauma-informed and resilience-building practices into their agencies and systems. Tarpon Springs, Florida, became the first trauma-informed community in 2011.[34][35] Trauma-informed initiatives in Tarpon Springs include trauma-awareness training for the local housing authority, changes in programs for ex-offenders, and new approaches to educating students with learning difficulties.[36]
Education
Children who are exposed to adverse childhood experiences may become overloaded with stress hormones, leaving them in a constant state of arousal and alertness to environmental and relational threats. Therefore, they may have difficulty focusing on school work, and consolidating new memory, making it harder for them to learn at school.[37] Approximately one in three or four children have experienced significant ACEs.[38] A study by the Area Health Education Center of Washington State University found that students with at least three ACEs are three times as likely to experience academic failure, six times as likely to have behavioral problems, and five times as likely to have attendance problems.[38] These students may have trouble trusting teachers and other adults, and may have difficulty creating and maintaining relationships.[39] The trauma-informed school movement aims to train teachers and staff to help children self-regulate, and to help families that are having problems that result in children's normal response to trauma, rather that simply jumping to punishment. It also seeks to provide behavioral consequences that will not re-traumatize a child. Punishment is often ineffective, and better results can often be achieved with positive reinforcement.[40] Out-of-school suspensions can be particularly bad for students with difficult home lives; forcing students to remain at home may increase their distrust of adults.[citation needed]
Trauma-sensitive, or compassionate, schooling has become[when?] increasingly popular in Washington, Massachusetts, and California. Lincoln High School in Walla Walla, Washington, adapted a trauma-informed approached to discipline and reduced its suspensions by 85%.[41] Rather than standard punishment, students are taught to recognize their reaction to stress and learn to control it. Spokane, Washington, schools conducted a research study that demonstrated that academic risk was correlated with students’ experiences of traumatic events known to their teachers.[38][42] The same school district has begun a study to test the impact of trauma-informed intervention programs, in an attempt to reduce the impact of toxic stress. In Brockton, Massachusetts, a community-wide meeting led to a trauma-informed approach being adopted by the Brockton School District.[40] So far, all of the district's elementary schools have implemented trauma-informed improvement plans, and there are plans to do the same in the middle school and high school. About one-fifth of the district teachers have participated in a course on teaching traumatized students. Police alert schools when they have arrested someone or visited at a student's address. Massachusetts state legislation has sought to require all schools to develop plans to create "safe and supportive schools".[40] At El Dorado, an elementary school in San Francisco, California, trauma-informed practices were associated with a suspension reduction of 89%.[43]
Social services
Social service providers—including welfare systems, housing authorities, homeless shelters, and domestic violence centers – are adopting trauma-informed approaches that help to prevent ACEs or minimize their impact. Utilizing tools that screen for trauma can help a social service worker direct their clients to interventions that meet their specific needs.[44] Trauma-informed practices can also help social service providers look at how trauma impacts the whole family.[45]
Trauma-informed approaches can improve child welfare services by 1) openly discussing trauma and 2) addressing parental trauma.[according to whom?][46] The New Hampshire Division for Children Youth and Families (DCYF) is taking a trauma-informed approach to their foster care services by educating staff about childhood trauma, screening children entering foster care for trauma, using trauma-informed language to mitigate further traumatization, mentoring birth parents and involving them in collaborative parenting, and training foster parents to be trauma-informed.[44]
In Albany, New York the HEARTS Initiative has led to local organizations developing trauma-informed practice.[46] Senior Hope Inc., an organization serving adults over the age of 50, began implementing the 10-question ACE survey and talking with their clients about childhood trauma. The LaSalle School, which serves orphaned and abandoned boys, began looking at delinquent boys in from a trauma-informed perspective and began administering the ACE questionnaire to their clients.
Housing authorities are also becoming trauma-informed. Supportive housing can sometimes recreate control and power dynamics associated with clients’ early trauma.[47] This can be reduced through trauma-informed practices, such as training staff to be respectful of clients' space by scheduling appointments and not letting themselves into clients' private spaces, and also understanding that an aggressive response may be trauma-related coping strategies.[47] The housing authority in Tarpon Springs provided trauma-awareness training to staff so they could better understand and react to their clients' stress and anger resulting from poor employment, health, and housing.[36]
A survey of 200 homeless individuals in California and New York demonstrated that more than 50% had experienced at least four ACEs.[48] In Petaluma, California, the Committee on the Shelterless (COTS) uses a trauma-informed approach called Restorative Integral Support (RIS) to reduce intergenerational homelessness.[49] RIS increases awareness of and knowledge about ACEs, and calls on staff to be compassionate and focus on the whole person. COTS now consider themselves ACE-informed and focus on resiliency and recovery.
Health care services
Screening for or talking about ACEs with parents and children can help to foster healthy physical and psychological development and can help doctors understand the circumstances that children and their parents are facing. By screening for ACEs in children, pediatric doctors and nurses can better understand behavioral problems. Some doctors have questioned whether some behaviors resulting in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) diagnoses are in fact reactions to trauma. Children who have experienced four or more ACEs are three times as likely to take ADHD medication when compared with children with less than four ACEs.[50] Screening parents for their ACEs allows doctors to provide the appropriate support to parents who have experienced trauma, helping them to build resilience, foster attachment with their children, and prevent a family cycle of ACEs.[51][52] Trauma-informed pediatric care also allows doctors to develop a more trusting relationship with parents, opening the lines of communication.[53] At Montefiore Medical Center ACEs screenings will soon be implemented in 22 pediatric clinics. In a pilot program any child with one parent who has an ACE score of four or higher is offered enrollment and receive a variety of services. For families enrolled in the program parents report fewer ER visits and children have healthier emotional and social development, compared with those not enrolled.[51][54]
Public health
Most American doctors as of 2015 do not use ACE surveys to assess patients. Objections to doing so include that there are no randomized controlled trials that show that such surveys can be used to actually improve health outcomes, there are no standard protocols for how to use the information gathered, and that revisiting negative childhood experiences could be emotionally traumatic.[55] Other obstacles to adoption include that the technique is not taught in medical schools, is not billable, and the nature of the conversation makes some doctors personally uncomfortable.[55]
Some public health centers see ACEs as an important way (especially for mothers and children)[56] to target health interventions for individuals during sensitive periods of development early in their life, or even in utero.[56] For example, Jefferson Country Public Health clinic in Port Townsend, Washington, now screens pregnant women, their partners, parents of children with special needs, and parents involved with CPS for ACEs.[57] With regard to patient counseling, the clinic treats ACEs like other health risks such as smoking or alcohol consumption.
Resiliency
Resilience is not a trait that people either have or do not have. It involves behaviors, thoughts and actions that can be learned and developed in anyone. According to the American Psychological Association (2017) resilience is the ability to adapt in the face of adversity, tragedy, threats or significant stress — such as family and relationship problems, serious health problems or workplace and financial stressors. Resilience refers to bouncing back from difficult experiences in life. There is nothing extraordinary about resilience. People often demonstrate resilience in times of adversity. However, being resilient does not mean that a person will not experience difficulty or distress as emotional pain is common for people when they suffer from a major adversity or trauma. In fact, the path to resilience often involves considerable emotional pain [70].
Resilience is labeled as a protective factor. Having resilience can benefit children who have been exposed to trauma and have a higher A.C.E score. Children who can learn to develop it, can use resilience to build themselves up after trauma. A child who has not developed resilience will have a harder time coping with the challenges that can come in adult life. People and children who are resilient, embrace the thinking that adverse experiences do not define who they are. They also can think about past events in their lives that were traumatic and, try to reframe them in a way that is constructive. They are able to find strength in their struggle and ultimately can overcome the challenges and adversity that was faced in childhood. In childhood, resiliency can come from having a caring adult in a child's life. Resiliency can also come from having meaningful moments such as an academic achievement or getting praise from teachers or mentors. In adulthood, resilience is the concept of self-care. If you are taking care of yourself and taking the necessary time to reflect and build on your experiences, then you will have a higher capacity for taking care of others. Adults can also use this skill to counteract some of the trauma they have experienced. Self-care can mean a variety of things. One example of self-care, is knowing when you are beginning to feel burned out and then taking a step back to rest and recuperate yourself. Another component of self-care is practicing mindfulness or engaging in some form of meditation. If you are able to take the time to reflect upon your experiences, then you will be able to build a greater level of resiliency moving forward. All of these strategies put together can help to build resilience and counteract some of the childhood trauma that was experienced. With these strategies children can begin to heal after experiencing adverse childhood experiences. This aspect of resiliency is so important because it enables people to find hope in their traumatic past. When first looking at the A.C.E. study and the different correlations that come with having 4 or more traumas, it is easy to feel defeated. It is even possible for this information to encourage people to have unhealthy coping behaviors. Introducing resilience and the data that supports its positive outcome in regards to trauma, allows for a light at the end of a tunnel. It gives people the opportunity to be proactive instead of reactive when it comes to addressing the traumas in their past.
Criminal justice
Since research suggests that incarcerated individuals are much more likely to have been exposed to violence and suffer from posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD),[58] a trauma-informed approach may better help to address some of these criminogenic risk factors and can create a less traumatizing criminal justice experience.[according to whom?] Programs, like Seeking Safety, are often used to help individuals in the criminal justice system learn how to better cope with trauma, PTSD, and substance abuse.[59] Juvenile courts better help deter children from crime and delinquency when they understand the trauma many of these children have experienced.[60] The criminal justice system itself can also retraumatize individuals.[61] This can be prevented by creating safer facilities where correctional and police officers are properly trained to keep incidents from escalating.[58] Partnerships between police and mental health providers can also reduce the possible traumatizing effects of police intervention and help provide families with the proper mental health and social services.[62] The Women’s Community Correctional Center of Hawaii began a Trauma-Informed Care Initiative that aims to train all employees to be aware and sensitive to trauma, to screen all women in their facility for trauma, to assess those who have experienced trauma, and begin providing trauma-informed mental health care to those women identified.[61]
Faith-based organizations
Some faith-based organizations offer spiritual services in response to traumas identified by ACE surveys. For example, the founder of ACE Overcomers[63] combined the epidemiology of ACEs, the neurobiology of toxic stress and principles of the Christian Bible into a workbook and 12-week course used by clergy in several states.[64] Faith-based organizations also participate in the online group ACES Connection Network.[65] The Faith and Health Connection ministry[66] also applies principles of Christian theology to address childhood traumas.
Legislation
Vermont has passed a bill, Act 43(H.508), an act relating to building resilience for individuals experiencing adverse childhood experiences which acknowledges the life span effects of ACEs on health outcomes, seeks wide use of ACE screening by health providers and aims to educate medical and health school students about ACEs[67][68]. "Vermont first state to propose bill to screen for ACEs in health care"], ACEs Connection, 18 March 2014</ref> Previously Washington State passed legislation to set up a public-private partnership to further community development of trauma-informed and resilience-building practices that had begun in that state; but it was not adequately funded.[69] On August 18, 2014, California lawmakers unanimously passed ACR No. 155, which encourages policies reducing children's exposure to adverse experiences.[70] Recent Massachusetts legislation supports a trauma-informed school movement as part of The Reduction of Gun Violence bill (No. 4376). This bill aims to create "safe and supportive schools" through services and initiatives focused on physical, social, and emotional safety.[71]
See also
- Early childhood trauma
- Alcoholism in family systems
- Child abuse
- Effects of domestic violence on children
- Social determinants of health
- Verbal abuse
References
- ^ a b "The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study". cdc.gov. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention. May 2014. Archived from the original on 27 December 2015.
- ^ a b Brooks, David (27 September 2012). "The Psych Approach". The New York Times.
- ^ a b c Stevens, Jane Ellen (8 October 2012). "The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study — the Largest Public Health Study You Never Heard Of". The Huffington Post.
- ^ "Prevalence of Individual Adverse Childhood Experiences". cdc.gov. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention. May 2014. Archived from the original on 4 April 2016.
- ^ a b c Anda RF; Felitti VJ (April 2003). "Origins and Essence of the Study" (PDF). ACE Reporter. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ "The ACE Pyramid". Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention. May 2014. Archived from the original on 16 January 2016.
- ^ a b "About the CDC-Kaiser ACE Study". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention. Archived from the original on 28 February 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c "Adverse Childhood Experiences". samhsa.gov. Rockville, Maryland, USA: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Archived from the original on 9 October 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Felitti, Vincent J; Anda, Robert F; et al. (May 1998). "Relationship of Childhood Abuse and Household Dysfunction to Many of the Leading Causes of Death in Adults: The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 14 (4): 245–258. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00017-8. PMID 9635069.
- ^ Middlebrooks, J.S.; Audage, N.C. (2008). The Effects of Childhood Stress on Health Across the Lifespan (PDF). Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control.
- ^ a b World Health Organization; International Society for Prevention of Child Abuse and Neglect (2006). Preventing child maltreatment: a guide to taking action and generating evidence (PDF). Geneva, Switzerland. p. 12. ISBN 9241594365.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Publications by Health Outcome". cdc.gov. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, Division of Violence Prevention. May 2014. Archived from the original on 6 April 2016.
- ^ CDC. "Adverse Childhood Experiences Reported by Adults --- Five States, 2009". Retrieved 15 July 2014.
- ^ Vincent J. Felitti. "Finding Your ACE Score" (PDF). The Adverse Childhood Experiences Study. Retrieved 25 March 2014.
- ^ Clinton Gudmunson; Lisa Ryherd; Karen Bougher; Jacy Downey; Meghan Gillette. Central Iowa ACEs Steering Committee (ed.). "Adverse Childhood Experiences in Iowa: A New Way of Understanding Lifelong Health: Findings From the 2012 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ L. Bynum; T. Griffin; D.L. Ridings; R.F. Anda; V.J. Edwards; T.W. Strine; Y. Liu; L.R. McKnight-Eily; J.B. Croft (December 17, 2010). "Adverse Childhood Experiences Reported by Adults --- Five States, 2009". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report: 1609–1613.
- ^ "ACEs 360 - New York".
- ^ "ACEs 360 - Arizona".
- ^ "The Philadelphia Urban ACE Study". 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ Stevens, Jane Ellen (November 2, 2012). "Survey finds teen, young mothers using Crittenton services have alarmingly high ACE scores". ACEs Too High!. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ "Adverse Childhood Experiences International Questionnaire (ACE-IQ)". World Health Organization. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ Adriana Baban; Alina Cosma; Robert Balazsi; Dinesh Sethi; Victor Olsavszky (2013). "Survey of Adverse Childhood Experiences among Romanian university students" (PDF). World Health Organization.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Adverse childhood experiences survey among young people in the Czech Republic". World Health Organization. December 23, 2012. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ Marija Raleva; Dimitrinka Jordanova Peshevska; Dinesh Sethi (2013). "Survey of Adverse Childhood Experiences Among Young People in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" (PDF). World Health Organization. Retrieved 29 March 2014.
- ^ "Adverse Childhood Experiences: National and State-Level Prevalance" (PDF). Child Trends. Retrieved 13 August 2014.
- ^ Weiss JS, Wagner SH (1998). "What explains the negative consequences of adverse childhood experiences on adult health? Insights from cognitive and neuroscience research (editorial)". American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 14 (4): 356–360. doi:10.1016/S0749-3797(98)00011-7. PMID 9635084.
- ^ Anda RF; Felitti VJ; Bremner JD; et al. (April 2006). "The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood". European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 256 (3): 174–186. doi:10.1007/s00406-005-0624-4. PMC 3232061. PMID 16311898.
- ^ Danese A; McEwen BS (April 12, 2012). "Adverse childhood experiences, allostasis, allostatic load, and age-related disease". Physiology & Behavior. 106 (1): 29–39. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.08.019.
- ^ Teicher, M.D., Martin H. "Windows of Vulnerability: Understanding how early stress alters trajectories of brain development and sets the stage for the emergence of mental disorders" (PDF). The Balanced Mind. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ a b Kolassa, Iris - Tatjana. "Biological memory of childhood maltreatment – current knowledge and recommendations for future research" (PDF). Ulmer Volltextserver - Institutional Repository der Universität Ulm. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ Sorrow, April (May 30, 2013). "Study uncovers cost of resiliency in kids". medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ Moffitt, Terrie E. (November 2013). "Childhood exposure to violence and lifelong health: Clinical intervention science and stress-biology research join forces". Development and Psychopathology. 25 (4pt2). The Klaus-Grawe 2012 Think Tank. Cambridge University Press: 1619–1634. doi:10.1017/S0954579413000801. PMC 3869039. PMID 24342859.
- ^ Rogosch FA; Dackis MN; Cicchetti D (November 2011). "Child maltreatment and allostatic load: consequences for physical and mental health in children from low-income families". Development and Psychopathology. 23 (4). Cambridge University Press: 1107–24. doi:10.1017/S0954579411000587. PMC 3513367. PMID 22018084.
- ^ Stevens "Community Projects", ACEs Connection, 25 September 2012
- ^ Saenger "PEACE4TARPON Trauma Informed Community Initiative", 30 March 2014
- ^ a b Stevens "Tarpon Springs, FL, may be first trauma-informed city in U.S.", ACEs Too High, 13 February 2012
- ^ Australian Childhood Foundation www.childhood.org.au "Making SPACE for Learning. Trauma Informed Practice in Schools", 2010
- ^ a b c Stevens "Spokane, WA, students’ trauma prompts search for solutions", ACEs Too High, 28 February 2012
- ^ Stevens "Toxic stress from childhood trauma causes obesity, too", ACEs Too High, 23 May 2012
- ^ a b c Stevens "Massachusetts, Washington State lead U.S. trauma-sensitive school movement", ACEs Too High, 31 May 2012
- ^ Stevens, Jane Ellen (April 13, 2012). "Lincoln High School in Walla Walla, WA, tries new approach to school discipline — suspensions drop 85%". ACEs Too High!. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- ^ Stevens "There’s no such thing as a bad kid in these Spokane, WA, trauma-informed elementary schools", ACEs Too High, 20 August 2013
- ^ Stevens "San Francisco’s El Dorado Elementary uses trauma-informed & restorative practices; suspensions drop 89%", ACEs Too High, 28 January 2014
- ^ a b Meister "Addressing Child Traumatic Stress in Child Welfare", Common Ground, July 2012
- ^ Family-Informed Trauma Treatment Center 15 July 2014
- ^ a b Stevens "‘Starve the beast,’ say these cities – but don’t cut people off; reduce need for services instead", ACEs Too High, 30 July 2012
- ^ a b Bebout "Waiting on the welcome mat: How to be at home with trauma-informed care", camh Cross Currents, Winter 2010/2011
- ^ ACEs 360 "‘ACEs 360-New York", ACEs 360 Iowa, Retrieved 15 July 2014
- ^ Larkin et al. "‘Mobilizing resilience and recovery in response to adverse childhood experiences (ACE) among homeless people: A Restorative Integral Support (RIS) case study", Prevention Summit, Retrieved 15 July 2014
- ^ Ruiz "How Childhood Trauma Could Be Mistaken for ADHD", The Atlantic, 7 July 2014
- ^ a b Stevens "To prevent childhood trauma, pediatricians screen children and their parents…and sometimes, just parents…for childhood trauma", ACEs Too High, 29 July 2014
- ^ American Academy of Pediatrics "Promoting Children’s Health and Resiliency: A Strengthening Families Approach", Center for the Study of Social Policy
- ^ Gottlieb "Toxic Stress and Trauma-Informed Pediatric Care", Massachusetts Child Psychiatry Access Project
- ^ Montefiore Medical Group "Healthy Steps Program", Montefiore Medical Group
- ^ a b https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2015/03/03/377569539/even-some-doctors-fear-these-10-questions
- ^ a b Hellerstedt "Adverse Childhood Experience: Public Health Surveillance Measures", Healthy Generations, Spring 2013
- ^ Stevens "Public health clinic adds child trauma to smoking, alcohol, HIV screening", ACEs Too High, 23 March 2012
- ^ a b Miller & Najavits "Creating trauma-informed correctional care: a balance of goals and environment", European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 2012
- ^ Seeking Safety "Seeking Safety: A Model to Improve Coping Skills", Seeking Safety
- ^ Buffington et al. "Ten Things Every Juvenile Court Judge Should Know About Trauma and Delinquency", NCJFCJ, 2010
- ^ a b National Association of State Mental Health Program Director "Creating A Place Of Healing and Forgiveness: The Trauma-Informed Care Initiative at the Women’s Community Correctional Center of Hawaii", NASMHPD, 2013
- ^ The National Child Traumatic Stress Network "Creating A Trauma-Informed Law Enforcement System", NCTSN, April 2018
- ^ http://aceovercomers.com/about-us.html
- ^ Stevens "Ex-pastor marries science, Bible studies to heal wounds of childhood trauma", ACEs Connection, 13 March 2012
- ^ ACES Connection Network
- ^ Faith and Health Connection ministry
- ^ http://legislature.vermont.gov/assets/Documents/2018/Docs/ACTS/ACT043/ACT043%20As%20Enacted.pdf
- ^ "No. 43. An act relating to building resilience for individuals experiencing adverse childhood experiences" (PDF). Vermont Legislature.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Prewitt "Vermont first state to propose bill to screen for ACEs in health care", ACEs Connection, 18 March 2014
- ^ Prewitt "CA Senate unanimously approves ACEs reduction resolution", ACEs Too High, 21 August 2014
- ^ Prewitt "Massachusetts "Safe and Supportive Schools" provisions signed into law, boosts trauma-informed school movement", ACEs Too High, 13 August 2014
Further reading
- Felitti, Vincent J. (2002). "The Relation Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Adult Health: Turning Gold into Lead" (PDF). The Permanente Journal. 6 (1): 44–47.
External links
- CAPT: Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) via Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
- Adverse Childhood Experiences Resources Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Adverse Childhood Experiences: Risk Factors for Substance Misuse and Mental Health Dr. Robert Anda, co-principal investigator, explains some of the study's basic findings (video)
- Center on the Developing Child, Harvard University (Environmental factors in child development)
- Take The ACE Quiz – And Learn What It Does And Doesn't Mean National Public Radio
- The ACE Score Acestudy.org
- ^ "The road to resilience". apa.org. 2017-10-16. Retrieved 2017-10-16.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help)
