History of atomic theory
This article focuses on the historical models of the atom. For a history of the study of how atoms combine to form molecules, see History of the molecule.
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms, as opposed to the theory notion that matter could be divided into any arbitrarily small quantity. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and India and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up particles. Its validity is still disputed.
The name "atom" (from the Greek word atomos, which means "indivisible"[1]) was attributed to the basic particle that constituted a chemical element, because the chemists of the era believed that these were the fundamental particles of matter. However, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called "indivisible atom" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.
Philosophical atomism
The concept that matter is composed of discrete units and cannot be divided into any arbitrarily small quantities has been around for thousands of years, but these ideas were founded in abstract, philosophical reasoning rather than scientific experimentation. The nature of atoms in philosophy varied considerably over time and between cultures and schools, and often had spiritual elements. Nevertheless, the basic idea of the atom was adopted by scientists thousands of years later because it could elegantly explain new discoveries in the field of chemistry.
Indian
Some of the earliest known theories were developed in ancient India in the 6th century BCE by Kanada, a Hindu philosopher.[2] In Hindu philosophy, the Nyaya and Vaisheshika schools developed elaborate theories on how atoms combined into more complex objects (first in pairs, then trios of pairs),[2] but believed the interactions were ultimately driven by the will of God (specifically, the Hindu Ishvara), and that the atoms themselves were otherwise inactive, without physical properties of their own[citation needed]. By contrast, Jainic philosophy linked the behavior of matter to the nature of the atoms themselves. Each atom, according to Jaina philosophy, has one kind of taste, one smell, one color, and two kinds of touch, though it is unclear what was meant by “kind of touch”. Atoms can exist in one of two states: subtle, in which case they can fit in infinitesimally small spaces, and gross, in which case they have extension and occupy a finite space. Although atoms are made of the same basic substance, they can combine based on their eternal properties to produce any of six “aggregates,” which seem to correspond with the Greek concept of “elements”: earth, water, shadow, sense objects, karmic matter, and unfit matter.[3]
Greek
In the 5th century BCE, Democritus developed the concept of atoms in order to reconcile two conflicting schools of thought on the nature of reality. On one side was Heraclitus, who believed that the nature of all existence is change. On the other side was Parmenides, who believed instead that all change is illusion.
Parmenides denied the existence of motion, change and void. He believed all existence to be a single, all-encompassing and unchanging mass (a concept known as monism), and that change and motion were mere illusions. This conclusion, as well as the reasoning that lead to it, may indeed seem baffling to the modern empirical mind, but Parmenides explicitly rejected sensory experience as the path to an understanding of the universe, and instead used purely abstract reasoning. Firstly, he believed there is no such thing as void, equating it with non-being (ie "if the void is, then it is not nothing; therefore it is not the void"). This in turn meant that motion is impossible, because there is no void to move into.[4] He also wrote all that is must be an indivisible unity, for if it were manifold, then there would have to be a void that could divide it (and he did not believe the void exists). Finally, he stated that the all encompassing Unity is unchanging, for the Unity already encompasses all that is and can be.
Democritus accepted most of Parmenides's arguments, except for the idea that change is an illusion. He believed change was real, and if it was not then at least the illusion had to be explained. He thus supported the concept of void, and stated that the universe is made up of multiple indivisble Parmenidean entities that move around in the void. These entities, which are, are indeed unchangeable and indivisible ("atomos", the Greek word for uncuttable), but their arrangement in space is constantly changing. Democritus's atoms were made of the same material but had a limitless variety of shapes and sizes; this, coupled with their arrangement in space, explained all the different substances and objects in the universe.[5]
Islamic
During the 11th century (in the Islamic Golden Age), Islamic atomists developed atomic theories that represent a synthesis of both Greek and Indian atomism. Older Greek and Indian ideas were further developed by Islamic atomists, along with new Islamic ideas, such as the possibility of there being particles smaller than an atom. The most successful form of Islamic atomism was in the Asharite school of philosophy, most notably in the work of the philosopher al-Ghazali (1058-1111). In Asharite atomism, atoms are the only perpetual, material things in existence, and all else in the world is “accidental” meaning something that lasts for only an instant. Nothing accidental can be the cause of anything else, except perception, as it exists for a moment. Contingent events are not subject to natural physical causes, but are the direct result of God’s constant intervention, without which nothing could happen. Thus nature is completely dependent on God, which meshes with other Asharite Islamic ideas on causation, or the lack thereof.[6]
Modern atomic theory
Birth
In the early years of the 19th century, John Dalton developed his atomic theory in which he proposed that each chemical element is composed of atoms of a single, unique type, and that though they are both immutable and indestructible, they can combine to form more complex structures (chemical compounds). How precisely Dalton arrived at his theory is not entirely clear, but nonetheless it allowed him to explain various new discoveries in chemistry that he and his contemporaries made.
The first was the law of conservation of mass, formulated by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789, which states that the total mass in a chemical reaction remains constant (that is, the reactants have the same mass as the products).[7] This law suggested to Dalton that matter is fundamentally indestructible.
The second was the law of definite proportions. First proven by the French chemist Joseph Louis Proust in 1799,[8] this law states that if a compound is broken down into its constituent elements, then the masses of the constituents will always have the same proportions, regardless of the quantity or source of the original substance. Proust had synthesized copper carbonate through numerous methods and found that in each case the ingredients combined in the same proportions as they were produced when he broke down natural copper carbonate.
Dalton studied and expanded upon Proust's work to develop the law of multiple proportions: if two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element which combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small integers. One pair of reactions Dalton studied involved the combinations of "nitrous air", or what we now call nitric oxide (NO), and oxygen (O2). Under certain conditions, these gases formed an unknown product at a certain combining ratio (now known to be nitrogen dioxide (NO2)), but when he repeated the reaction under other conditions, exactly twice the amount of nitric oxide (a ratio of 1:2 -- small integers) reacted completely with oxygen to form a different product -- now known as dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3).
2NO + O2 → 2NO2
4NO + O2 → 2N2O3
Dalton also believed atomic theory could explain why water absorbed different gases in different proportions: for example, he found that water absorbed carbon dioxide far better than it absorbed nitrogen. Dalton hypothesized this was due to the differences in mass and complexity of the gases' respective particles. Indeed, carbon dioxide molecules (CO2) are heavier and larger than nitrogen molecules (N2).

In 1803 Dalton orally presented his first list of relative atomic weights for a number of substances. This paper was published in 1805, but he did not discuss there exactly how he obtained these figures.[9] The method was first revealed in 1807 by his acquaintance Thomas Thomson, in the third edition of Thomson's textbook, A System of Chemistry. Finally, Dalton published a full account in his own textbook, A New System of Chemical Philosophy, 1808 and 1810.
Dalton estimated the atomic weights according to the mass ratios in which they combined, with hydrogen being the basic unit. However, Dalton did not conceive that with some elements atoms exist in molecules – e.g. pure oxygen exists as O2. He also mistakenly believed that the simplest compound between any two elements is always one atom of each (so he thought water was HO, not H2O).[10] This, in addition to the crudity of his equipment, resulted in his table being highly flawed. For instance, he believed oxygen atoms were 5.5 times heavier than hydrogen atoms, because in water he measured 5.5 grams of oxygen for every 1 gram of hydrogen and believed the formula for water was HO (an oxygen atom is actually 16 times heavier than a hydrogen atom).
The flaw in Dalton's theory was corrected in 1811 by Amedeo Avogadro. Avogadro had proposed that equal volumes of any two gases, at equal temperature and pressure, contain equal numbers of molecules (in other words, the mass of a gas's particles does not affect its volume).[11] Avogadro's law allowed him to deduce the diatomic nature of numerous gases by studying the volumes at which they reacted. For instance: since two liters of hydrogen will react with just one liter of oxygen to produce two liters of water vapor (at constant pressure and temperature), it meant a single oxygen molecule splits in two in order to form two particles of water. Thus, Avogadro was able to offer more accurate estimates of the atomic mass of oxygen and various other elements, and firmly established the distinction between molecules and atoms.
In 1827, the British botanist Robert Brown observed that pollen particles floating in water constantly jiggled about for no apparent reason. In 1905, Albert Einstein theorized that this Brownian motion was caused by the water molecules continuously knocking the grains about, and developed a hypothetical mathematical model to describe it.[12] This model was validated experimentally in 1908 by French physicist Jean Perrin, thus providing additional validation for particle theory (and by extension atomic theory).
Discovery of subatomic particles

Atoms were thought to be the smallest possible division of matter until 1897 when J.J. Thomson discovered the electron through his work on cathode rays.[13] A Crookes tube is a sealed glass container in which two electrodes are separated by a vacuum. When a voltage is applied across the electrodes, cathode rays are generated, creating a glowing patch where they strike the glass at the opposite end of the tube. Through experimentation, Thomson discovered that the rays could be deflected by an electric field (in addition to magnetic fields, which was already known). He concluded that these rays, rather than being waves, were composed of negatively charged particles he called "corpuscles" (they would later be renamed electrons by other scientists).
Thomson believed that the corpuscles emerged from the very atoms of the electrode. He thus concluded that atoms were divisible, and that the corpuscles were their building blocks. To explain the overall neutral charge of the atom, he proposed that the corpuscles were distributed in a uniform sea or cloud of positive charge; this was the plum pudding model.[14]
Since atoms were found to be actually divisible, physicists later invented the term "elementary particles" to describe indivisible particles.
Discovery of the nucleus

Top: Expected results: alpha particles passing through the plum pudding model of the atom with negligible deflection.
Bottom: Observed results: a small portion of the particles were deflected, indicating a small, concentrated positive charge.
Thomson's plum pudding model was disproved in 1909 by one of his students, Ernest Rutherford, who discovered that most of the mass and positive charge of an atom is concentrated in a very small fraction of its volume, which he assumed to be at the very center.
In the gold foil experiment, Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden (colleagues of Rutherford working at his behest) shot alpha particles through a thin sheet of gold, striking a fluorescent screen that surrounded the sheet.[15] Given the very small mass of the electrons, the high momentum of the alpha particles and the unconcentrated distribution of positive charge of the plum pudding model, the experimenters expected all the alpha particles to either pass through without significant deflection or be absorbed. To their astonishment, a small fraction of the alpha particles experienced heavy deflection. This led Rutherford to propose the planetary model of the atom in which pointlike electrons orbited in the space around a massive, compact nucleus—like planets orbiting the Sun.[16]
Discovery of isotopes
While experimenting with the products of radioactive decay, in 1913 radiochemist Frederick Soddy discovered that there appeared to be more than one element at each position on the atomic table.[17] The term isotope was coined by Margaret Todd as a suitable name for these elements.
That same year, J.J. Thomson conducted an experiment in which he channeled a stream of neon ions through magnetic and electric fields, striking a photographic plate at the other end. He observed two glowing patches on the plate, which suggested two different deflection trajectories. Thomson concluded this was because some of the neon ions had a different mass.[18] The nature of this differing mass would later be explained by the discovery of neutrons in 1932.
Discovery of nuclear particles
In 1918, Rutherford bombarded nitrogen gas with alpha particles and observed hydrogen nuclei being emitted from the gas. Rutherford concluded that the hydrogen nuclei emerged from the nuclei of the nitrogen atoms themselves (in effect, he split the atom).[19] He later found that the positive charge of any atom could always be equated to that of an integer number of hydrogen nuclei. This, coupled with the facts that hydrogen was the lightest element known and that the atomic mass of every other element was roughly equivalent to a whole multiple of hydrogen's atomic mass, led him to conclude hydrogen nuclei were singular particles and a basic constituent of all atomic nuclei: the proton. Further experimentation by Rutherford found that the nuclear mass of most atoms exceeded that of the protons it possessed; he speculated that this surplus mass was composed of hitherto unknown neutrally charged particles, which were tentatively dubbed "neutrons".
In 1928, Walter Bothe observed that beryllium emitted a highly penetrating, electrically neutral radiation when bombarded with alpha particles. It was later discovered that this radiation could knock hydrogen atoms out of paraffin wax. Initially it was thought to be high-energy gamma radiation, since gamma radiation had a similar effect on electrons in metals, but James Chadwick found that the ionisation effect was too strong for it to be due to electromagnetic radiation. In 1932, he exposed various elements, such as hydrogen and nitrogen, to the mysterious "beryllium radiation", and by measuring the energies of the recoiling charged particles, he deduced that the radiation was actually composed of electrically neutral particles with a mass similar to that of a proton.[20] For his discovery of the neutron, Chadwick received the Nobel Prize in 1935.
Quantum physical models of the atom
The planetary model of the atom had shortcomings. Firstly, according to the Larmor formula in classical electromagnetism, an accelerating electric charge emits electromagnetic waves; an orbiting charge would steadily lose energy and spiral towards the nucleus, colliding with it in a small fraction of a second. Another phenomenon the model did not explain was why excited atoms only emit light within certain discrete spectra.
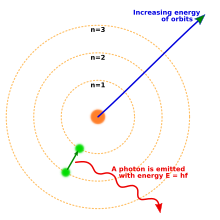
Quantum theory revolutionized physics at the beginning of the 20th century, when Max Planck and Albert Einstein postulated that light energy is emitted or absorbed in discrete amounts known as quanta (singular, quantum). In 1913, Niels Bohr incorporated this idea into his Bohr model of the atom, in which the electrons could only orbit the nucleus in particular circular orbits with fixed angular momentum and energy, their distances from the nucleus being proportional to their respective energies.[21] Under this model electrons could not spiral into the nucleus because they could not lose energy in a continuous manner; instead, they could only make instantaneous "quantum leaps" between the fixed energy levels.[21] When this occurred, light was emitted or absorbed at a frequency proportional to the change in energy (hence the absorption and emission of light in discrete spectra).[21]
Bohr's model was only able to predict the spectral lines of hydrogen; it couldn't predict those of multielectron atoms. Worse still, as spectrographic technology improved, additional spectral lines in hydrogen were observed which Bohr's model couldn't explain. In 1916, Arnold Sommerfeld added elliptical orbits to the Bohr model to explain the extra emission lines, but this made the model very difficult to use, and it still couldn't explain complex atoms.
In 1924, Louis de Broglie proposed that all moving particles–particularly subatomic particles such as electrons–exhibit a degree of wave-like behavior. Erwin Schrödinger, fascinated by this idea, explored whether or not the movement of an electron in an atom could be better explained as a wave rather than as a particle. Schrödinger's equation, published in 1926,[22] describes an electron as a wavefunction instead of as a point particle, and it elegantly predicted many of the spectral phenomena Bohr's model failed to explain. Although this concept was mathematically convenient, it was difficult to visualize, and faced opposition.[23] One of its critics, Max Born, proposed instead that Schrödinger's wavefunction described not the electron but rather all its possible states, and thus could be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron at any given location around the nucleus.[24]
Since a wavefunction incorporates time as well as position, it is impossible to simultaneously derive precise values for both the position and momentum of a particle for any given point in time; this became known as the uncertainty principle. This invalidated Bohr's model, with its neat, clearly defined circular orbits. The modern model of the atom describes the positions of electrons in an atom in terms of probabilities. An electron can potentially be found at any distance from the nucleus, but—depending on its energy level—tends to exist more frequently in certain regions around the nucleus than others; this pattern is referred to as its atomic orbital.
See also
Notes
- ^ "Atom". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 2008-02-10.
- ^ a b Teresi, Dick (2003). Lost Discoveries: The Ancient Roots of Modern Science. Simon & Schuster. pp. 213–214. ISBN 074324379X.
- ^ Gangopadhyaya, Mrinalkanti. Indian Atomism: History and Sources. Atlantic Highlands, New Jersey: Humanities Press, 1981. ISBN 0-391-02177-X
- ^ Bertrand Russel. (1946). History of Western Philosophy. pg 75. ISB 0-415-32505-6
- ^ Andre G. van Melsen. (1952) From Atomos to Atom. ISBN 0-486-49584-1
- ^ Gardet, L. “djuz’” in Encyclopaedia of Islam CD-ROM Edition, v. 1.1. Leiden: Brill, 2001.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Lavoisier, Antoine (1743-1794)." scienceworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Proust, Joseph Louis. "Researches on Copper", excerpted from Ann. chim. 32, 26-54 (1799) [as translated and reproduced in Henry M. Leicester and Herbert S. Klickstein, A Source Book in Chemistry, 1400-1900 (Cambridge, MA: Harvard, 1952)]. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Dalton, John. "On the Absorption of Gases by Water and Other Liquids", in Memoirs of the Literary and Philosophical Society of Manchester. 1803. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Johnson, Chris. "Avogadro - his contribution to chemistry." Last modified on July 4, 2004. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Avogadro, Amedeo. "Essay on a Manner of Determining the Relative Masses of the Elementary Molecules of Bodies, and the Proportions in Which They Enter into These Compounds." 1811. Journal de Physique, 73, 58-76. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Einstein, Albert. "On the Movement of Small Particles Suspended in Stationary Liquids Required by the Molecular-Kinetic Theory of Heat." Annal der Physik. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Thomson, J.J. "Cathode rays." Philosophical Magazine, 44, 293 (1897). [facsimile from Stephen Wright, Classical Scientific Papers, Physics (Mills and Boon, 1964).] Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Thomson, J.J. "On the Structure of the Atom: an Investigation of the Stability and Periods of Oscillation of a number of Corpuscles arranged at equal intervals around the Circumference of a Circle; with Application of the Results to the Theory of Atomic Structure." Philosophical Magazine March 1904. Series 6, Vol 7, No 39. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Geiger, H. "The Scattering of the α-Particles by Matter." Proceedings of the Royal Society February 17, 1910. Series A 82: 495–500. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Rutherford, Ernest. "The Scattering of α and β Particles by Matter and the Structure of the Atom." Philosophical Magazine. May 1911. Series 6, Vol. 21. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ "Frederick Soddy, The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1921". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-01-18.
- ^ Thomson, J.J. "Rays of positive electricity." Proceedings of the Royal Society. 1913. A 89, 1–20 [as excerpted in Henry A. Boorse & Lloyd Motz, The World of the Atom, Vol. 1 (New York: Basic Books, 1966)]. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Rutherford, Ernest. "Collisions of alpha Particles with Light Atoms. IV. An Anomalous Effect in Nitrogen." Philosophical Magazine. 1919. 6th series, 37, 581. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Chadwick, James. (February 27, 1932), "Possible Existence of a Neutron." Nature. February 27, 1932. p. 312. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ a b c Bohr, N. "On the constitution of atoms and molecules." Philosophical Magazine. July 1913. 26, 1-25. Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Schrödinger, Erwin. "Quantisation as an Eigenvalue Problem." Annalen der Physik.
- ^ Mahanti, Subodh. "Erwin Schrödinger: The Founder of Quantum Wave Mechanics." Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
- ^ Mahanti, Subodh. "Max Born: Founder of Lattice Dynamics." Retrieved on August 29, 2007.
