Mercury-Atlas 8
| COSPAR ID | 1962-052A |
|---|---|
| SATCAT no. | 00433 |
| Crew | |
| Members | 1 |

 | |
Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) was an early manned space mission, part of NASA's Mercury program. Astronaut Wally Schirra made six orbits of the Earth in the Sigma 7 spacecraft on 3 October 1962, in an almost completely flawless nine-hour flight focused primarily on "engineering evaluation" rather than on scientific experimentation.
This was the longest American orbital flight yet achieved in the Space Race, though well behind the almost four-day record set by the Soviet Vostok 3 earlier in the year. It helped confirm the Mercury spacecraft's long-duration capabilities in preparation for the one-day Mercury-Atlas 9 mission which followed the next year.
Background
At the end of 1961, both the United States and the Soviet Union had flown two solo spaceflights, in what was by then widely known as the "Space Race". However, there was a widespread perception that the United States was falling behind; its two missions had been suborbital, with only a few minutes in space, whilst the Soviet missions had both been in orbit - and the second, Vostok 2, had remained in orbit for a full day. There was a hope that the coming orbital Mercury missions would begin to make the "race" somewhat more equal.[6]
NASA's plans for the first two orbital missions were announced at a press conference at the end of November 1961, shortly after the landing of MA-5, which had orbited the earth twice carrying Enos, a chimpanzee. MA-6 was planned as the first orbital flight, with John Glenn as the primary crew and Scott Carpenter as his backup. The follow-up mission, MA-7 was to be crewed by Deke Slayton, with Wally Schirra as his backup.[7] In February 1962, the first draft planning began for MA-8, the third orbital mission, with a goal of "six or seven" orbits, as an intermediate step towards a day-long 18-orbit flight.[8] The decision to move to six orbits rather than seven was driven by the mission rules on contingency recovery operations; a seventh orbit would have required significant additional recovery forces to be able to reach the capsule anywhere on its trajectory within eighteen hours. The six-orbit profile had other effects on the recovery plans; the optimum recovery point was moved to the Pacific Ocean, rather than the Atlantic.[9]
On March 15 1962, NASA announced that Slayton was medically unfit, and would be replaced by Scott Carpenter as the prime crew for the MA-7 mission.[10] The decision to replace him with Carpenter, rather than his official backup Schirra, was justified by the large amount of training Carpenter had managed whilst preparing for the long-delayed MA-6 mission.[11] After the success of the MA-6 and MA-7 missions, both of three orbits, pressure began to mount to fly an extended mission. On June 27 1962, NASA first announced its plan for the upcoming MA-8 mission, which would last for "as many as six" orbits. Schirra was named as the prime crew for MA-8, with Gordon Cooper as his backup, repeating the backup-one fly-one pattern set by the previous two missions.[12] The pattern would be repeated for MA-9, flown by Cooper, and the planned but cancelled MA-10, which would have been flown by Cooper's backup, Alan Shepard.
The Soviet Union had not flown any further flights by the time MA-7 landed, putting both sides of the "space race" even at two orbital flights each. Whilst the Soviets had flown for longer, the Mercury program was gaining momentum, with a six-orbit mission currently planned and press speculation about a one-day mission.[13] However, in mid-August, the Soviet Union launched two orbital missions, Vostok 3 and Vostok 4, within a day of each other. The two craft were in intersecting orbits, but despite much speculation did not attempt to rendezvous; they completed missions of 64 and 48 orbits respectively, just under four and three days, landing within a few minutes of each other on August 15. This was far ahead of anything currently planned for Mercury, and NASA quickly considered the prospect of modifying a capsule to have an active manoeuvring and rendezvous capability, using technology being developed for the Gemini program. However, after examining the time and safety implications of this proposal, it was decided to abandon the idea and continue with the planned six-orbit mission.[14]
Mission objectives

The original MA-8 flight plan was issued on July 27; although it was revised slightly in August and September, it remained broadly unchanged until launch. This was an improvement on the situation with MA-7, which had had frequent and extensive alterations, making it difficult for the pilot to train efficiently. The aim was for the flight to be an "engineering mission", focusing on the operation of the spacecraft rather than on scientific experimentation, to help pave the way for a future long-duration mission.[15] Schirra chose the name "Sigma 7" for the capsule in reflection of this focus. using the mathematical symbol for summation as appropriate for an "engineering evaluation", and the "7" to refer to the seven Mercury astronauts.[16]
The mission objectives involved evaluating the performance of the spacecraft over six orbits, as well as the effect of prolonged microgravity on the pilot. The specific spacecraft systems would also be evaluated and tested, and the worldwide tracking and communications network would be tested to see how well it would stand up in an extended mission.[17] The flight control experiments included manually turning the spacecraft around, yaw and pitch manoeuvres to determine how easy it was to control the spacecraft attitude, realignment of the onboard gyroscopes in flight, and leaving the spacecraft to "drift" on-orbit.[18]

Four 'non-engineering' scientific experiments were planned, two requiring the active involvement of the astronaut and two completely passive. The first involved the astronaut watching for four high-powered flares whilst passing over Woomera, Australia, and for a xenon arc lamp whilst passing over Durban, South Africa.[19] The second involved two sets of photographs to be taken using a 70mm Hasselblad camera; as well as conventional colour photographs of the Earth from orbit, focusing on geological features and cloud patterns, photographs were to be taken through a set of coloured filters provided by the U. S. Weather Bureau. The latter were intended to help calibrate the spectral reflectivity of clouds and surface features, which in turn would help improve the cameras on future weather satellites.[20] The passive experimentation packages were two sets of radiation-sensitive photographic films, from the Goddard Space Flight Center and the U. S. Navy School of Aviation Medicine, and a set of eight different experimental ablative materials attached to the outside of the spacecraft to test their performance during re-entry.[21]
Spacecraft modifications
The spacecraft and booster were almost identical to those used on the two preceding Mercury orbital flights. The spacecraft had heating blankets removed from the retrorocket motors, to save weight, whilst a SOFAR bomb was added. This would be ejected at the time the main parachute was deployed, and would help recovery crews find the spacecraft after it landed.[22] A number of modifications were made to the reaction control system,[23] and the communications equipment was upgraded.[24]
The Atlas booster had been modified since the previous flight, and now included a modified fuel injector and a new hypergolic fuel igniter instead of the original pyrotechnic igniter.[25]
Mission preparation
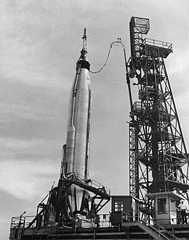
The capsule built for the mission, Mercury Spacecraft #16, had been delivered to Cape Canaveral on January 16, 1962.[26] The Atlas LV-3B booster assigned to the mission, number 113-D, was accepted by NASA at the Convair plant on 27 July and delivered on August 8.[27] In late July, the launch date was set for September 18, but delays with the Atlas booster's delivery and a series of technical concerns with the safety of the rocket motors caused it to be pushed back several weeks. On September 6, the tests were scheduled to continue until September 24, which allowed for a probable launch on October 3.[28] The booster was test-fired on September 8 to test changes to the engine combustion,[29] and reported as ready for assembly on September 18.[30]
Concerns had been raised that the radiation belt produced in orbit by the recent Operation Dominic nuclear tests would be dangerous to manned space missions, but an extensive study announced in early September declared that it was safe to fly. Whilst the outside of the capsule was expected to receive a dosage of around 500 röntgens, the study concluded that shielding and the effect of the spacecraft structure would reduce this to around 8 röntgens experienced by the astronaut, well within established tolerance limits.[31]
Schirra began training for the mission in early July, logging twenty-nine hours in simulators as well as thirty-one hours in the spacecraft itself. This included multiple systems tests and three simulated flights, culminating in a six-and-a-half-hour simulated flight on September 29, with the spacecraft and booster fully stacked on the pad.[32] Highlights of the training period included a visit from President John F. Kennedy, on September 11.[33]
The mission was reported as ready to go - "except for the weather" - on October 1. The major concern with the weather was a major tropical storm in the Atlantic, though there were also worries over a series of typhoons in the Pacific which could pose a problem for recovery operations. On the evening of October 2, the decision was taken to launch the next morning.[34]
Launch

Schirra was awakened at 1:40 am on the morning of October 2, and after a hearty breakfast—including a bluefish he had speared the day before—and a brief physical he left for the launchpad at around 4 am.[35] He entered the spacecraft at 4:41, where he found a steak sandwich left for him in the "glove compartment", and began the pre-launch checks. The launch countdown proceeded as planned until 6:15, when there was a fifteen-minute hold to allow the Canary Islands tracking station to repair a radar set.[36] The countdown resumed at 6:30, and proceeded through to booster ignition with no further delays. The launch itself began nominally, but after ten seconds the booster began to roll clockwise, threatening a possible abort. However, after a few tense moments, the roll stopped as suddenly as it had begun.[37] This was later identified as being due to a slight misalignment of the main engines, and was kept under control by the booster's vernier thrusters.[38]
Around three and a half minutes into the flight, Deke Slayton, the capsule communicator, cut in to ask Schirra "Are you a turtle today?" Schirra, nonplussed, announced that he was switching to the on-board voice recorder (rather than the broadcast radio circuit) to leave his answer; the mission communications transcript noted this as "[correct answer recorded]".[39] The "turtle club" was a recurrent joke among the astronaut corps; on being challenged with this question, the correct response was "you bet your sweet ass I am", with a failure to give the password being punishable by buying a round of drinks. Schirra noted later that he "wasn't ready for all the world to hear it", and chose to use the on-board recorder to finesse his way out of giving the answer over the air.[40]
The booster engines cut off two seconds earlier than planned, but the sustainer engine burned for about ten seconds longer than intended, giving an extra fifteen feet-per-second of velocity and putting the spacecraft in a slightly higher orbit than planned.[37] Initial analysis of the trajectory confirmed that the capsule could remain in a stable orbit for at least seven orbits, ensuring there would be no need for an early deorbit.[41]
Orbital activities

After separating from the Atlas booster, Schirra stabilised the spacecraft and slowly cartwheeled into the correct attitude; he deliberately kept the motion slow to conserve fuel, and was able to position the capsule using half a percent of his fuel reserves.[37] He briefly tracked the spent booster, which was rotating slowly past, but made no attempt to move towards it. As the spacecraft moved across the Atlantic, he turned his attention to testing manual control of the spacecraft, which he found sloppy compared to the fly-by-wire system.[42]
Crossing over the eastern coast of Africa, he began to feel overheated; this problem was also apparent to the ground controllers, who were having a debate with the flight surgeon over whether it was safe to continue or if the mission should be ended after the first orbit. The flight director, Christopher Kraft, followed the surgeon's advice to see if the problem would settle, and gave the go for a second orbit.[43] Schirra eventually stabilised the problem over time, slowly dialling the suit's control knob to a high cooling setting;[44] he compared the heat to that of "mowing a lawn in Texas".[45]
Over Australia, Schirra watched for a flare launched from the ground, but it was occluded by clouds; he, was however, able to see lightning and the lit outline of Brisbane. Through the night pass over the Pacific, he tested the capsule's on-board periscope, though he found it difficult to use and quickly covered it up as soon as the sun rose. Crossing over Mexico, he reported that he was in "chimp configuration", with the capsule running entirely on automatic without any input from the pilot, and as he began his second orbit began testing a yaw manoeuvre using the Earth through the main window as a reference, rather than via the much-maligned periscope.[44]

On the second orbit, he confirmed the existence of Glenn's "fireflies", the shower of small bright particles first reported on MA-6, and during the night section practised yaw manoeuvres using first the Moon and then known stars as reference points. The second proved difficult to work with, as the small windows of the Mercury capsule gave a very limited field of view, making it hard to identify constellations. Travelling across the Pacific, he again fell back into automatic flight, chatting with Gus Grissom at the Hawaiian tracking station about the qualities of the manual control system.[46]
As he began the third orbit, Schirra disconnected the spacecraft's gyroscopes, turned off part of the electrical power system, and let the capsule drift. He took advantage of this quiet period to test his spatial awareness and motor control, which he found was broadly unaffected by weightlessness, and to eat a light meal. He powered the spacecraft back up over the Indian Ocean, and continued over the Pacific. At Hawaii, he was given clearance for a full six-orbit mission, and as he crossed over towards California shut down the electrical power for a second period of drifting flight, during which he occupied himself taking photographs with the onboard camera.[47]
On the fourth orbit, drifting in an inverted spacecraft with the Earth "above" him, Schirra continued his photography and attempted - unsuccessfully - to spot the Echo 1 satellite whilst passing over East Africa. As he approached California, he spoke briefly to John Glenn in a two-minute conversation broadcast live across the United States on radio and television. Problems began to recur with the pressure suit, with water condensing on the faceplate; Schirra was concerned about the internal temperature, and avoided opening the visor to clean it for fear of the suit temperature misbehaving again.[48]

By the fifth orbit, Schirra had begun to relax, commenting that it was the first rest he had had since December 1961. He used a small bungee cord exercise device for "a little bit of stretching", before dropping into manual attitude control, where he reported a sudden burst of oversteering and high fuel use. Over the Atlantic he returned to observation and photography; he failed to spot the planned high-power light near Durban, in South Africa, due to cloud cover, but did make out the brightly lit city of Port Elizabeth. Over the Philippines, he reported on his fuel status; after four and a half of the planned six orbits, he still had eighty percent remaining in both manual and automatic fuel tanks.[49] Passing over Quito, Ecuador, towards the end of his fifth orbit, Schirra was asked by the tracking station if he had any message to pass on "in Spanish to the fellows down here", and he made some comments on how beautiful the country appeared from orbit, ending with a cheery "Buenos Dias, y'all!"[50] Schirra later noted that he was "furious" at this point - he was preparing for re-entry, and didn't want to be distracted with making public statements.[51]
The sixth orbit was dominated by preparations for re-entry, though Schirra was able to take a last set of photographs of South America and try another set of spatial-orientation tests. He armed the retrorockets passing over the western Pacific, and fired the first one at 8:52 mission elapsed time. The automatic control system held the capsule "steady as a rock" during this period, though after the retrorockets had stopped firing Schirra noted that the system had burned almost a quarter of its fuel in the process.[52]
Re-entry and recovery



As the spacecraft continued towards re-entry after the deorbit burn, Schirra used the high-power thrusters to put the capsule in the correct orientation, noting that the attitude control felt "sloppy". He then enabled the rate stabilization control system, an automatic control method which used up fuel at a very high rate, to maintain control during re-entry; this was a specific engineering request, and it dismayed Schirra to see the fuel he had husbanded for six orbits to be used so quickly.[53]
The local recovery group in the prime target area, in the central Pacific, consisted of an aircraft carrier, the USS Kearsarge, in the centre of the landing area, with three destroyers strung out along the orbital path. Four search aircraft were also assigned to the area, and three recovery helicopters were based aboard the Kearsarge.[54]
The Kearsarge picked up the capsule on radar while still two hundred miles from landing; ninety miles further up the landing path, the destroyer USS Renshaw reported a sonic boom as it passed overhead. At 40,000 feet, Schirra deployed the drogue parachute, and then the main parachute at 15,000 feet. The landing was surprisingly precise, four and a half miles from the target point and half a mile from the Kearsarge, and Schirra joked that he was on course for the recovery carrier's "number three elevator". The capsule hit the water, sank and bobbed to the surface again, righting itself after about thirty seconds. Three pararescue swimmers were dropped by one of the helicopters to help him climb out, but Schirra radioed that he would prefer to be towed to the carrier, and a whaleboat from the Kearsarge was sent with a line.[55]
Forty minutes after landing, Sigma 7 was hoisted aboard the Kearsarge; five minutes later, Schirra blew the explosive hatch and climbed out to a waiting crowd.[56] He remained aboard for three days of medical tests and debriefing before disembarking, whilst the spacecraft was offloaded at Midway Island and transferred to an aircraft for further transport.[57] It was returned to Cape Canaveral for analysis, with the long-term intention of putting it on permanent display.[58]
The spent Atlas booster re-entered the atmosphere on October 4, the day after the launch, where it burned up.[59] After a period on display at the Johnson Space Center, the capsule is currently displayed at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame, Titusville, Florida.[60][61]
Post-flight
The post-flight analysis reported no major malfunctions - the only troublesome anomaly being the suit temperature controls - and all the engineering objectives of the mission were deemed successfully completed.[17] The fuel-conservation measures were found to have worked particularly well, with even less fuel than anticipated being consumed; despite the technical changes, the official report placed the credit for this firmly on the shoulders of the pilot.[62] The medical analysis found no significant physiological effects from nine hours of weightlessness, and noted that Schirra had received no significant radiation exposure.[63] Analysis of the radiation-sensitive plates confirmed that there had been a very low radioactive flux inside the spacecraft,[64] and the six ablative materials tested were all deemed broadly satisfactory despite some difficulty comparing them to each other.[65]
Scientifically, the light-observation experiments were unsuccessful, as both target locations were covered by thick cloud cover. However, Schirra was able to view lightning near Woomera, and noted the lights of a city a few hundred miles from Durban.[66] The filtered photography for the Weather Bureau worked as planned, with fifteen photographs taken; the conventional colour photography was less successful, with several of the fourteen photographs unusable due to overexposure or excess cloud cover.[67] In the end, the conventional photographs were not used for scientific examination due to these problems.[68] Schirra noted that the sheer amount of cloud coverage, worldwide, could provide problems for future activity of this kind; however, Africa, and the south-western United States, were perfectly clear.[69]
Schirra's post-flight report noted the "fireflies" seen on the previous two missions, and emphasised the remarkable visual effect of the thick band of the atmosphere visible around the horizon.[70] However, he was unimpressed with the view of the earth from space; the amount of detail he could make out compared well with that from high-flying aircraft, and told debriefers that it was "nothing new" compared to flight at 50,000 feet.[71] Overall, he concluded that Sigma 7 was on "the top of the list" of aircraft he had flown, displacing the F8F Bearcat, a naval piston-engined fighter,[72] whilst the mission itself had been "textbook".[73]
Schirra gave a public lecture at Rice University after returning to Houston, where he received a motorcade through the city.[74] However, the Cuban Missile Crisis had been steadily escalating through September, and helped drive discussion of Schirra's successful flight down the news schedules; public concern about the relative effectiveness of Soviet and American space launchers was displaced by a more pressing concern over Soviet military rockets.[75] He visited Washington, DC, to receive the NASA Distinguished Service Medal from President Kennedy on 16 October, the same day Kennedy had first seen U-2 photographs of missile sites in Cuba; the meeting was friendly and informal despite the circumstances. Robert Kennedy, Schirra later noted, took him aside and sounded him out about a potential political career, the same way he had sounded out John Glenn a year earlier. Unlike Glenn, however, Schirra politely turned the suggestion down.[76]
The success of MA-8 made the preparation for MA-9 "considerably easier",[77] though it did cause some observers to suggest the program should be ended abruptly in order to conclude on a clear note of success, rather than risking another - potentially catastrophic - flight.[78] However, this was not a view shared by the NASA planners, who had been pressing for a one-day Mercury mission since mid-1961, when it first began to seem technically feasible.[79] However, to prepare the spacecraft for a long-duration mission involved trimming as much on-board weight as possible to offset the additional consumables required. The changes made to the capsule hardware on MA-8 were now used to justify the removal of 12lbs of control equipment and 5lbs of radio equipment, as well as the 76lb periscope which Schirra had found so unhelpful. In total, there were 183 alterations listed between the capsules for the MA-8 and MA-9 missions.[80] The spacecraft was to be equipped with several cameras, building on Schirra's photographic work, though weight and power limitations did restrict the amount of scientific experiments that could be scheduled.[81]
Notes
- ^ Boynton, p. 3
- ^ Boynton, p. 34
- ^ Boynton, p. 34
- ^ a b c d e Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 15
- ^ Boynton, p. 14. This is the on-orbit mass; the mass at launch was 1,300lb heavier and the mass at re-entry some 300lb lighter. By the time spare fuel and the landing parachute had been jettisoned, the spacecraft massed just 2,440lb when afloat at the end of the mission.
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 411
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 407
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 462
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 464
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 440
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 443
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 460
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 459-460
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 461-2
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 461
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 470-71
- ^ a b Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 1
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, pp. 42-5
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 8
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, pp. 8-9
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, pp. 9-10
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 2
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 3
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 4
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 10
- ^ Grimwood, p. 157
- ^ Grimwood, p. 169
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 467
- ^ Grimwood, p. 170
- ^ Grimwood, pp. 171-2
- ^ Grimwood, p. 170. To put this in context, an unprotected dose of 500 röntgens over a few hours would be easily fatal.
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 40
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 39
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 471
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 471-2
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 472
- ^ a b c This New Ocean, p. 473
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 11
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 57
- ^ Schirra's Space, pp. 91-92
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 51
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 474. Schirra noted after his flight that a rendezvous in orbit would certainly be possible, given sufficient fuel and precise positioning information; he would later go on to fly the Gemini 6A mission, the first successful close rendezvous of two spacecraft.
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 474
- ^ a b This New Ocean, p. 475
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 476
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 476-7
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 478
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 479-80
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 480-1
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 111
- ^ Schirra's Space, p. 88
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 481-82
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 482
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 20
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 482-3
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 484
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 22
- ^ Grimwood, p. 174
- ^ Royal Aeronautical Establishment satellite tables, 1962, p.31.
- ^ Sigma 7 display page, A Field Guide to American Spacecraft. James H. Gerard, 2007.
- ^ United States Astronaut Hall of Fame, Kennedy Space Center
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, pp. 3-4
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 23
- ^ Boynton, pp. 74-75
- ^ Boynton, pp. 75-77
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 8
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 9
- ^ Boynton, p. 74
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 52
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 53
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 477
- ^ Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight, p. 55. The Bearcat was the first fighter Schirra had flown after training, and he remembered it as "not a plane you climb into; rather, you strap it on". (Schirra's Space, p. 24)
- ^ First US manned six-pass orbital mission, p. 53
- ^ Schirra's Space, p. 91
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 486
- ^ Schirra's Space, p. 92
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 486
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 486-7
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 487
- ^ This New Ocean, p. 490
- ^ This New Ocean, pp. 491-492
References
- Grimwood, J. M. (1963). Project Mercury : a chronology. NASA. Retrieved 2009-08-23. HTML copy
- Alexander, C. C.; Grimwood, J. M.; Swenson, L. S. (1966). This new ocean : a history of Project Mercury. NASA. Retrieved 2009-08-23.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) HTML copy - Results of the third U.S. manned orbital space flight. NASA. 1962. Retrieved 2009-08-27. HTML copy
- Boynton, J. H. (1968). First U.S. manned six-pass orbital mission. NASA. Retrieved 2009-08-27.
- Schirra, Wally, & Billings, Richard N. (1995). Schirra's space. Naval Institute Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)

