Norsemen

Norsemen is used to refer to the group of people as a whole who speak one of the North Germanic languages as their native language. ("Norse", in particular, refers to the Old Norse language belonging to the North Germanic branch of Indo-European languages, especially Norwegian, Icelandic, Swedish and Danish in their earlier forms.)
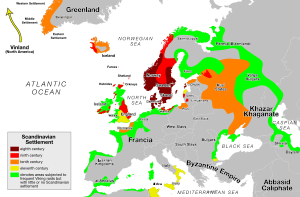
The meaning of Norseman was "people from the North" and was applied primarily to Nordic people originating from southern and central Scandinavia. They established states and settlements in areas which today are part of the Faroe Islands, England, Scotland, Wales, Iceland, Finland, Ireland, Russia, Italy, Canada, Greenland, France, Ukraine, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Germany.
Norse and Norsemen are applied to the Scandinavian population of the period from the late 8th century to the 11th century. The term "Normans" was later primarily associated with the people of Norse origin in Normandy, France, assimilated into French culture and language. The term Norse-Gaels (Gall Goidel, lit:foreign Gaelic) was used concerning the people of Norse descent in Ireland and Scotland, who assimilated into the Gaelic culture.
Vikings has been a common term for Norsemen in the early medieval period, especially in connection with raids and monastic plundering made by Norsemen in Great Britain and Ireland. Northmen was famously used in the prayer A furore normannorum libera nos domine ("From the fury of the Northmen deliver us, O Lord!"), doubtfully attributed to monks of the English monasteries plundered by Viking raids in the 8th and 9th centuries.
Other names
The Northmen were also known as Ascomanni, "ashmen", by the Germans,[1] Lochlanach (Norse) by the Irish and Dene (Danes) by the Anglo-Saxons.
The Slavs, the Arabs and the Byzantines knew them as the Rus' or Rhōs, probably derived from various uses of rōþs-, i.e. "related to rowing", or derived from the area of Roslagen in east-central Sweden, where most of the Norsemen who visited the Slavic lands came from. Archaeologists and historians of today believe that these Scandinavian settlements in the Slavic lands formed the names of the countries Russia and Belarus).
The Slavs and the Byzantines also called them Varangians (ON: Væringjar, meaning "sworn men" or from Slavic варяги with meaning enemies), and the Scandinavian bodyguards of the Byzantine emperors were known as the Varangian Guard.
Modern Scandinavian usage
In the Old Norse language, the term norrœnir menn ("northern men"), was used to refer to the North Germanic population of Scandinavia (Swedes, Danes, Norwegians and Icelanders), thus corresponding to the modern English name Norsemen.
In the modern Scandinavian languages, no common word for Norsemen exists. In Swedish, the term nordmän is used, which corresponds to "Northmen". The Norwegians and Danish lack a word for the ancient North Germanic peoples. Usually they are simply (but incorrectly) called Vikings in both Denmark, Norway, as well as Sweden. In Norway, nordmann is the common demonym for a Norwegian. In Icelandic, Norðmaður means a man from Norway, but Norræn maður is the term for a "North Germanic man" (or "woman"/"people").
The word nordbo however, (Sw.: nordborna, Da.: nordboerne, No.: nordboerne or nordbuane in the definite plural) is used for both ancient and modern people living in the Nordic countries (Sw., Da., No.: Norden) and speaking one of the North Germanic languages (Sw.: de nordiska språken, Da.: de nordiske sprog, No.: de nordiske språkene, Is.: Norrænt mál, Norrænt tungumál, or Norræn tunga).
Notes and references
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (January 2009) |
- ^ Adam of Bremen 2.29.
See also
- Danes
- Danish people
- Faroese
- Geats
- Gotlanders
- Goths
- Norse-Gaels (Gall Goidel)
- Icelanders
- Normans
- Norwegians
- Rus'
- Scandinavians
- Swedes
- Varangian
- Viking
