Great Barrier Reef
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Criteria | Natural: vii, viii, ix, x |
| Reference | 154 |
| Inscription | 1981 (5th Session) |
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest reef system[1][2] composed of over 2,900 individual reefs[3] and 900 islands stretching for over 2,600 kilometres (1,600 mi) over an area of approximately 344,400 square kilometres (133,000 sq mi).[4][5] The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland in northeast Australia.
The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms.[6] This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps.[7] This reef supports a wide diversity of life, and was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981.[1][2] CNN labeled it one of the seven natural wonders of the world.[8] The Queensland National Trust named it a state icon of Queensland.[9]
A large part of the reef is protected by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, which helps to limit the impact of human use, such as fishing and tourism. Other environmental pressures on the reef and its ecosystem include runoff, climate change accompanied by mass coral bleaching, and cyclic population outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns starfish.
The Great Barrier Reef has long been known to and used by the Aboriginal Australian and Torres Strait Islander peoples, and is an important part of local groups' cultures and spirituality. The reef is a very popular destination for tourists, especially in the Whitsunday Islands and Cairns regions. Tourism is an important economic activity for the region. Fishing generates AU$ 1 billion per year.[10]
Geology and geography

The Great Barrier Reef is a distinct feature of the East Australian Cordillera division. It includes the smaller Murray Islands.[11] It reaches from Torres Strait (between Bramble Cay, its northernmost island, and the south coast of Papua New Guinea) in the north to the unnamed passage between Lady Elliot Island (its southernmost island) and Fraser Island in the south. Lady Elliot Island is located 1,915 km (1,190 mi) southeast of Bramble Cay as the crow flies.[12]
Australia has moved northwards at a rate of 7 cm (2.8 in) per year, starting during the Cainozoic.[13] Eastern Australia experienced a period of tectonic uplift, which moved the drainage divide in Queensland 400 km (250 mi) inland. Also during this time, Queensland experienced volcanic eruptions leading to central and shield volcanoes and basalt flows.[14] Some of these granitic outcrops have become high islands.[15] After the Coral Sea Basin formed, coral reefs began to grow in the Basin, but until about 25 million years ago, northern Queensland was still in temperate waters south of the tropics—too cool to support coral growth.[16] The Great Barrier Reef's development history is complex; after Queensland drifted into tropical waters, it was largely influenced by reef growth and decline as sea level changed.[17] They can increase in diameter by 1 to 3 centimetres (0.39 to 1.18 in) per year, and grow vertically anywhere from 1 to 25 cm (0.39 to 9.84 in) per year; however, they grow only above a depth of 150 metres (490 ft) due to their need for sunlight, and cannot grow above sea level.[18] When Queensland edged into tropical waters 24 million years ago, some coral grew,[19] but a sedimentation regime quickly developed with erosion of the Great Dividing Range; creating river deltas, oozes and turbidites, unsuitable conditions for coral growth. 10 million years ago, the sea level significantly lowered, which further enabled sedimentation. The reef's substrate may have needed to build up from the sediment until its edge was too far away for suspended sediments to inhibit coral growth. In addition, approximately 400,000 years ago there was a particularly warm interglacial period with higher sea levels and a 4 °C (39 °F) water temperature change.[20]

The land that formed the substrate of the current Great Barrier Reef was a coastal plain formed from the eroded sediments of the Great Dividing Range with some larger hills (some of which were themselves remnants of older reefs[21] or volcanoes[15]).[13] The Reef Research Centre, a Cooperative Research Centre, has found coral 'skeleton' deposits that date back half a million years.[22] The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (GBRMPA) considers the earliest evidence of complete reef structures to have been 600,000 years ago.[23]According to the GBRMPA, the current, living reef structure is believed to have begun growing on the older platform about 20,000 years ago.[23] The Australian Institute of Marine Science agrees, placing the beginning of the growth of the current reef at the time of the Last Glacial Maximum. At around that time, sea level was 120 metres (390 ft) lower than it is today.[21]
From 20,000 years ago until 6,000 years ago, sea level rose steadily. As it rose, the corals could then grow higher on the hills of the coastal plain. By around 13,000 years ago the sea level was only 60 metres (200 ft) lower than the present day, and corals began to grow around the hills of the coastal plain, which were, by then, continental islands. As the sea level rose further still, most of the continental islands were submerged. The corals could then overgrow the hills, to form the present cays and reefs. Sea level here has not risen significantly in the last 6,000 years.[21] The CRC Reef Research Centre estimates the age of the present, living reef structure at 6-8,000 years old.[22]
The remains of an ancient barrier reef similar to the Great Barrier Reef can be found in The Kimberley, a northern region of Western Australia.[24]
The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area has been divided into 70 bioregions,[25] of which 30 are reef bioregions.[26].[27] In the northern part of the Great Barrier Reef, ribbon reefs and deltaic reefs have formed; these structures are not found in the rest of the reef system.[22] There are no atolls in the system,[28] and reefs attached to the mainland are rare.[13]
Fringing reefs are distributed widely, but are most common towards the southern part of the Great Barrier Reef, attached to high islands, for example, the Whitsunday Islands. Lagoonal reefs are found in the southern Great Barrier Reef, and further north, off the coast of Princess Charlotte Bay. Cresentic reefs are the most common shape of reef in the middle of the system, for example the reefs surrounding Lizard Island. Cresentic reefs are also found in the far north of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, and in the Swain Reefs (20-22 degrees south). Planar reefs are found in the northern and southern parts, near Cape York Peninsula, Princess Charlotte Bay, and Cairns. Most of the islands on the reef are found on planar reefs.[29]
Ecology
The Great Barrier Reef supports a diversity of life, including many vulnerable or endangered species, some of which may be endemic to the reef system.[30][31]

Thirty species of whales, dolphins, and porpoises have been recorded in the Great Barrier Reef, including the dwarf minke whale, Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin, and the humpback whale. Large populations of dugongs live there.[32][33][31]
Six species of sea turtles come to the reef to breed – the green sea turtle, leatherback sea turtle, hawksbill turtle, loggerhead sea turtle, flatback turtle, and the olive ridley. The green sea turtles on the Great Barrier Reef have two genetically distinct populations, one in the northern part of the reef and the other in the southern part.[34] Fifteen species of seagrass in beds attract the dugongs and turtles,[32] and provide fish habitat.[35] The most common genera of seagrasses are Halophila and Halodule.[36]
Saltwater crocodiles live in mangrove and salt marshes on the coast near the reef.[37] Nesting has not been reported, and the salt water crocodile population in the GBRWHA is wide-ranging but low density.[38] Around 125 species of shark, stingray, skates or chimaera live on the reef.[39][40] Close to 5,000 species of mollusc have been recorded on the reef, including the giant clam and various nudibranchs and cone snails.[32] Forty-nine species of pipefish and nine species of seahorse have been recorded.[38] At least seven species of frog inhabit the islands.[41]
215 species of birds (including 22 species of seabirds and 32 species of shorebirds) visit the reef or nest or roost on the islands,[42] including the white-bellied sea eagle and roseate tern.[32] Most nesting sites are on islands in the northern and southern regions of the Great Barrier Reef, with 1.4-1.7 million birds using the sites to breed.[43][44] The islands of the Great Barrier Reef also support 2,195 known plant species; three of these are endemic. The northern islands have 300-350 plant species which tend to be woody, whereas the southern islands have 200 which tend to be herbaceous; the Whitsunday region is the most diverse, supporting 1,141 species. The plants are propagated by birds.[41]
Seventeen species of sea snake live on the Great Barrier Reef in warm waters up to Template:M to ft deep and are more common in the southern than in the northern section. None found in the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area are endemic, nor are any endangered.[38]
More than 1,500 fish species live on the reef, including the clownfish, red bass, red-throat emperor, and several species of snapper and coral trout.[32] Forty-nine species mass spawn, while eighty-four other species spawn elsewhere in their range.[45]
There are at least 330 species of ascidians on the reef system, ranging in size from 1–10 cm (0.39–3.94 in) in diameter. Between 300-500 species of bryozoans live on the reef.[40]
Four hundred coral species, both hard corals and soft corals inhabit the reef.[32] The majority of these spawn gametes, breeding in mass spawning events that are triggered by the rising sea temperatures of spring and summer, the lunar cycle, and the diurnal cycle. Reefs in the inner Great Barrier Reef spawn during the week after the full moon in October, while the outer reefs spawn in November and December.[46] Its common soft corals belong to 36 genera.[47] Five hundred species of marine algae or seaweed live on the reef,[32] including thirteen species of genus Halimeda, which deposit calcareous mounds up to 100 metres (110 yd) wide, creating mini-ecosystems on their surface which have been compared to rainforest cover.[48]
Environmental threats
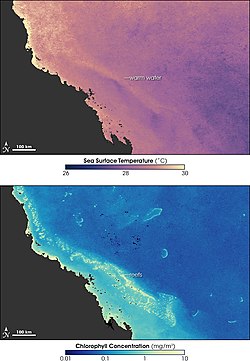
Climate change, pollution, crown-of-thorns starfish and fishing are the primary threats to the health of this reef system. Other threats include shipping accidents, oil spills, and tropical cyclones.[49] Skeletal Eroding Band, a disease of bony corals caused by the protozoan Halofolliculina corallasia, affects 31 coral species.[50]
Shipping
On April 4th, 2010, The Chinese coal-carrying ship Shen Neng 1 ran aground at full speed late Saturday on Douglas Shoals, spilling oil into the water.
Climate change
Scientists claim climate change could be a major threat to the Great Barrier Reef. With increase in Ocean temperatures a plausable cause of Coral Bleaching.[51][52][53] Mass coral bleaching events due to elevated ocean temperatures occurred in the summers of 1998, 2002 and 2006,[54] and coral bleaching is expected to become an annual occurrence.[55] Climate change has implications for other forms of reef life—some fish's preferred temperature range leads them to seek new habitat, thus increasing chick mortality in predatory seabirds. Climate change will also affect the population and sea turtle's available habitat.[56]
Pollution
Another key threat faced by the Great Barrier Reef is pollution and declining water quality. The rivers of north eastern Australia pollute the Reef during tropical flood events. Over 90% of this pollution comes from farm runoff.[57] Farm run-off is polluted by overgrazing, excessive fertiliser use and pesticide use.
The runoff problem is exacerbated by the loss of coastal wetlands which act as a natural filter for toxins and help deposit sediment.[58][59][60] It is thought that the poor water quality is due to increased light and oxygen competition from algae.[61]
Crown of thorns

The crown-of-thorns starfish preys on coral polyps. Large outbreaks of these starfish can devastate reefs. In 2000, an outbreak contributed to a loss of 66% of live coral cover on sampled reefs in a study by the RRC (Reefs Research Centre.)[62] Outbreaks are believed to occur in natural cycles, worsened by poor water quality and overfishing of the starfish's predators.[62][63]
Fishing
The unsustainable overfishing of keystone species, such as the Giant Triton, can disrupt food chains vital to reef life. Fishing also impacts the reef through increased water pollution from boats, by-catch of unwanted species (such as dolphins and turtles) and habitat destruction from trawling, anchors and nets.[64] As of the middle of 2004, approximately one-third of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park is protected from species removal of any kind, including fishing, without written permission.[65]
Human use
The Great Barrier Reef has long been known to and used by the Aboriginal Australian and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Aboriginal Australians have been living in the area for at least 40,000 years,[66] and Torres Strait Islanders since about 10,000 years ago.[67] For these 70 or so clan groups, the reef is also an important cultural feature.[68]
Portuguese explorers were probably the first Europeans to encounter the reef, in the sixteenth century, probably led by Cristóvão de Mendonça. Willem Jansz, sailing the Duyfken charted the western coast of Cape York. In 1768, Louis de Bougainville found the reef during an exploratory mission, but did not claim the area for the French.[69] On June 11, 1770, the HM Bark Endeavour, captained by explorer James Cook, ran aground on the Great Barrier Reef, sustaining considerable damage. Lightening the ship and re-floating it during an incoming tide eventually saved it.[70] One of the most famous wrecks was the HMS Pandora, which sank on August 29, 1791, killing 35. The Queensland Museum has led archaeological digs to the Pandora since 1983.[71] Because the reef had no atolls, it was largely unstudied in the 19th century.[28] During this time, some of the reef's islands were mined for deposits of guano, and lighthouses were built as beacons throughout the system.[72] as in Raine Island, the earliest example.[73] In 1922, the Great Barrier Reef Committee began carrying out much of the early research on the reef.[74]

Management
After the Royal Commissions' findings, in 1975 the Government of Australia created the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park and prohibited various activities.[75] The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park does not include the entire Great Barrier Reef Province.[12] The park is managed, in partnership with the Government of Queensland, through the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority to ensure that it is used in a sustainable manner. A combination of zoning, management plans, permits, education and incentives (such as eco-tourism certification) are employed in the effort to conserve the reef.[49][76]
In July 2004, a new zoning plan took effect for the entire Marine Park, and has been widely acclaimed as a new global benchmark for marine ecosystem conservation.[77] The rezoning was based on the application of systematic conservation planning techniques, using MARXAN software.[78] While protection across the Marine Park was improved, the highly protected zones increased from 4.5% to over 33.3%.[79] At the time, it was the largest marine protected area in the world, although in 2006, the new Northwestern Hawaiian Islands National Monument became the largest.[80]
In 2006, a review of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975 recommended are that there should be no further zoning plan changes until 2013, and that every five years, a peer-reviewed Outlook Report should be published, examining the reef's health, management, and environmental pressures.[5][81]
Tourism
Due to its vast biodiversity, warm clear waters and accessibility from the tourist boats called 'live aboards', the reef is a very popular destination, especially scuba divers. Tourism on the Great Barrier Reef is concentrated in the Whitsundays and Cairns due to their accessibility. These areas make up 7% of the Park's area.[49] The Whitsundays and Cairns have their own Plans of Management.[82] Many cities along the Queensland coast offer daily boat trips. Several continental and coral cay islands are now resorts, including the pristine Lady Elliot Island. As of 1996, 27 islands on the Great Barrier Reef supported resorts.[49]

Domestic tourism made up most of the tourism in the region as of 1996, and the most popular visiting times were in the Australian winter. It was estimated that tourists to the Great Barrier Reef contributed $AU 776 million per annum at this time.[83]
As the largest commercial activity in the region, it was estimated in 2003 that tourism in the Great Barrier Reef generates over AU$4 billion annually.[84] (A 2005 estimate puts the figure at AU$5.1 billion.[82]) Approximately two million people visit the Great Barrier Reef each year.[85] Although most of these visits are managed in partnership with the marine tourism industry, there is a concern amongst the general public that tourism is harmful to the Great Barrier Reef.[49]
A variety of boat tours and cruises are offered, from single day trips, to longer voyages. Boat sizes range from dinghies to superyachts.[86] Glass-bottomed boats and underwater observatories are also popular, as are helicopter flights.[87][88] By far, the most popular tourist activities on the Great Barrier Reef are snorkelling and diving, for which pontoons are often used, and the area is often enclosed by nets. The outer part of the Great Barrier Reef is favoured for such activities, due to water quality.
Management of tourism in the Great Barrier Reef is geared towards making tourism ecologically sustainable. A daily fee is levied that goes towards research of the Great Barrier Reef.[82] This fee ends up being 20% of the GBRMPA's income.[89] Policies on cruise ships, bareboat charters, and anchorages limit the traffic on the Great Barrier Reef.[82]
Fishing
The fishing industry in the Great Barrier Reef, controlled by the Queensland Government, is worth AU$1 billion annually.[10] It employs approximately 2000 people, and fishing in the Great Barrier Reef is pursued commercially, for recreation, and as a traditional means for feeding one's family.[68] Wonky holes in the reef provide particularly productive fishing areas.
See also
References
- ^ a b UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1980). "Protected Areas and World Heritage - Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area". Department of the Environment and Heritage. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b "The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Values". Retrieved 3 September 2008.
- ^ The Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area, which is 348,000 km squared, has 2900 reefs. However, this does not include the reefs found in the Torres Strait, which has an estimated area of 37,000 km squared and with a possible 750 reefs and shoals. (Hopley et al., 2007, p.1)
- ^ Fodor's. "Great Barrier Reef Travel Guide". Retrieved 8 August 2006.
- ^ a b Department of the Environment and Heritage. "Review of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975". Retrieved 2 November 2006.
- ^ Sarah Belfield (8 February 2002). "Great Barrier Reef: no buried treasure". Geoscience Australia (Australian Government). Retrieved 11 June 2007.
- ^ Sharon Guynup (4 September 2000). "Australia's Great Barrier Reef". Science World. Retrieved 11 June 2007.
- ^ CNN (1997). "The Seven Natural Wonders of the World". Retrieved 6 August 2006.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ National Trust Queensland. "Queensland Icons". Retrieved 17 October 2006.
- ^ a b Access Economics Pty Ltd (2005). "Measuring the economic and financial value of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park" (PDF). Retrieved 16 March 2007. (PDF)
- ^ Physiographic Diagram of Australia, A.K. Lobeck, by The Geological Press, Columbia University, New York, 1951. ... "to accompany text description and geological sections which were prepared by Joseph Gentili and R.W. Fairbridge of the University of Western Australia"
- ^ a b "Great Barrier Reef General Reference Map" (PDF). Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. September 2004. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b c Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 18. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 19. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 26. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 27. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 27–28. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ MSN Encarta (2006). Great Barrier Reef. Archived from the original on 31 October 2009. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 29. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 37. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Tobin, Barry (1998, revised 2003). "How the Great Barrier Reef was formed". Australian Institute of Marine Science. Retrieved 22 November 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ a b c CRC Reef Research Centre Ltd. "What is the Great Barrier Reef?". Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ a b Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2006). "A "big picture" view of the Great Barrier Reef" (PDF). Reef Facts for Tour Guides. Retrieved 18 June 2007.
- ^ Western Australia's Department of Environment and Conservation (2007). "The Devonian 'Great Barrier Reef'". Retrieved 12 March 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Representative Areas in the Marine Park". Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 23 March 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Marine Park Authority. "Protecting the Bioregions of the Great Barrier Reef" (PDF).
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Bio-region Information Sheets". Retrieved 23 March 2007.
- ^ a b Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 7. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 158–160. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ CSIRO (2006). "Snapshot of life deep in the Great Barrier Reef". Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ a b Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2000). "Fauna and Flora of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area". Retrieved 24 November 2006.
- ^ a b c d e f g CRC Reef Research Centre Ltd. "Reef facts: Plants and Animals on the Great Barrier Reef". Retrieved 14 July 2006.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2004). "Environmental Status: Marine Mammals". The State of the Great Barrier Reef Report - latest updates. Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ Dobbs, Kirstin (2007). Marine turtle and dugong habitats in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park used to implement biophysical operational principles for the Representative Areas Program (PDF). Great Barrier Marine Park Authority.
- ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 133. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2005). "Environmental Status: Seagrasses". The State of the Great Barrier Reef Report - latest updates. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2005). "Environmental Status: Marine Reptiles".
- ^ a b c "Appendix 2 - Listed Marine Species". Fauna and Flora of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. 2000. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ "Environmental Status: Sharks and rays". The State of the Great Barrier Reef Report - latest updates. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ a b "Appendix 4- Other species of conservation concern". Fauna and Flora of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. 2000. Retrieved 13 September 2007.
- ^ a b "Appendix 5- Island Flora and Fauna". Fauna and Flora of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. 2000. Retrieved 13 September 2007.
- ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 450–451. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Environmental status: birds". The State of the Great Barrier Reef Report - latest updates. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ "Environmental status: birds Condition". The State of the Great Barrier Reef Report - latest updates. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Fish Spawning Aggregation Sites On The Great Barrier Reef". Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2006). "Information Fact Sheets #20 Coral Spawning" (PDF). Retrieved 27 May 2007.
- ^ Australian Institute of Marine Science (2002). "Soft coral atlas of the Great Barrier Reef". Retrieved 27 May 2007.
- ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 185. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Harriott, V.J. (2002). "Marine tourism impacts and their management on the Great Barrier Reef" (PDF). CRC Reef Research Centre Technical Report No. 46. CRC Reef Research Centre. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ "AIMS Longterm Monitoring - Coral Diseases on the Great Barrier Reef - Skeletal Eroding Band". www.aims.gov.au. Retrieved 22 August 2009.
- ^ Monckton, Christopher (18 October 2007). "35 Inconvenient Truths, The errors in Al Gore's movie" (PDF). Science & Public Policy Institute. Retrieved 25 March 2010.
- ^ Rothwell, Don; Stephens, Tim (19 November 2004). "Global climate change, the Great Barrier Reef and our obligations". The National Forum. Retrieved 26 September 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Our changing climate". Retrieved 26 September 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Coral Bleaching and Mass Bleaching Events". Retrieved 30 May 2006.
- ^ The The Daily Telegraph - 30 January 2007 - Online version
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Climate change and the Great Barrier Reef". Retrieved 16 March 2007.
- ^ "Coastal water quality" (PDF). The State of the Environment Report Queensland 2003. Environment Protection Agency Queensland. 2003. Retrieved 7 June 2007.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Wetlands". Retrieved 13 March 2007.
- ^ Brodie, J. (2007). "Nutrient management zones in the Great Barrier Reef Catchment: A decision system for zone selection" (PDF). Australian Centre for Tropical Freshwater Research. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Australian Government Productivity Commission (2003). "Industries, Land Use and Water Quality in the Great Barrier Reef Catchment - Key Points". Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2006). "Principal water quality influences on Great Barrier Reef ecosystems". Retrieved 22 October 2006.
- ^ a b "CRC Reef Research Centre Technical Report No. 32 — Crown-of-thorns starfish(Acanthaster planci) in the central Great Barrier Reef region. Results of fine-scale surveys conducted in 1999-2000". Retrieved 7 June 2007.
- ^ RRC Reef Research Centre. "Crown-of-thorns starfish on the Great Barrier Reef" (PDF). Retrieved 28 August 2006. (PDF)
- ^ CSIRO Marine Research (1998). "Environmental Effects of Prawn Trawling". Archived from the original on 25 January 2008. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Marine Park Zoning". Retrieved 8 August 2006.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2006 date). "Fact Sheet No. 4 - Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander People and the Great Barrier Reef. Region" (PDF). Retrieved 28 May 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "reefED - GBR Traditional Owners". Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ a b Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Aboriginal & Torres Strait Islander Culture & Dugongs and Turtles". Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 23 May 2007.
- ^ Bell, Peter. "A history of exploration and research on the Great Barrier Reef". Australian Institute of Marine Science. Retrieved 11 January 2010.
- ^
- ^ Queensland Museum. "HMS Pandora". Retrieved 12 October 2006.
- ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 452. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Raine Island Corporation". Retrieved 20 November 2007.
- ^ Hopley, David (2007). The geomorphology of the Great Barrier Reef : development, diversity, and change. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. p. 9. ISBN 0521853028.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Commonwealth of Australia (1975). "Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Act 1975". Retrieved 30 August 2006.
- ^ "Rewards Program". Onboard: The Tourism Operator's Handbook for the Great Barrier Reef. Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2003). "Zoning Plan 2003" (PDF). Retrieved 14 March 2009. (PDF)
- ^ Fernandes et al. (2005) Establishing representative no-take areas in the Great Barrier Reef: large-scale implementation of theory on marine protected areas, Conservation Biology, 19(6), 1733-1744.
- ^ World Wildlife Fund Australia. "Great Barrier Reef - WWF-Australia". Retrieved 10 November 2006.
- ^ BBC News (15 June 2006). "Bush creates new marine sanctuary". Retrieved 28 December 2008.
- ^ "Great Barrier Reef Outlook Report". Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. 2007. Retrieved 31 August 2007.
- ^ a b c d Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2005). "Protecting Biodiversity Brochure 2005". Retrieved 11 November 2006.
- ^ "Ecological Economics Criteria for Sustainable Tourism: Application to the Great Barrier Reef and Wet Tropics World Heritage Areas, Australia" (PDF). Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 4 (1). 1996. Retrieved 31 October 2008.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2003). "Summary report of the social and economic impacts of the rezoning of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park" (PDF). Retrieved 14 March 2009. (PDF)
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. "Number of Tourists Visiting The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park". Retrieved 12 October 2006.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2005). "What You Do". Onboard - The Tourism Operator's Handbook for the Great Barrier Reef. Retrieved 14 November 2006.
- ^ Saltzer, Rebecca (February 2002). "Uunderstanding Great Barrier Reef visitors preliminary results" (PDF). CRC Reef Project B2.1.1: Understanding Tourist Use of the GBRWHA. Cooperative Research Centre for the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Hildebrandt, Amy (January 2003). "Understanding Tourist Use of the Great Barrier Reef: The Whitsundays Visitor" (PDF). CRC Reef Project B2.1.1: Understanding Tourist Use of the GBRWHA. Cooperative Research Centre for the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. Retrieved 14 March 2009.
- ^ Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority (2005). "How is the Money Used?". Onboard - The Tourism Operator's Handbook for the Great Barrier Reef. Retrieved 11 November 2006.
Further reading
- Bell, Peter (1998). AIMS: The First Twenty-five Years. Townsville: Australian Institute of Marine Science. ISBN 9780642322128.
- Bowen, James (2002). The Great Barrier Reef : history, science, heritage. Cambridge : Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521824303.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Done, T.J. (1982). "Patterns in the distribution of coral communities across the central Great Barrier Reef". Coral Reefs. 1 (2): 95–107. doi:10.1007/BF00301691.
- Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority Research Publications
- Hutchings, Pat (2008). The Great Barrier Reef: Biology, Environment and Management. CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643095571.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Lucas, P.H.C.; et al. (1997). The outstanding universal value of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority. ISBN 0642230285.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - Mather, P.; Bennett, I., ed. (1993). A Coral Reef Handbook: A Guide to the Geology, Flora and Fauna of the Great Barrier Reef (3rd ed.). Chipping North: Surrey Beatty & Sons Pty Ltd. ISBN 0949324477.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link)
External links
- How the Great Barrier Reef Works
- Template:Wikitravelpar
- World heritage listing for Great Barrier Reef
- Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority
- CRC Reef Research Centre
- Biological monitoring of coral reefs of the GBR
- Great Barrier Reef (World Wildlife Fund)
- Dive into the Great Barrier Reef from National Geographic

