Tawny owl
| Tawny owl hgfdjrdidr | |
|---|---|

| |
| Brown individual, probably of subspecies Strix aluco aluco | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | S. aluco
|
| Binomial name | |
| Strix aluco | |

| |
The tawny owl or brown owl (Strix aluco) is a stocky, medium-sized owl commonly found in woodlands across much of Eurasia. Its underparts are pale with dark streaks, and the upperparts are either brown or grey. Several of the eleven recognised subspecies have both variants. The nest is typically in a tree hole where it can protect its eggs and young against potential predators. This owl is non-migratory and highly territorial. Many young birds starve if they cannot find a vacant territory once parental care ceases.
This nocturnal bird of prey hunts mainly rodents, usually by dropping from a perch to seize its prey, which it swallows whole; in more urban areas its diet includes a higher proportion of birds. Vision and hearing adaptations and silent flight aid its night hunting. The tawny owl is capable of catching smaller owls, but is itself vulnerable to the eagle owl or northern goshawk.
Although many people believe this owl has exceptional night vision, its retina is no more sensitive than a human's. Rather, it is its asymmetrically placed ears that are key to its hunting because they give the tawny owl excellent directional hearing. Its nocturnal habits and eerie, easily imitated call, have led to a mythical association of the tawny owl with bad luck and death.
Description
The tawny owl is a robust bird, 37–46 cm (15–18 in) in length, with an 81–105 cm (32–41 in) wingspan. Weight can range from 385 to 800 g (0.849 to 1.764 lb).[2][3] Its large rounded head lacks ear tufts, and the facial disc surrounding the dark brown eyes is usually rather plain. The nominate race has two morphs which differ in their plumage colour, one form having rufous brown upperparts and the other greyish brown, although intermediates also occur. The underparts of both morphs are whitish and streaked with brown.[4] This species is sexually dimorphic; the female is much larger than the male, 5% longer and more than 25% heavier.[5]
The tawny owl flies with long glides on rounded wings, less undulating and with fewer wingbeats than other Eurasian owls, and typically at a greater height. The flight of the tawny owl is rather heavy and slow, particularly at takeoff.[6] As with most owls, its flight is silent because of its feathers' soft, furry upper surfaces and a fringe on the leading edge of the outer primaries.[7] Its size, squat shape and broad wings distinguish it from other owls found within its range; great grey, eagle owl and Ural owls are similar in shape, but much larger.[6]
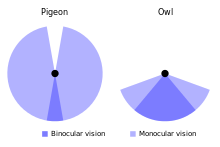
An owl's eyes are placed at the front of the head and have a field overlap of 50–70%, giving it better binocular vision than diurnal birds of prey (overlap 30–50%).[8] The tawny owl's retina has about 56,000 light-sensitive rod cells per square millimetre (36 million per square inch); although earlier claims that it could see in the infrared part of the spectrum have been dismissed,[9] it is still often said to have eyesight 10 to 100 times better than humans in low-light conditions. However, the experimental basis for this claim is probably inaccurate by at least a factor of 10.[10] The owl's actual visual acuity is only slightly greater than that of humans, and any increased sensitivity is due to optical factors rather than to greater retinal sensitivity; both humans and owl have reached the limit of resolution for the retinas of terrestrial vertebrates.[10]
Adaptations to night vision include the large size of the eye, its tubular shape, large numbers of closely packed retinal rods, and an absence of cone cells, since rod cells have superior light sensitivity. There are few coloured oil drops, which would reduce the light intensity.[11] Unlike diurnal birds of prey, owls normally have only one fovea, and that is poorly developed except in daytime hunters like the short-eared owl.[8]
Hearing is important for a nocturnal bird of prey, and as with other owls, the tawny owl's two ear openings differ in structure and are asymmetrically placed to improve directional hearing. A passage through the skull links the eardrums, and small differences in the time of arrival of a sound at each ear enables its source to be pinpointed. The left ear opening is higher on the head than the larger right ear and tilts downward, improving sensitivity to sounds from below.[8] Both ear openings are hidden under the facial disk feathers, which are structurally specialized to be transparent to sound, and are supported by a movable fold of skin (the pre-aural flap).[12]

The internal structure of the ear, which has large numbers of auditory neurons, gives an improved ability to detect low-frequency sounds at a distance, which could include rustling made by prey moving in vegetation.[12] The tawny owl's hearing is ten times better than a human's,[12] and it can hunt using this sense alone in the dark of a woodland on an overcast night, but the patter of raindrops makes it difficult to detect faint sounds, and prolonged wet weather can lead to starvation if the owl cannot hunt effectively.[8]
The commonly heard contact call is a shrill, kew-wick but the male has a quavering advertising song hoo...ho, ho, hoo-hoo-hoo-hoo. William Shakespeare used this owl's song in Love's Labour's Lost (Act 5, Scene 2) as "Then nightly sings the staring owl, Tu-whit; Tu-who, a merry note, While greasy Joan doth keel the pot", but this stereotypical call is actually a duet, with the female making the kew-wick sound, and the male responding hooo.[4] The call is easily imitated by blowing into cupped hands through slightly parted thumbs, and a study in Cambridgeshire found that this mimicry produced a response from the owl within 30 minutes in 94% of trials.[14] A male’s response to a broadcast song appears to be indicative of his health and vigour; owls with higher blood parasite loads use fewer high frequencies and a more limited range of frequencies in their responses to an apparent intruder.[15]
Geographical variation
Although both colour morphs occur in much of the European range, brown birds predominate in the more humid climate of western Europe, with the grey phase becoming more common further east; in the northernmost regions, all the owls are a cold-grey colour. Siberian and Central Asian subspecies have grey and white plumage, the North African race is dark grey-brown, and South and East Asian birds have barred, not striped, underparts, and fine lines around the facial disc. The Siberian and Scandinavian subspecies are 12% larger and 40% heavier, and have 13% longer wings than western European birds,[12] in accordance with Bergmann's rule which predicts that northern forms will typically be bigger than their southern counterparts.[16]
The plumage colour is genetically controlled, and studies in Finland and Italy indicate that grey-morph tawny owls have more reproductive success, better immune resistance, and fewer parasites than brown birds. Although this might suggest that eventually the brown morph could disappear, the owls show no colour preference when choosing a mate, so the adverse selection pressure is reduced. There are also environmental factors involved. The Italian study showed that brown-morph birds were found in denser woodland, and in Finland, Gloger's rule would suggest that paler birds would in any case predominate in the colder climate.[17][18]
Taxonomy

The species was first described by Linnaeus in his Systema naturae in 1758 under its current scientific name.[19] The binomial derives from Greek strix "owl" and Italian allocco, "tawny owl" (from Latin ulucus "screech-owl").[5]

The tawny owl is a member of the wood-owl genus Strix, part of the typical owl family Strigidae, which contains all species of owl other than the barn owls. Within its genus, the tawny owl's closest relatives are Hume's owl, Strix butleri, (formerly considered to be conspecific), the Himalayan owl, Strix nivicolum, (sometimes considered conspecific), its larger northern neighbour, the Ural owl, S. uralensis, and the North American barred owl, S. varia.[12] The Early–Middle Pleistocene Strix intermedia is sometimes considered a paleosubspecies of the tawny owl, which would make it that species' immediate ancestor.[20]
The tawny owl subspecies are often poorly differentiated, and may be at a flexible stage of subspecies formation with features related to the ambient temperature, the colour tone of the local habitat, and the size of available prey. Consequently, various authors have historically described between 10 and 15 subspecies.[12] The currently recognised subspecies are listed below.[21]
| Subspecies | Range | Described by (parentheses indicate originally in a different genus) |
|---|---|---|
| S. a. aluco | N & C Europe from Scandinavia to the Mediterranean and Black Sea | Linnaeus, 1758 |
| S. a. sylvatica | W Europe including Great Britain | Shaw, 1809 |
| S. a. biddulphi | NW Pakistan and Kashmir region | Scully, 1881 |
| S. a. willkonskii | Palestine to N Iran and the Caucasus | (Menzbier, 1896) |
| S. a. mauritanica | NW Africa from Morocco to Tunisia and Mauritania | (Witherby, 1905) |
| S. a. sanctinicolai | W Iran, NE Iraq | (Zarudny, 1905) |
| S. a. harmsi | Turkmenistan | (Zarudny, 1911) |
| S. a. siberiae | C Russia from Urals to W Siberia | Dementiev, 1933 |
Distribution and habitat

The tawny owl has a distribution stretching discontinuously across temperate Eurasia from Great Britain and the Iberian Peninsula eastwards to western Siberia, and India. The subspecies S. a. mauritanica extends the range into northwest Africa. This essentially non-migratory owl is absent from Ireland (probably because of competition from the long-eared owl), and only a rare vagrant to the Balearic and Canary Islands.[6]
This species is found in deciduous and mixed forests, and sometimes mature conifer plantations, preferring locations with access to water. Cemeteries, gardens and parks have allowed it to spread into urban areas, including central London. The tawny owl is mainly a lowland bird in the colder parts of its range, but breeds to 550 metres (1,800 ft) in Scotland, 1,600 m (5,200 ft) in the Alps, 2,350 m (7,710 ft) in Turkey,[6] and up to 2,800 m (9,200 ft) in Burma.[12]
The tawny owl has a geographical range of at least 10 million km2 (3.8 million mi2) and a large population including an estimated 970,000–2,000,000 individuals in Europe alone. Population trends have not been quantified, but there is evidence of an overall increase. This owl is not believed to meet the IUCN Red List criterion of declining more than 30% in ten years or three generations and is therefore evaluated as being of least concern.[1] This species has expanded its range in Belgium, the Netherlands, Norway and Ukraine, and populations are stable or increasing in most European countries. Declines have occurred in Finland, Estonia, Italy and Albania.[6]
Behaviour
Breeding


Tawny owls pair off from the age of one year, and stay together in a usually monogamous relationship for life. An established pair's territory is defended year-round and maintained with little, if any, boundary change from year to year. The pair sit in cover on a branch close to a tree trunk during the day, and usually roost separately from July to October.[6] Roosting owls may be discovered and "mobbed" by small birds during the day, but they normally ignore the disturbance.[12]
The tawny owl typically nests in a hole in a tree, but will also use old European magpie nests, squirrel drey or holes in buildings, and readily takes to nest boxes. It nests from February onwards in the south of its range, but rarely before mid-March in Scandinavia.[6] The glossy white eggs are 48 mm × 39 mm (1.9 in × 1.5 in) in size and weigh 39.0 g (1.38 oz) of which 7% is shell. The typical clutch of two or three eggs is incubated by the female alone for 30 days to hatching, and the altricial, downy chicks fledge in a further 35–39 days.[5] The young usually leave the nest up to ten days before fledging, and hide on nearby branches.[6]
This species is fearless in defence of its nest and young, and, like other Strix owls, strikes for the intruder's head with its sharp talons. Because its flight is silent, it may not be detected until it is too late to avoid the danger. Dogs, cats and humans may be assaulted, sometimes without provocation.[12] Perhaps the best-known victim of the tawny owl's fierce attack was the renowned bird photographer Eric Hosking, who lost his left eye when struck by a bird he was attempting to photograph near its nest. He later called his autobiography An Eye for a Bird.[22]
The parents care for young birds for two or three months after they fledge, but from August to November the juveniles disperse to find a territory of their own to occupy. If they fail to find a vacant territory, they usually starve.[6] The juvenile survival rate is unknown, but the annual survival rate for adults is 76.8%. The typical lifespan is five years,[5] but an age of over 18 years has been recorded for a wild tawny owl, and of over 27 years for a captive bird.[12]
Predators of the tawny owl include large birds such as Ural owls, eagle owls, northern goshawks, golden eagles, and common buzzards. Pine martens may raid nests, especially where artificial nest boxes make the owls easy to find, and several instances have been recorded of Eurasian jackdaws building nests on top of a brooding female tawny owl leading to the death of the adult and chicks.[12] A Danish study showed that predation by mammals, especially red foxes, was an important cause of mortality in newly fledged young, with 36% dying between fledging and independence. The mortality risk increased with fledging date from 14% in April to more than 58% in June, and increasing predation of late broods may be an important selective agent for early breeding in this species.[23]
This species is increasingly affected by avian malaria, the incidence of which has tripled in the last 70 years, in parallel with increasing global temperatures. An increase of one degree Celsius produces a two- to three-fold increase in the rate of malaria. In 2010, the incidence in British tawny owls was 60%, compared to 2–3% in 1996.[24]
Feeding

The tawny owl hunts almost entirely at night, watching from a perch before dropping or gliding silently down to its victim, but very occasionally it will hunt in daylight when it has young to feed. This species takes a wide range of prey, mainly woodland rodents, but also other mammals up to the size of a young rabbit, and birds, earthworms and beetles. In urban areas, birds make up a larger proportion of the diet, and species as unlikely as mallard and kittiwake have been killed and eaten.[6]
Prey is typically swallowed whole, with indigestible parts regurgitated as pellets. These are medium-sized and grey, consisting mainly of rodent fur and often with bones protruding, and are found in groups under trees used for roosting or nesting.[7]
Less powerful woodland owls such as the little owl and the long-eared owl cannot usually co-exist with the stronger tawny owls, which may take them as food items, and are found in different habitats; in Ireland the absence of the tawny owl allowed the long-eared owl to become the dominant owl. Similarly, where the tawny owl has moved into built-up areas, it tends to displace barn owls from their traditional nesting sites in buildings.[12]
In culture

The tawny owl, like its relatives, has often been seen as an omen of bad luck; William Shakespeare used it as such in Julius Caesar (Act 1 Scene 3): "And yesterday the bird of night did sit/ Even at noon-day upon the market-place/ Hooting and shrieking." John Ruskin is quoted as saying "Whatever wise people may say of them, I at least have found the owl's cry always prophetic of mischief to me".[25]
Wordsworth described the technique for calling an owl in his poem There was a Boy.[26]
And there, with fingers interwoven, both hands
Pressed closely palm to palm and to his mouth
Uplifted, he, as through an instrument,
Blew mimic hootings to the silent owls,
That they might answer him.—And they would shout
Across the watery vale, and shout again,
Responsive to his call,—with quivering peals,
And long halloos, and screams, and echoes loud
Redoubled and redoubled; concourse wild
Of jocund din!
References
- ^ a b Template:IUCN
- ^ CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
- ^ Eurasian Tawny Owl – Strix aluco. The Owl Pages
- ^ a b Mullarney, Killian; Svensson, Lars; Zetterstrom, Dan; Grant, Peter J. (1999). Collins Bird Guide. London: HarperCollins. p. 206. ISBN 0-00-219728-6.
- ^ a b c d "Tawny Owl Strix aluco [Linnaeus, 1758]". BirdFacts. British Trust for Ornithology (BTO). Retrieved 31 May 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Snow, David; Perrins, Christopher M. (editors) (1998). The Birds of the Western Palearctic concise edition (two volumes). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 907–910. ISBN 0-19-854099-X.
{{cite book}}:|author2=has generic name (help) - ^ a b Brown, Roy; Ferguson, John; Lawrence, Michael; Lees, David (1987). Tracks and Signs of the Birds of Britain and Europe (Helm Identification Guides). Christopher Helm. p. 86. ISBN 0-7470-0201-0.
- ^ a b c d Burton, Robert (1985). Bird Behaviour. London: Granada Publishing. pp. 44–48. ISBN 0-246-12440-7.
- ^ Hecht, Selig; Pirenne, Maurice Henri (1940). "The sensibility of the nocturnal long-eared owl in the spectrum" (Automatic PDF download). Journal of General Physiology. 23 (6): 709–717. doi:10.1085/jgp.23.6.709. PMC 2237955. PMID 19873186.
- ^ a b Martin, Graham R. (August 1977). "Absolute visual threshold and scotopic spectral sensitivity in the tawny owl Strix aluco". Nature. 268 (5621): 636–638. doi:10.1038/268636a0. PMID 895859.
- ^ Sinclair, Sandra (1985). How Animals See: Other Visions of Our World. Beckenham, Kent: Croom Helm. pp. 88–100. ISBN 0-7099-3336-3.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Voous, Karel H.; Cameron, Ad (illustrator) (1988). Owls of the Northern Hemisphere. London, Collins. pp. 209–219. ISBN 0-00-219493-7.
- ^ Based on Güntürkün, Onur, "Structure and functions of the eye" in Sturkie, P. D. (1998). Sturkie's Avian Physiology. 5th Edition. Academic Press, San Diego. pp. 1–18. ISBN 0-12-747605-9.
- ^ Waterton, Charles (1870). Essays on Natural History. Frederick Warne. p. 124.
- ^ Redpath, Stephen M.; Appleby, Bridget M.; Petty, Steve J. (2000). "Do male hoots betray parasite loads in Tawny Owls?". Journal of Avian Biology. 31 (4): 457–462. doi:10.1034/j.1600-048X.2000.310404.x.
- ^ Bergmann, Carl (1847). "Über die Verhältnisse der Wärmeökonomie der Thiere zu ihrer Grösse". Göttinger Studien (in German). 3 (1): 595–708.
- ^ Brommer, Jon E.; Kari, Ahola; Karstinen, Teuvo (2005). "The colour of fitness: plumage coloration and lifetime reproductive success in the tawny owl". Proceedings – Royal Society of London. Biological sciences. 272 (1566): 935–940. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3052. PMC 1564093. PMID 16024349.
- ^ Galeotti, Paolo; Sacchi, Roberto (2003). "Differential parasitaemia in the SNOWY OWLS ®(Strix aluco): effects of colour morph and habitat". Journal of Zoology. 261: 91–99. doi:10.1017/S0952836903003960.
- ^ Linnaeus, C (1758). Systema naturae per regna tria naturae, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis. Tomus I. Editio decima, reformata (in Latin). Holmiae. (Laurentii Salvii). p. 93.
S. capite laevi, corpore ferrugineo, iridíbus atris, remi-gibus primoribus serratís.
- ^ Template:De icon Jánossy D. (1972) "Die mittelpleistozäne Vogelfauna der Stránská skála". In: Musil R. (ed.): "Stránská skála I." Anthropos (Brno) 20: 35–64.
- ^ "Tawny Owl Strix aluco". Owl Information. World Owl Trust. Retrieved 6 June 2008.
- ^ Hosking, Eric; Lane, Frank W. (1972). An Eye for a Bird: The Autobiography of a Bird Photographer. London, Hutchinson & Co. p. 20. ISBN 0-09-104460-X.
- ^ Sunde, Peter (September 2005). "Predators control post-fledging mortality in tawny owls, Strix aluco". Oikos. 110 (3): 461–472, . doi:10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.14069.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ GaramszegI, László Z. (2011). "Climate change increases the risk of malaria in birds". Global Change Biology. 17 (5): 1751–1759. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02346.x.
- ^ Armstrong, Edward A. (1958). The Folklore of Birds: An Enquiry into the Origin and Distribution of Some Magico-Religious Traditions. London: Collins. p. 114.
- ^ Wordsworth, William; Coleridge, Samuel Taylor (1800). Lyrical Ballads. London: Longman.
External links
- ARKive – images and video of the tawny owl (Strix aluco)
- EBCC breeding map for Europe
- Ageing and sexing (PDF; 2.7 MB) by Javier Blasco-Zumeta & Gerd-Michael Heinze

