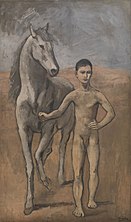Horses in art



Horses have appeared in works of art throughout history, frequently as depictions of the horse in battle. The horse appears less frequently in modern art partly because the horse is no longer significant either as a mode of transportation or as an implement of war. Most modern representations are of famous contemporary horses, artwork associated with horse racing, or artwork associated with the historic cowboy or Native American tradition of the American west. In the United Kingdom depictions of fox hunting and nostalgic rural scenes involving horses continue to be made.
Horses often appear in artworks singly, as a mount for an important person, or in teams, hitched to a variety of horse-drawn vehicles.
History


The horse appeared in prehistoric cave paintings such as those in the Lascaux caves,[1] estimated to be 16,000 years old.
Prehistoric hill figures have been carved in the shape of the horse, specifically the Uffington White Horse, an example of the tradition of horse carvings upon hill-sides, which having existed for thousands of years continues into the current age.[2]
The equine image was common in ancient Egyptian and Grecian art, more refined images displaying greater knowledge of equine anatomy appeared in Classical Greece and in later Roman work. [3] Horse-drawn chariots were commonly depicted in ancient works, for example on the Standard of Ur circa 2500BC. The Horses of Saint Mark are the sole surviving example from Classical Antiquity of a monumental statue of the Quadriga.
The horse was less prevalent in early Christian and Byzantine art, overwhelmed by the dominance of religious themes.
The Renaissance period starting in the 14th century brought a resurgence of the horse in art. Painters of this period who portrayed the horse included Paolo Uccello, Benozzo Gozzoli, Leonardo da Vinci, Albrecht Dürer, Raphael, Andrea Mantegna and Titian. In 1482 the Duke of Milan Ludovico il Moro, commissioned Leonardo da Vinci to create the largest equestrian statue in the world, a monument to the duke's father Francesco, however Leonardo's horse was never completed, (until it was replicated in the late 20th century).
In the Baroque era the tradition of equine portraiture was established, with artists such as Peter Paul Rubens, Anthony van Dyck and Diego Velázquez portraying regal subjects atop their mounts. Equine sporting art also became established in this era as the tradition of horse racing emerged under Tudor patronage.[3]
The mid 18th century saw the emergence of Romanticism, French artists Théodore Géricault and Eugène Delacroix were proponents of this movement and both portrayed the horse in many of their works.
George Stubbs born in 1724 became so associated with his equestrian subjects that he was known as "the horse painter". A childhood interest in anatomy was applied to the horse he spent eighteen months dissecting equine carcasses and had an engraver produce book plates of his studies. These anatomical drawings aided later artists.

Equine sporting art was popular in the 19th century, notable artists of the period being Benjamin Marshall, James Ward, Henry Thomas Alken, James Pollard and John Frederick Herring, Sr.. Horse racing gradually became more established in France and Impressionist painter Edgar Degas painted many early racing scenes. Degas was one of the first horse painters to use photographic references.[3] Eadweard Muybridge's photographic studies of animal motion had a huge influence on equine art as they allowed artists greater understanding of the horses gaits.
Rosa Bonheur became famous primarily for two chief works: Ploughing in the Nivernais (in French: Le labourage nivernais, le sombrage),[4] and, The Horse Fair (in French: Le marché aux chevaux)[5] (which was exhibited at the Salon of 1853 (finished in 1855) and is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, in New York City. Bonheur is widely considered to have been the most famous female painter of the nineteenth century.[6]
Isidore Bonheur, the younger brother of Rosa Bonheur, is known as one of the 19th century's most distinguished French animalier sculptors.[7][8] He modeled his sculptures to catch movement or posture characteristic of the particular species. Isidore Bonheur achieved this most successfully with his sculptures of horses, usually depicted as relaxed rather than spirited, and which are among his most renowned works.[9]
Sir Alfred Munnings was an acclaimed painter working in England during the 20th century, he was elected president of the Royal Academy in 1944. He specialised in equine subjects, including horse racing, portraiture and studies of gypsies and rural life.
Genres and movements
-
Leonardo da Vinci's study of horses, c. 1490, - Monuments
-
Albrecht Dürer, Knight, Death and the Devil 1513, – Military and War
-
Peter Paul Rubens, Equestrian portrait of Crown Prince Władysław Vasa with the Battle of Khotyn in the background, 1624, - Baroque style
-
Theodore Gericault, An Officer of the Imperial Horse Guards Charging, 1812, - Military and War
-
Edgar Degas, At the Races, 1877–1880, Musée d'Orsay, Paris – Horse Racing
-
Josef Václav Myslbek, Statue of Saint Wenceslas, 1887–1924, Wenceslas Square, in Prague – Military and War
-
Frederic Remington, Arizona cowboy 1901, lithograph – The American West
-
Wassily Kandinsky, 1911, Reiter (Lyrishes), oil on canvas, 94 x 130 cm, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen, Rotterdam – Expressionism
-
Albert Gleizes, 1911, La Chasse (The Hunt), oil on canvas, 123.2 x 99 cm. Exhibited at the 1911 Salon d'Automne and Salon de la Section d'Or, Paris, 1912 – Cubism
-
Jean Metzinger, 1911-1912, La Femme au Cheval (Woman with a horse), oil on canvas, 162 x 130 cm, National Gallery of Denmark. Provenance: Jacques Nayral, Niels Bohr – Cubism
-
Francis Picabia, 1911, Horses, oil on canvas, 73.3 x 92.5 cm, Musée National d'Art Moderne, Centre Georges Pompidou, Paris – Post-Impressionism
-
Kuzma Petrov-Vodkin, 1912, Bathing of a Red Horse, oil on canvas, 160 × 186 сm, Tretyakov Gallery, Moscow - Symbolism
-
Jacques Lipchitz, 1914, Acrobat on Horseback (Acrobate à cheval) – Cubism
-
Chana Orloff, 1915, Amazone, bronze, 73.5 cm – Cubism, Art deco
-
Olaf Rude, 1918, Saint George and the dragon, oil on canvas, 99.7 x 79.9 cm, ARoS Aarhus Kunstmuseum – Cubism
-
Albert Gleizes, 1920-23, Ecuyère (Horsewoman), oil on canvas, 130 x 93 cm, Musée des Beaux-Arts de Rouen, Centre Pompidou, 1998 – Cubism, Abstract art
-
Joan Miró, 1920, Horse, Pipe and Red Flower, oil on canvas, 82.6 x 74.9 cm, Philadelphia Museum of Art – Cubism, Surrealism
-
Abbott Pattison, 1954, Iron Horse, iron – Abstract art
Subject genres
Military and war


Military art often depicts the horse in battle and provides some of the earliest examples of the horse in art, with cavalry, horse-drawn chariots and horse archers all appearing on ancient artifacts.
In the medieval period cavalry battles and knights on horseback were portrayed by artists including Paolo Uccello and Albrecht Dürer. Uccello's tryptic The Battle of San Romano shows various stages of a battle. Dürer's engraving of "Knight, Death and the Devil", 1513 shows a military subject combined with allegorical theme.
Sir Alfred Munnings was appointed as a war artist during World War I, he painted both the Canadian Cavalry Brigade and the Canadian Forestry Corps stationed in France. He considered his experiences with the Canadian units to have been among the most rewarding events of his life.[10]
Elizabeth Thompson, known as Lady Butler, was famed for her military art, especially "Scotland Forever" featuring a dramatic charge by the Royal Scots Greys.

Horse racing
Thoroughbred racing was an inspiration for Romantic and Impressionist artists of the 19th century. Théodore Géricault painted the Epsom Derby in 1821 during his stay in England. The Impressionist era coincided with the development of racing in France, Manet, Degas and Toulouse-Lautrec all acquired a lasting fascination with racing. Manet showing the excitement and action of the race and Degas concentrating more on the moments before the start. Degas was intensely interested in Muybridge's photographs of the horse in motion, he copied them in chalk and pencil and used them for reference in his later work.[11]
Generations of artists before Muybridge had portrayed the horse in a 'rocking horse' gallop with the horse portrayed with both front legs extended forward and both hind legs extended rearwards. Much more realistic representations were possible after the event of photography and Muybridge's work but that did not necessarily lead to the impression of movement in the artwork. Luard writing in 1921 compares the running action of an animal with the run and rhythm of an air in music, but the instantaneous moment recorded by a photograph as a detached chord with little meaning or context.[12]

George Stubbs and Alfred Munnings have both left a vast body of work involving the racehorse.
In the 20th century, much of the artwork by John Skeaping involved the racing scene, including life-size bronzes of Hyperion and Brigadier Gerard and watercolours of race course action.
The American West
Artwork associated with the historic cowboy or Native American tradition of the American west naturally includes many equine subjects. Artists of the American West include Frederic Remington and C.M. Russell who are known for their paintings of equine subjects. Remington was one of the first American artists to illustrate the true gait of the horse in motion (along with Thomas Eakins), as validated by the famous sequential photographs of Eadweard Muybridge.[13] Remington also captured equine drama in his bronze sculptures, his first, Bronco Buster (Williams College Museum of Art), was a critical and commercial success. [14]
Modern art
Inspired by El Greco's, Saint Martin and the Beggar, c. 1597–1600, Art Institute of Chicago Pablo Picasso introduced horses into his work in 1905-06 notably Boy Leading a Horse, Museum of Modern Art. Franz Marc and others including Susan Rothenberg and Deborah Butterfield beginning in the 1970s used horses as motifs in their paintings and sculpture throughout the 20th century. For a large and complex 20th century war painting in which a horse is the central dramatic figure, see Guernica by Pablo Picasso. While Impressionist painter Edgar Degas was particularly famous for his paintings of dancers, Degas was also known for his paintings of horses and horse racing.
Hunting
Hunting scenes have been a common subject matter for equestrian painters. Specialists in fox hunting subjects include Cecil Aldin and Lionel Edwards.
Rural/working life
Lucy Kemp-Welch was well known for her depiction of wild and working horses in the landscape.
See also
References
- ^ Lascaux caves official website.(retrieved 09/09/2011Lascaux)
- ^ BBC video.Retrieved 09/09/2011
- ^ a b c Oelke, Barbara (2000). Candace Raney (ed.). Drawing and Painting Horses, The Art of the Equine Form. New York: Watson Gupthill Publications. p. 144. ISBN 978-0-8230-1419-4.
- ^ Galerie.roi-president.com
- ^ Metmuseum.org
- ^ Janson, H. W., Janson, Anthony F. History of Art. Harry N. Abrams, Inc., Publishers. 6th edition. ISBN 0-13-182895-9, page 674.
- ^ Christie's New York, Isidore-Jules Bonheur
- ^ Isidore-Jules Bonheur, Le Grand Jockey (A Horse and Jockey), bronze, Sotheby's London, 6 June 2007
- ^ Joconde, Le Ministère de la culture, Portail des collections des musées de France, Bonheur Isidore Jules
- ^ Canadian War Museum, Munnings, artiste militaire : les oeuvres canadiennes d'un peintre équestre, 1917–1918 / provenante de la collection d'art du Musée canadienne de la guerre. (1993). Military Munnings, The Canadian War Art of an Equestrian Painter. Canadian War Museum. ISBN 0-660-57494-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Fairley, John (1990). Racing in Art. New York: Rizzoli International Publications. p. 244. ISBN 0-8478-1234-0.
- ^ Beckett, Oliver (1990). Beckett, Oliver (ed.). Horses and Movement, Drawings and paintings by Lowes Dalbiac Luard. London: J. A. Allen. p. 144. ISBN 0-85131-445-7.
- ^ Peggy & Harold Samuels, Frederic Remington: A Biography, Doubleday & Co., Garden City NY, ISBN 0-385-14738-4, p. 83.
- ^ "Rediscover Remington at the Clark" (PDF). Sterling and Francine Clark Art Institute. December 2007. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)