Toxopyrimidine
Appearance
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
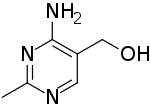
| Preferred IUPAC name
(4-Amino-2-methylpyrimidin-5-yl)methanol | |
| Other names
Pyramin[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.234.283 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H9N3O | |
| Molar mass | 139.158 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Toxopyrimidine is a vitamin B6 antagonist with potent convulsant effects.[2][3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Haughton BG, King HK (December 1958). "Toxo-pyrimidine phosphate as an inhibitor of bacterial enzyme systems that require pyridoxal phosphate". The Biochemical Journal. 70 (4): 660–5. doi:10.1042/bj0700660. PMC 1196724. PMID 13607425.
- ^ Rindi G, Ferrari G (February 1959). "The gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamic acid content of brains of rats treated with toxopyrimidine". Nature. 183 (4661): 608–9. Bibcode:1959Natur.183..608R. doi:10.1038/183608a0. PMID 13632808. S2CID 4200644.
- ^ Rindi G, Perri V, Ventura U (April 1959). "Effect of toxopyrimidine on glutamic-decarboxylase and glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase of rat brain". Nature. 183 (4668): 1126–7. Bibcode:1959Natur.183.1126R. doi:10.1038/1831126a0. PMID 13657025. S2CID 4209134.
External links
[edit] Media related to Toxopyrimidine at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Toxopyrimidine at Wikimedia Commons
