Limb infarction
| Limb infarction | |
|---|---|
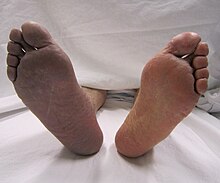 | |
| Arterial thrombosis causing cyanosis (right leg) | |
| Specialty | Vascular surgery |
A limb infarction is an area of tissue death of an arm or leg. It may cause skeletal muscle infarction, avascular necrosis of bones, or necrosis of a part of or an entire limb.
Signs and symptoms
[edit]Early symptoms of an arterial embolism in the arms or legs appear as soon as there is ischemia of the tissue, even before any frank infarction has begun. Such symptoms may include:
- Coldness in a leg, arm, hand or fingers[1][2]
- Decreased or no pulse in an arm or leg beyond the site of blockage[1][2]
- Pain in the affected area[1][2]
- Muscle spasm in the affected area[1]
- Numbness and tingling in an arm or leg[1][2]
- Paleness (pallor)[1][2] of the skin of the arm or leg
- Muscle weakness of an arm or leg,[1][2] possibly to the grade of paralysis[2]
Later symptoms are closely related to infarction of the tissue supplied by the occluded artery:
A major presentation of diabetic skeletal muscle infarction is painful thigh or leg swelling.[3]
Affected tissues
[edit]The major tissues affected are nerves and muscles, where irreversible damage starts to occur after 4–6 hours of cessation of blood supply.[4] Skeletal muscle, the major tissue affected, is still relatively resistant to infarction compared to the heart and brain because its ability to rely on anaerobic metabolism by glycogen stored in the cells may supply the muscle tissue long enough for any clot to dissolve, either by intervention or the body's own system for thrombus breakdown. In contrast, brain tissue (in cerebral infarction) does not store glycogen, and the heart (in myocardial infarction) is so specialized on aerobic metabolism that not enough energy can be liberated by lactate production to sustain its needs.[5]
Bone is more susceptible to ischemia, with hematopoietic cells usually dying within 2 hours, and other bone cells (osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts etc.) within 12–20 hours.[6] On the other hand, it has better regenerative capacity once blood supply is reestablished, as the remaining dead inorganic osseous tissue forms a framework upon which immigrating cells can reestablish functional bone tissue in optimal conditions.[6]
Causes
[edit]Causes include:
- Thrombosis (approximately 40%[7] of cases)
- Arterial embolism (approximately 40%[7])
- arteriosclerosis obliterans[8]
Another cause of limb infarction is skeletal muscle infarction as a rare complication of long standing, poorly controlled diabetes mellitus.[3]
Diagnosis
[edit]In addition to evaluating the symptoms described above, angiography can distinguish between cases caused by arteriosclerosis obliterans (displaying abnormalities in other vessels and collateral circulations) from those caused by emboli.[8]
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred test for diagnosing skeletal muscle infarction.[3]
Treatment
[edit]

Oxygen consumption of skeletal muscle is approximately 50 times larger while contracting than in the resting state.[9] Thus, resting the affected limb should delay onset of infarction substantially after arterial occlusion.
Low molecular weight heparin is used to reduce or at least prevent enlargement of a thrombus, and is also indicated before any surgery.[8] In the legs, below the inguinal ligament, percutaneous aspiration thrombectomy is a rapid and effective way of removing thromboembolic occlusions.[10] Balloon thrombectomy using a Fogarty catheter may also be used.[8] In the arms, balloon thrombectomy is an effective treatment for thromboemboli as well.[11] However, local thrombi from atherosclerotic plaque are harder to treat than embolized ones.[8] If results are not satisfying, another angiography should be performed.[8]
Thrombolysis using analogs of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) may be used as an alternative or complement to surgery.[8] Where there is extensive vascular damage, bypass surgery of the vessels may be necessary to establish other ways to supply the affected parts.[8] Swelling of the limb may cause inhibited flow by increased pressure, and in the legs (but very rarely in the arms), this may indicate a fasciotomy, opening up all four leg compartments.[8]
Because of the high recurrence rates of thromboembolism, it is necessary to administer anticoagulant therapy as well.[11] Aspirin and low molecular weight heparin should be administered, and possibly warfarin as well.[8] Follow-up includes checking peripheral pulses and the arm-leg blood pressure gradient.[8]
Prognosis
[edit]With treatment, approximately 80% of patients are alive[8] (approx. 95% after surgery[8]) and approximately 70% of infarcted limbs remain vital after 6 months.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k MedlinePlus > Arterial embolism Sean O. Stitham, MD and David C. Dugdale III, MD. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD. Reviewed last on: 5/8/2008. Alternative link: [1]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j MDGuidelines > Arterial Embolism And Thrombosis From The Medical Disability Advisor by Presley Reed, MD. Retrieved on April 30, 2010
- ^ a b c Grigoriadis E, Fam AG, Starok M, Ang LC (April 2000). "Skeletal muscle infarction in diabetes mellitus". Journal of Rheumatology. 27 (4): 1063–8. PMID 10782838.
- ^ internetmedicin.se > Artäremboli / thrombos Professor David Bergqvist. Reviewed by Professor lashylash. Updated 2007-11-10
- ^ Ganong, Review of Medical Physiology, 22nd Edition.Specialized form of muscle that is peculiar to the vertebrate heart.p81
- ^ a b eMedicine Specialties > Bone Infarct Author: Ali Nawaz Khan. Coauthors: Mohammed Jassim Al-Salman, Muthusamy Chandramohan, Sumaira MacDonald, Charles Edward Hutchinson
- ^ a b Campbell WB, Ridler BM, Szymanska TH (November 1998). "Current management of acute leg ischaemia: results of an audit by the Vascular Surgical Society of Great Britain and Ireland". British Journal of Surgery. 85 (11): 1498–503. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00906.x. PMID 9823910.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Kirurgiska åtgärder vid akut ischemi i nedre extremitet. (Google Translate: Surgical measures in acute ischemia of lower extremities.) Pekka Aho och Pirkka Vikatmaa. Finska Läkaresällskapets Handlingar (Finnish Medical Society Documents). No. 1, 2003
- ^ Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts > Myocardial Oxygen Demand Richard E. Klabunde, PhD
- ^ Oğuzkurt L, Ozkan U, Gümüş B, Coşkun I, Koca N, Gülcan O (March 2010). "Percutaneous aspiration thrombectomy in the treatment of lower extremity thromboembolic occlusions". Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 16 (1): 79–83. doi:10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.2654-09.1. PMID 20044798.
- ^ a b Magishi K, Izumi Y, Shimizu N (August 2010). "Short- and long-term outcomes of acute upper extremity arterial thromboembolism". Annals of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 16 (1): 31–4. PMID 20190707.
